Zhi Zeng
Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
MT-Mark: Rethinking Image Watermarking via Mutual-Teacher Collaboration with Adaptive Feature Modulation
Dec 22, 2025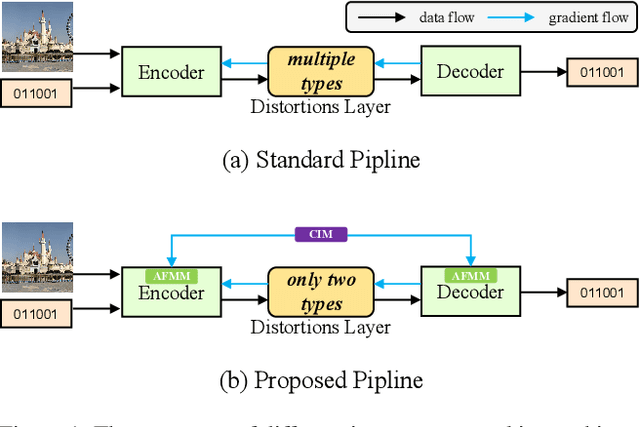
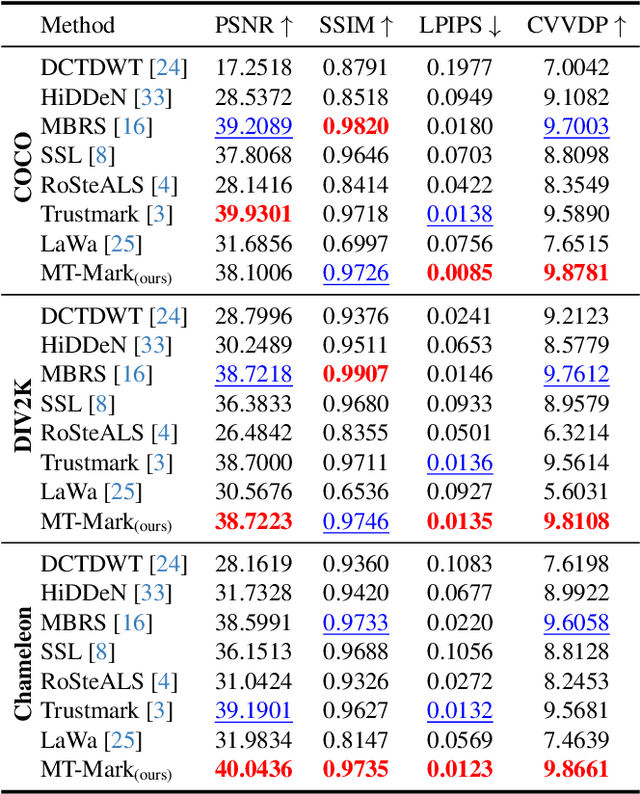
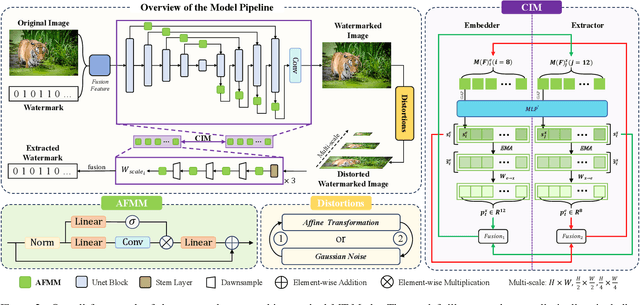
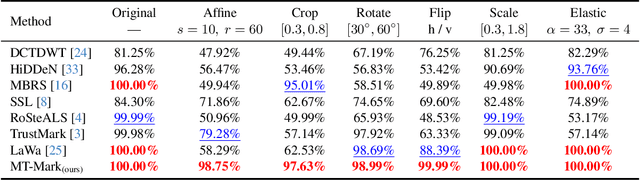
Abstract:Existing deep image watermarking methods follow a fixed embedding-distortion-extraction pipeline, where the embedder and extractor are weakly coupled through a final loss and optimized in isolation. This design lacks explicit collaboration, leaving no structured mechanism for the embedder to incorporate decoding-aware cues or for the extractor to guide embedding during training. To address this architectural limitation, we rethink deep image watermarking by reformulating embedding and extraction as explicitly collaborative components. To realize this reformulation, we introduce a Collaborative Interaction Mechanism (CIM) that establishes direct, bidirectional communication between the embedder and extractor, enabling a mutual-teacher training paradigm and coordinated optimization. Built upon this explicitly collaborative architecture, we further propose an Adaptive Feature Modulation Module (AFMM) to support effective interaction. AFMM enables content-aware feature regulation by decoupling modulation structure and strength, guiding watermark embedding toward stable image features while suppressing host interference during extraction. Under CIM, the AFMMs on both sides form a closed-loop collaboration that aligns embedding behavior with extraction objectives. This architecture-level redesign changes how robustness is learned in watermarking systems. Rather than relying on exhaustive distortion simulation, robustness emerges from coordinated representation learning between embedding and extraction. Experiments on real-world and AI-generated datasets demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in watermark extraction accuracy while maintaining high perceptual quality, showing strong robustness and generalization.
DiFaR: Enhancing Multimodal Misinformation Detection with Diverse, Factual, and Relevant Rationales
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Generating textual rationales from large vision-language models (LVLMs) to support trainable multimodal misinformation detectors has emerged as a promising paradigm. However, its effectiveness is fundamentally limited by three core challenges: (i) insufficient diversity in generated rationales, (ii) factual inaccuracies due to hallucinations, and (iii) irrelevant or conflicting content that introduces noise. We introduce DiFaR, a detector-agnostic framework that produces diverse, factual, and relevant rationales to enhance misinformation detection. DiFaR employs five chain-of-thought prompts to elicit varied reasoning traces from LVLMs and incorporates a lightweight post-hoc filtering module to select rationale sentences based on sentence-level factuality and relevance scores. Extensive experiments on four popular benchmarks demonstrate that DiFaR outperforms four baseline categories by up to 5.9% and boosts existing detectors by as much as 8.7%. Both automatic metrics and human evaluations confirm that DiFaR significantly improves rationale quality across all three dimensions.
RealityAvatar: Towards Realistic Loose Clothing Modeling in Animatable 3D Gaussian Avatars
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Modeling animatable human avatars from monocular or multi-view videos has been widely studied, with recent approaches leveraging neural radiance fields (NeRFs) or 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) achieving impressive results in novel-view and novel-pose synthesis. However, existing methods often struggle to accurately capture the dynamics of loose clothing, as they primarily rely on global pose conditioning or static per-frame representations, leading to oversmoothing and temporal inconsistencies in non-rigid regions. To address this, We propose RealityAvatar, an efficient framework for high-fidelity digital human modeling, specifically targeting loosely dressed avatars. Our method leverages 3D Gaussian Splatting to capture complex clothing deformations and motion dynamics while ensuring geometric consistency. By incorporating a motion trend module and a latentbone encoder, we explicitly model pose-dependent deformations and temporal variations in clothing behavior. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in capturing fine-grained clothing deformations and motion-driven shape variations. Our method significantly enhances structural fidelity and perceptual quality in dynamic human reconstruction, particularly in non-rigid regions, while achieving better consistency across temporal frames.
Each Fake News is Fake in its Own Way: An Attribution Multi-Granularity Benchmark for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Social platforms, while facilitating access to information, have also become saturated with a plethora of fake news, resulting in negative consequences. Automatic multimodal fake news detection is a worthwhile pursuit. Existing multimodal fake news datasets only provide binary labels of real or fake. However, real news is alike, while each fake news is fake in its own way. These datasets fail to reflect the mixed nature of various types of multimodal fake news. To bridge the gap, we construct an attributing multi-granularity multimodal fake news detection dataset \amg, revealing the inherent fake pattern. Furthermore, we propose a multi-granularity clue alignment model \our to achieve multimodal fake news detection and attribution. Experimental results demonstrate that \amg is a challenging dataset, and its attribution setting opens up new avenues for future research.
DiffMAC: Diffusion Manifold Hallucination Correction for High Generalization Blind Face Restoration
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Blind face restoration (BFR) is a highly challenging problem due to the uncertainty of degradation patterns. Current methods have low generalization across photorealistic and heterogeneous domains. In this paper, we propose a Diffusion-Information-Diffusion (DID) framework to tackle diffusion manifold hallucination correction (DiffMAC), which achieves high-generalization face restoration in diverse degraded scenes and heterogeneous domains. Specifically, the first diffusion stage aligns the restored face with spatial feature embedding of the low-quality face based on AdaIN, which synthesizes degradation-removal results but with uncontrollable artifacts for some hard cases. Based on Stage I, Stage II considers information compression using manifold information bottleneck (MIB) and finetunes the first diffusion model to improve facial fidelity. DiffMAC effectively fights against blind degradation patterns and synthesizes high-quality faces with attribute and identity consistencies. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of DiffMAC over state-of-the-art methods, with a high degree of generalization in real-world and heterogeneous settings. The source code and models will be public.
GO-FEAP: Global Optimal UAV Planner Using Frontier-Omission-Aware Exploration and Altitude-Stratified Planning
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Autonomous exploration is a fundamental problem for various applications of unmanned aerial vehicles(UAVs). Existing methods, however, are demonstrated to static local optima and two-dimensional exploration. To address these challenges, this paper introduces GO-FEAP (Global Optimal UAV Planner Using Frontier-Omission-Aware Exploration and Altitude-Stratified Planning), aiming to achieve efficient and complete three-dimensional exploration. Frontier-Omission-Aware Exploration module presented in this work takes into account multiple pivotal factors, encompassing frontier distance, nearby frontier count, frontier duration, and frontier categorization, for a comprehensive assessment of frontier importance. Furthermore, to tackle scenarios with substantial vertical variations, we introduce the Altitude-Stratified Planning strategy, which stratifies the three-dimensional space based on altitude, conducting global-local planning for each stratum. The objective of global planning is to identify the most optimal frontier for exploration, followed by viewpoint selection and local path optimization based on frontier type, ultimately generating dynamically feasible three-dimensional spatial exploration trajectories. We present extensive benchmark and real-world tests, in which our method completes the exploration tasks with unprecedented completeness compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
GesGPT: Speech Gesture Synthesis With Text Parsing from GPT
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:Gesture synthesis has gained significant attention as a critical research area, focusing on producing contextually appropriate and natural gestures corresponding to speech or textual input. Although deep learning-based approaches have achieved remarkable progress, they often overlook the rich semantic information present in the text, leading to less expressive and meaningful gestures. We propose GesGPT, a novel approach to gesture generation that leverages the semantic analysis capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT. By capitalizing on the strengths of LLMs for text analysis, we design prompts to extract gesture-related information from textual input. Our method entails developing prompt principles that transform gesture generation into an intention classification problem based on GPT, and utilizing a curated gesture library and integration module to produce semantically rich co-speech gestures. Experimental results demonstrate that GesGPT effectively generates contextually appropriate and expressive gestures, offering a new perspective on semantic co-speech gesture generation.
Neural Copula: A unified framework for estimating generic high-dimensional Copula functions
May 23, 2022



Abstract:The Copula is widely used to describe the relationship between the marginal distribution and joint distribution of random variables. The estimation of high-dimensional Copula is difficult, and most existing solutions rely either on simplified assumptions or on complicating recursive decompositions. Therefore, people still hope to obtain a generic Copula estimation method with both universality and simplicity. To reach this goal, a novel neural network-based method (named Neural Copula) is proposed in this paper. In this method, a hierarchical unsupervised neural network is constructed to estimate the marginal distribution function and the Copula function by solving differential equations. In the training program, various constraints are imposed on both the neural network and its derivatives. The Copula estimated by the proposed method is smooth and has an analytic expression. The effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated on both real-world datasets and complex numerical simulations. Experimental results show that Neural Copula's fitting quality for complex distributions is much better than classical methods. The relevant code for the experiments is available on GitHub. (We encourage the reader to run the program for a better understanding of the proposed method).
Physics-informed ConvNet: Learning Physical Field from a Shallow Neural Network
Feb 07, 2022Abstract:Big-data-based artificial intelligence (AI) supports profound evolution in almost all of science and technology. However, modeling and forecasting multi-physical systems remain a challenge due to unavoidable data scarcity and noise. Improving the generalization ability of neural networks by "teaching" domain knowledge and developing a new generation of models combined with the physical laws have become promising areas of machine learning research. Different from "deep" fully-connected neural networks embedded with physical information (PINN), a novel shallow framework named physics-informed convolutional network (PICN) is recommended from a CNN perspective, in which the physical field is generated by a deconvolution layer and a single convolution layer. The difference fields forming the physical operator are constructed using the pre-trained shallow convolution layer. An efficient linear interpolation network calculates the loss function involving boundary conditions and the physical constraints in irregular geometry domains. The effectiveness of the current development is illustrated through some numerical cases involving the solving (and estimation) of nonlinear physical operator equations and recovering physical information from noisy observations. Its potential advantage in approximating physical fields with multi-frequency components indicates that PICN may become an alternative neural network solver in physics-informed machine learning.
Approaching the Limit of Image Rescaling via Flow Guidance
Nov 09, 2021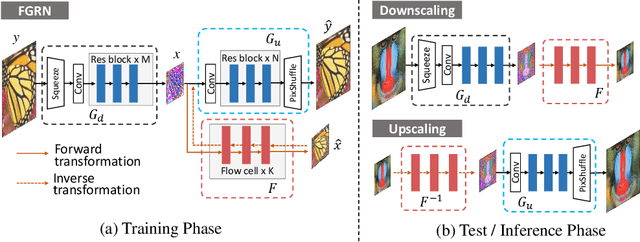
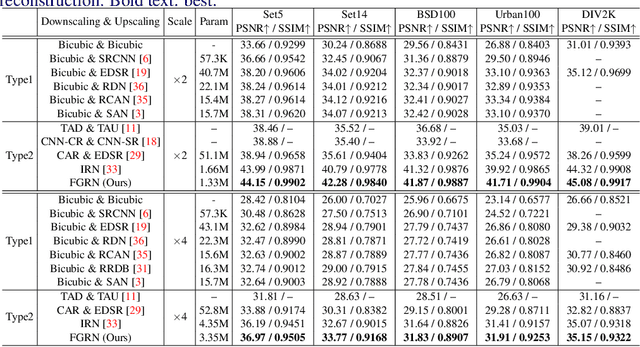
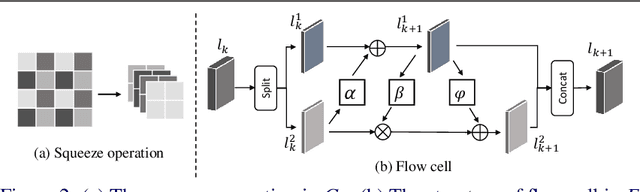
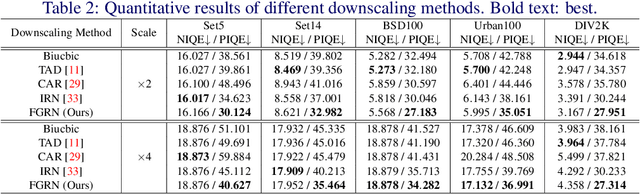
Abstract:Image downscaling and upscaling are two basic rescaling operations. Once the image is downscaled, it is difficult to be reconstructed via upscaling due to the loss of information. To make these two processes more compatible and improve the reconstruction performance, some efforts model them as a joint encoding-decoding task, with the constraint that the downscaled (i.e. encoded) low-resolution (LR) image must preserve the original visual appearance. To implement this constraint, most methods guide the downscaling module by supervising it with the bicubically downscaled LR version of the original high-resolution (HR) image. However, this bicubic LR guidance may be suboptimal for the subsequent upscaling (i.e. decoding) and restrict the final reconstruction performance. In this paper, instead of directly applying the LR guidance, we propose an additional invertible flow guidance module (FGM), which can transform the downscaled representation to the visually plausible image during downscaling and transform it back during upscaling. Benefiting from the invertibility of FGM, the downscaled representation could get rid of the LR guidance and would not disturb the downscaling-upscaling process. It allows us to remove the restrictions on the downscaling module and optimize the downscaling and upscaling modules in an end-to-end manner. In this way, these two modules could cooperate to maximize the HR reconstruction performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve state-of-the-art (SotA) performance on both downscaled and reconstructed images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge