Zitao Wang
Representation-Aware Distributionally Robust Optimization: A Knowledge Transfer Framework
Sep 11, 2025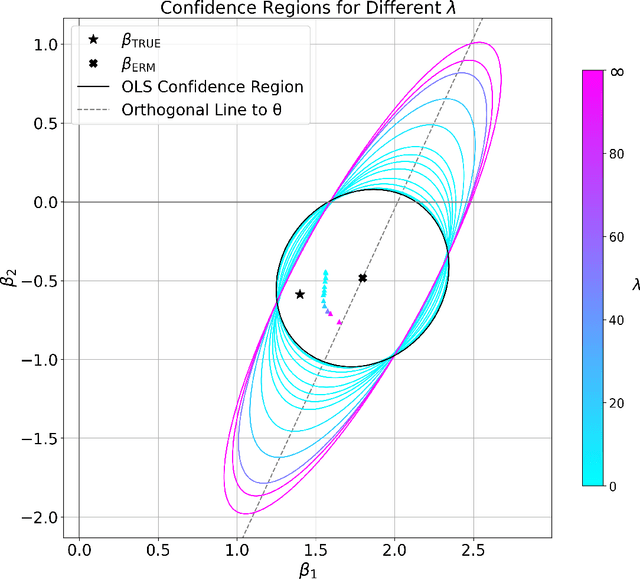
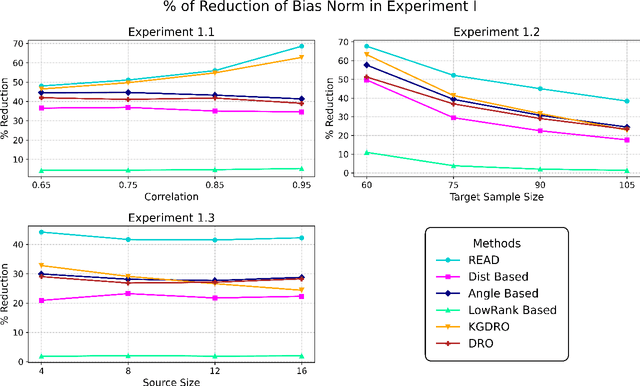
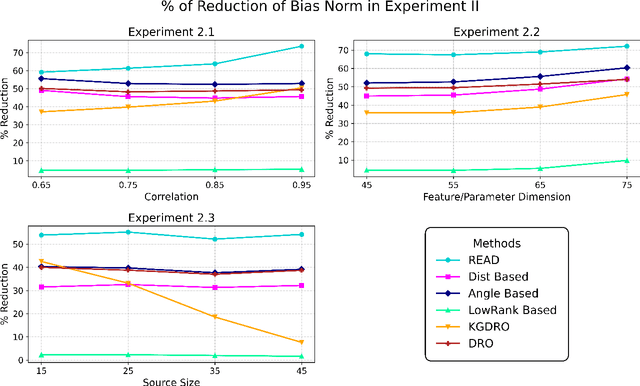
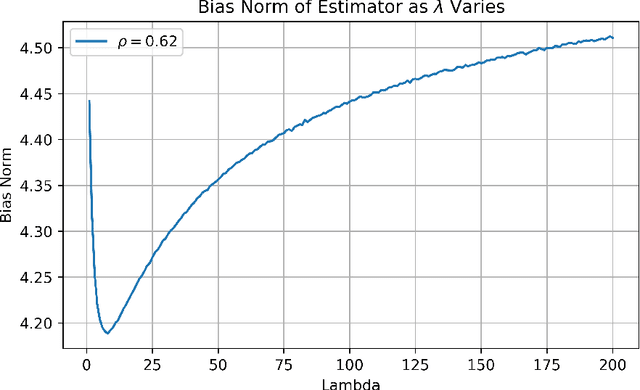
Abstract:We propose REpresentation-Aware Distributionally Robust Estimation (READ), a novel framework for Wasserstein distributionally robust learning that accounts for predictive representations when guarding against distributional shifts. Unlike classical approaches that treat all feature perturbations equally, READ embeds a multidimensional alignment parameter into the transport cost, allowing the model to differentially discourage perturbations along directions associated with informative representations. This yields robustness to feature variation while preserving invariant structure. Our first contribution is a theoretical foundation: we show that seminorm regularizations for linear regression and binary classification arise as Wasserstein distributionally robust objectives, thereby providing tractable reformulations of READ and unifying a broad class of regularized estimators under the DRO lens. Second, we adopt a principled procedure for selecting the Wasserstein radius using the techniques of robust Wasserstein profile inference. This further enables the construction of valid, representation-aware confidence regions for model parameters with distinct geometric features. Finally, we analyze the geometry of READ estimators as the alignment parameters vary and propose an optimization algorithm to estimate the projection of the global optimum onto this solution surface. This procedure selects among equally robust estimators while optimally constructing a representation structure. We conclude by demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework through extensive simulations and a real-world study, providing a powerful robust estimation grounded in learning representation.
Knowledge-Guided Wasserstein Distributionally Robust Optimization
Feb 12, 2025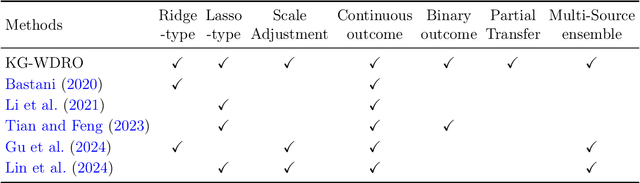
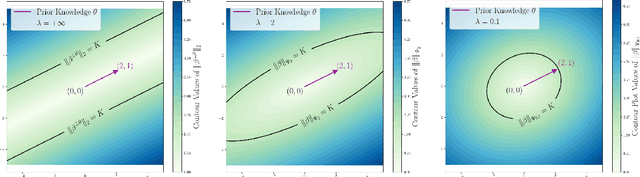
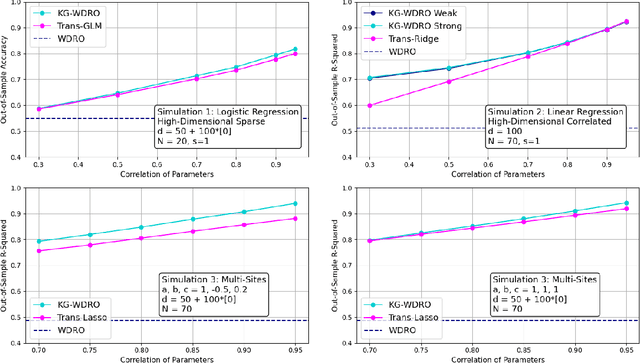
Abstract:Transfer learning is a popular strategy to leverage external knowledge and improve statistical efficiency, particularly with a limited target sample. We propose a novel knowledge-guided Wasserstein Distributionally Robust Optimization (KG-WDRO) framework that adaptively incorporates multiple sources of external knowledge to overcome the conservativeness of vanilla WDRO, which often results in overly pessimistic shrinkage toward zero. Our method constructs smaller Wasserstein ambiguity sets by controlling the transportation along directions informed by the source knowledge. This strategy can alleviate perturbations on the predictive projection of the covariates and protect against information loss. Theoretically, we establish the equivalence between our WDRO formulation and the knowledge-guided shrinkage estimation based on collinear similarity, ensuring tractability and geometrizing the feasible set. This also reveals a novel and general interpretation for recent shrinkage-based transfer learning approaches from the perspective of distributional robustness. In addition, our framework can adjust for scaling differences in the regression models between the source and target and accommodates general types of regularization such as lasso and ridge. Extensive simulations demonstrate the superior performance and adaptivity of KG-WDRO in enhancing small-sample transfer learning.
Continual Event Extraction with Semantic Confusion Rectification
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:We study continual event extraction, which aims to extract incessantly emerging event information while avoiding forgetting. We observe that the semantic confusion on event types stems from the annotations of the same text being updated over time. The imbalance between event types even aggravates this issue. This paper proposes a novel continual event extraction model with semantic confusion rectification. We mark pseudo labels for each sentence to alleviate semantic confusion. We transfer pivotal knowledge between current and previous models to enhance the understanding of event types. Moreover, we encourage the model to focus on the semantics of long-tailed event types by leveraging other associated types. Experimental results show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art baselines and is proficient in imbalanced datasets.
The Robust Semantic Segmentation UNCV2023 Challenge Results
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:This paper outlines the winning solutions employed in addressing the MUAD uncertainty quantification challenge held at ICCV 2023. The challenge was centered around semantic segmentation in urban environments, with a particular focus on natural adversarial scenarios. The report presents the results of 19 submitted entries, with numerous techniques drawing inspiration from cutting-edge uncertainty quantification methodologies presented at prominent conferences in the fields of computer vision and machine learning and journals over the past few years. Within this document, the challenge is introduced, shedding light on its purpose and objectives, which primarily revolved around enhancing the robustness of semantic segmentation in urban scenes under varying natural adversarial conditions. The report then delves into the top-performing solutions. Moreover, the document aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the diverse solutions deployed by all participants. By doing so, it seeks to offer readers a deeper insight into the array of strategies that can be leveraged to effectively handle the inherent uncertainties associated with autonomous driving and semantic segmentation, especially within urban environments.
EFormer: Enhanced Transformer towards Semantic-Contour Features of Foreground for Portraits Matting
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:The portrait matting task aims to extract an alpha matte with complete semantics and finely-detailed contours. In comparison to CNN-based approaches, transformers with self-attention allow a larger receptive field, enabling it to better capture long-range dependencies and low-frequency semantic information of a portrait. However, the recent research shows that self-attention mechanism struggle with modeling high-frequency information and capturing fine contour details, which can lead to bias while predicting the portrait's contours. To address the problem, we propose EFormer to enhance the model's attention towards semantic and contour features. Especially the latter, which is surrounded by a large amount of high-frequency details. We build a semantic and contour detector (SCD) to accurately capture the distribution of semantic and contour features. And we further design contour-edge extraction branch and semantic extraction branch for refining contour features and complete semantic information. Finally, we fuse the two kinds of features and leverage the segmentation head to generate the predicted portrait matte. Remarkably, EFormer is an end-to-end trimap-free method and boasts a simple structure. Experiments conducted on VideoMatte240K-JPEGSD and AIM datasets demonstrate that EFormer outperforms previous portrait matte methods.
Serial Contrastive Knowledge Distillation for Continual Few-shot Relation Extraction
May 11, 2023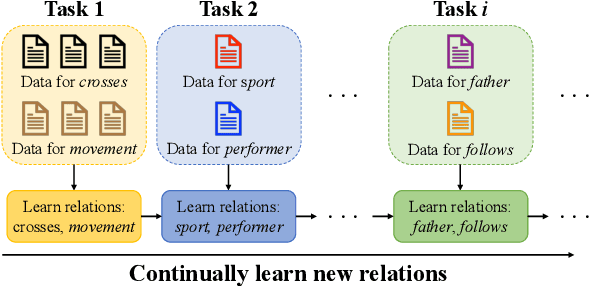
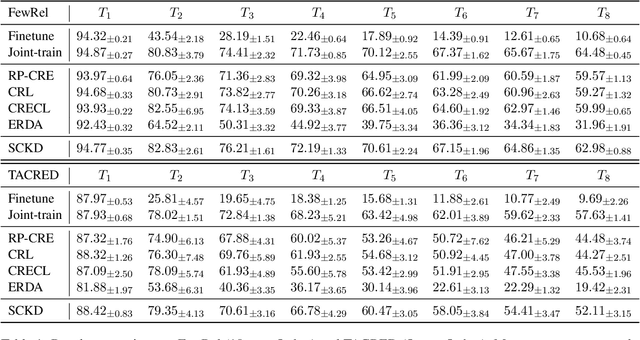
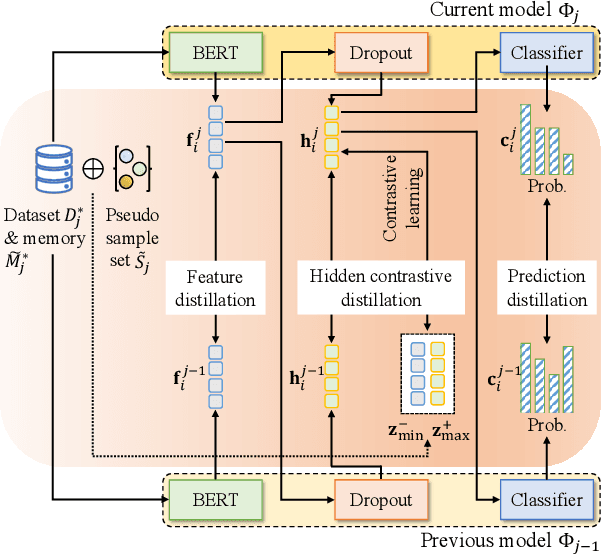
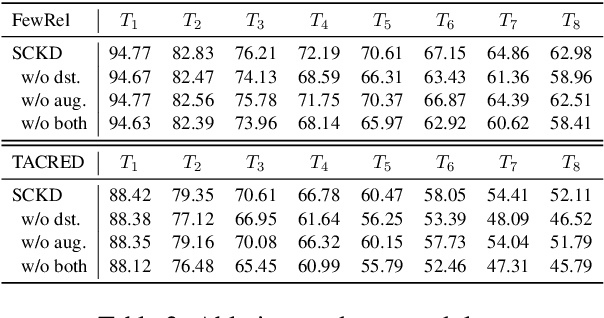
Abstract:Continual few-shot relation extraction (RE) aims to continuously train a model for new relations with few labeled training data, of which the major challenges are the catastrophic forgetting of old relations and the overfitting caused by data sparsity. In this paper, we propose a new model, namely SCKD, to accomplish the continual few-shot RE task. Specifically, we design serial knowledge distillation to preserve the prior knowledge from previous models and conduct contrastive learning with pseudo samples to keep the representations of samples in different relations sufficiently distinguishable. Our experiments on two benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of SCKD for continual few-shot RE and its superiority in knowledge transfer and memory utilization over state-of-the-art models.
AIM 2022 Challenge on Instagram Filter Removal: Methods and Results
Oct 17, 2022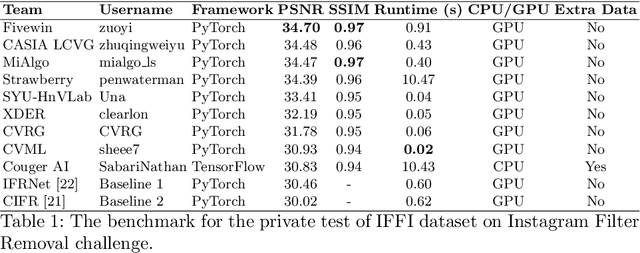

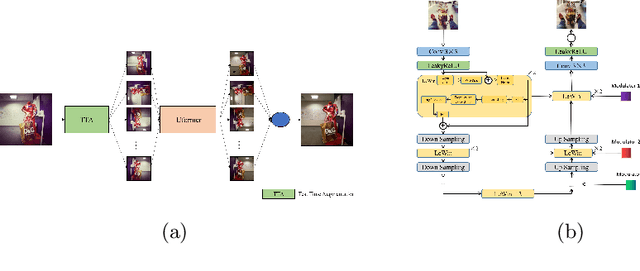
Abstract:This paper introduces the methods and the results of AIM 2022 challenge on Instagram Filter Removal. Social media filters transform the images by consecutive non-linear operations, and the feature maps of the original content may be interpolated into a different domain. This reduces the overall performance of the recent deep learning strategies. The main goal of this challenge is to produce realistic and visually plausible images where the impact of the filters applied is mitigated while preserving the content. The proposed solutions are ranked in terms of the PSNR value with respect to the original images. There are two prior studies on this task as the baseline, and a total of 9 teams have competed in the final phase of the challenge. The comparison of qualitative results of the proposed solutions and the benchmark for the challenge are presented in this report.
Enhancing Document-level Relation Extraction by Entity Knowledge Injection
Jul 23, 2022



Abstract:Document-level relation extraction (RE) aims to identify the relations between entities throughout an entire document. It needs complex reasoning skills to synthesize various knowledge such as coreferences and commonsense. Large-scale knowledge graphs (KGs) contain a wealth of real-world facts, and can provide valuable knowledge to document-level RE. In this paper, we propose an entity knowledge injection framework to enhance current document-level RE models. Specifically, we introduce coreference distillation to inject coreference knowledge, endowing an RE model with the more general capability of coreference reasoning. We also employ representation reconciliation to inject factual knowledge and aggregate KG representations and document representations into a unified space. The experiments on two benchmark datasets validate the generalization of our entity knowledge injection framework and the consistent improvement to several document-level RE models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge