Zichuan Lin
ProAct: Agentic Lookahead in Interactive Environments
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Existing Large Language Model (LLM) agents struggle in interactive environments requiring long-horizon planning, primarily due to compounding errors when simulating future states. To address this, we propose ProAct, a framework that enables agents to internalize accurate lookahead reasoning through a two-stage training paradigm. First, we introduce Grounded LookAhead Distillation (GLAD), where the agent undergoes supervised fine-tuning on trajectories derived from environment-based search. By compressing complex search trees into concise, causal reasoning chains, the agent learns the logic of foresight without the computational overhead of inference-time search. Second, to further refine decision accuracy, we propose the Monte-Carlo Critic (MC-Critic), a plug-and-play auxiliary value estimator designed to enhance policy-gradient algorithms like PPO and GRPO. By leveraging lightweight environment rollouts to calibrate value estimates, MC-Critic provides a low-variance signal that facilitates stable policy optimization without relying on expensive model-based value approximation. Experiments on both stochastic (e.g., 2048) and deterministic (e.g., Sokoban) environments demonstrate that ProAct significantly improves planning accuracy. Notably, a 4B parameter model trained with ProAct outperforms all open-source baselines and rivals state-of-the-art closed-source models, while demonstrating robust generalization to unseen environments. The codes and models are available at https://github.com/GreatX3/ProAct
Cross-Domain Offline Policy Adaptation via Selective Transition Correction
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:It remains a critical challenge to adapt policies across domains with mismatched dynamics in reinforcement learning (RL). In this paper, we study cross-domain offline RL, where an offline dataset from another similar source domain can be accessed to enhance policy learning upon a target domain dataset. Directly merging the two datasets may lead to suboptimal performance due to potential dynamics mismatches. Existing approaches typically mitigate this issue through source domain transition filtering or reward modification, which, however, may lead to insufficient exploitation of the valuable source domain data. Instead, we propose to modify the source domain data into the target domain data. To that end, we leverage an inverse policy model and a reward model to correct the actions and rewards of source transitions, explicitly achieving alignment with the target dynamics. Since limited data may result in inaccurate model training, we further employ a forward dynamics model to retain corrected samples that better match the target dynamics than the original transitions. Consequently, we propose the Selective Transition Correction (STC) algorithm, which enables reliable usage of source domain data for policy adaptation. Experiments on various environments with dynamics shifts demonstrate that STC achieves superior performance against existing baselines.
PIPCFR: Pseudo-outcome Imputation with Post-treatment Variables for Individual Treatment Effect Estimation
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:The estimation of individual treatment effects (ITE) focuses on predicting the outcome changes that result from a change in treatment. A fundamental challenge in observational data is that while we need to infer outcome differences under alternative treatments, we can only observe each individual's outcome under a single treatment. Existing approaches address this limitation either by training with inferred pseudo-outcomes or by creating matched instance pairs. However, recent work has largely overlooked the potential impact of post-treatment variables on the outcome. This oversight prevents existing methods from fully capturing outcome variability, resulting in increased variance in counterfactual predictions. This paper introduces Pseudo-outcome Imputation with Post-treatment Variables for Counterfactual Regression (PIPCFR), a novel approach that incorporates post-treatment variables to improve pseudo-outcome imputation. We analyze the challenges inherent in utilizing post-treatment variables and establish a novel theoretical bound for ITE risk that explicitly connects post-treatment variables to ITE estimation accuracy. Unlike existing methods that ignore these variables or impose restrictive assumptions, PIPCFR learns effective representations that preserve informative components while mitigating bias. Empirical evaluations on both real-world and simulated datasets demonstrate that PIPCFR achieves significantly lower ITE errors compared to existing methods.
EntroPIC: Towards Stable Long-Term Training of LLMs via Entropy Stabilization with Proportional-Integral Control
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Long-term training of large language models (LLMs) requires maintaining stable exploration to prevent the model from collapsing into sub-optimal behaviors. Entropy is crucial in this context, as it controls exploration and helps avoid premature convergence to sub-optimal solutions. However, existing reinforcement learning methods struggle to maintain an appropriate level of entropy, as the training process involves a mix of positive and negative samples, each affecting entropy in different ways across steps. To address this, we propose Entropy stablilization via Proportional-Integral Control (EntroPIC), a novel method that adaptively adjusts the influence of positive and negative samples by dynamically tuning their loss coefficients. This approach stabilizes entropy throughout training, ensuring efficient exploration and steady progress. We provide a comprehensive theoretical analysis for both on-policy and off-policy learning settings, demonstrating that EntroPIC is effective at controlling entropy in large-scale LLM training. Experimental results show that our method successfully maintains desired entropy levels, enabling stable and optimal RL training for LLMs.
Multi-agent In-context Coordination via Decentralized Memory Retrieval
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Large transformer models, trained on diverse datasets, have demonstrated impressive few-shot performance on previously unseen tasks without requiring parameter updates. This capability has also been explored in Reinforcement Learning (RL), where agents interact with the environment to retrieve context and maximize cumulative rewards, showcasing strong adaptability in complex settings. However, in cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL), where agents must coordinate toward a shared goal, decentralized policy deployment can lead to mismatches in task alignment and reward assignment, limiting the efficiency of policy adaptation. To address this challenge, we introduce Multi-agent In-context Coordination via Decentralized Memory Retrieval (MAICC), a novel approach designed to enhance coordination by fast adaptation. Our method involves training a centralized embedding model to capture fine-grained trajectory representations, followed by decentralized models that approximate the centralized one to obtain team-level task information. Based on the learned embeddings, relevant trajectories are retrieved as context, which, combined with the agents' current sub-trajectories, inform decision-making. During decentralized execution, we introduce a novel memory mechanism that effectively balances test-time online data with offline memory. Based on the constructed memory, we propose a hybrid utility score that incorporates both individual- and team-level returns, ensuring credit assignment across agents. Extensive experiments on cooperative MARL benchmarks, including Level-Based Foraging (LBF) and SMAC (v1/v2), show that MAICC enables faster adaptation to unseen tasks compared to existing methods. Code is available at https://github.com/LAMDA-RL/MAICC.
CausalMACE: Causality Empowered Multi-Agents in Minecraft Cooperative Tasks
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Minecraft, as an open-world virtual interactive environment, has become a prominent platform for research on agent decision-making and execution. Existing works primarily adopt a single Large Language Model (LLM) agent to complete various in-game tasks. However, for complex tasks requiring lengthy sequences of actions, single-agent approaches often face challenges related to inefficiency and limited fault tolerance. Despite these issues, research on multi-agent collaboration remains scarce. In this paper, we propose CausalMACE, a holistic causality planning framework designed to enhance multi-agent systems, in which we incorporate causality to manage dependencies among subtasks. Technically, our proposed framework introduces two modules: an overarching task graph for global task planning and a causality-based module for dependency management, where inherent rules are adopted to perform causal intervention. Experimental results demonstrate our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-agent cooperative tasks of Minecraft.
Learning Versatile Skills with Curriculum Masking
Oct 23, 2024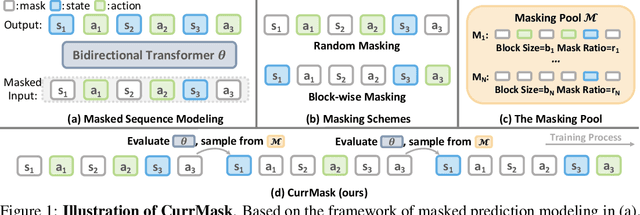
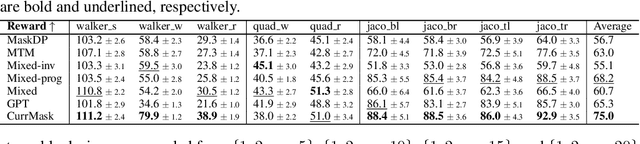
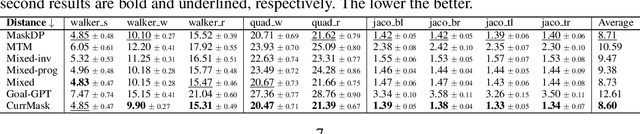
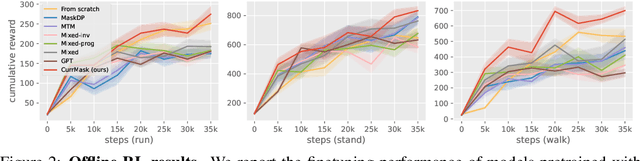
Abstract:Masked prediction has emerged as a promising pretraining paradigm in offline reinforcement learning (RL) due to its versatile masking schemes, enabling flexible inference across various downstream tasks with a unified model. Despite the versatility of masked prediction, it remains unclear how to balance the learning of skills at different levels of complexity. To address this, we propose CurrMask, a curriculum masking pretraining paradigm for sequential decision making. Motivated by how humans learn by organizing knowledge in a curriculum, CurrMask adjusts its masking scheme during pretraining for learning versatile skills. Through extensive experiments, we show that CurrMask exhibits superior zero-shot performance on skill prompting tasks, goal-conditioned planning tasks, and competitive finetuning performance on offline RL tasks. Additionally, our analysis of training dynamics reveals that CurrMask gradually acquires skills of varying complexity by dynamically adjusting its masking scheme.
Replay-enhanced Continual Reinforcement Learning
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:Replaying past experiences has proven to be a highly effective approach for averting catastrophic forgetting in supervised continual learning. However, some crucial factors are still largely ignored, making it vulnerable to serious failure, when used as a solution to forgetting in continual reinforcement learning, even in the context of perfect memory where all data of previous tasks are accessible in the current task. On the one hand, since most reinforcement learning algorithms are not invariant to the reward scale, the previously well-learned tasks (with high rewards) may appear to be more salient to the current learning process than the current task (with small initial rewards). This causes the agent to concentrate on those salient tasks at the expense of generality on the current task. On the other hand, offline learning on replayed tasks while learning a new task may induce a distributional shift between the dataset and the learned policy on old tasks, resulting in forgetting. In this paper, we introduce RECALL, a replay-enhanced method that greatly improves the plasticity of existing replay-based methods on new tasks while effectively avoiding the recurrence of catastrophic forgetting in continual reinforcement learning. RECALL leverages adaptive normalization on approximate targets and policy distillation on old tasks to enhance generality and stability, respectively. Extensive experiments on the Continual World benchmark show that RECALL performs significantly better than purely perfect memory replay, and achieves comparable or better overall performance against state-of-the-art continual learning methods.
Future-conditioned Unsupervised Pretraining for Decision Transformer
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Recent research in offline reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated that return-conditioned supervised learning is a powerful paradigm for decision-making problems. While promising, return conditioning is limited to training data labeled with rewards and therefore faces challenges in learning from unsupervised data. In this work, we aim to utilize generalized future conditioning to enable efficient unsupervised pretraining from reward-free and sub-optimal offline data. We propose Pretrained Decision Transformer (PDT), a conceptually simple approach for unsupervised RL pretraining. PDT leverages future trajectory information as a privileged context to predict actions during training. The ability to make decisions based on both present and future factors enhances PDT's capability for generalization. Besides, this feature can be easily incorporated into a return-conditioned framework for online finetuning, by assigning return values to possible futures and sampling future embeddings based on their respective values. Empirically, PDT outperforms or performs on par with its supervised pretraining counterpart, especially when dealing with sub-optimal data. Further analysis reveals that PDT can extract diverse behaviors from offline data and controllably sample high-return behaviors by online finetuning. Code is available at here.
Sample Dropout: A Simple yet Effective Variance Reduction Technique in Deep Policy Optimization
Feb 05, 2023Abstract:Recent success in Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) methods has shown that policy optimization with respect to an off-policy distribution via importance sampling is effective for sample reuse. In this paper, we show that the use of importance sampling could introduce high variance in the objective estimate. Specifically, we show in a principled way that the variance of importance sampling estimate grows quadratically with importance ratios and the large ratios could consequently jeopardize the effectiveness of surrogate objective optimization. We then propose a technique called sample dropout to bound the estimation variance by dropping out samples when their ratio deviation is too high. We instantiate this sample dropout technique on representative policy optimization algorithms, including TRPO, PPO, and ESPO, and demonstrate that it consistently boosts the performance of those DRL algorithms on both continuous and discrete action controls, including MuJoCo, DMControl and Atari video games. Our code is open-sourced at \url{https://github.com/LinZichuan/sdpo.git}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge