Yutong Sun
Integrating Pathology Foundation Models and Spatial Transcriptomics for Cellular Decomposition from Histology Images
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of digital pathology and modern deep learning has facilitated the emergence of pathology foundation models that are expected to solve general pathology problems under various disease conditions in one unified model, with or without fine-tuning. In parallel, spatial transcriptomics has emerged as a transformative technology that enables the profiling of gene expression on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained histology images. Spatial transcriptomics unlocks the unprecedented opportunity to dive into existing histology images at a more granular, cellular level. In this work, we propose a lightweight and training-efficient approach to predict cellular composition directly from H&E-stained histology images by leveraging information-enriched feature embeddings extracted from pre-trained pathology foundation models. By training a lightweight multi-layer perceptron (MLP) regressor on cell-type abundances derived via cell2location, our method efficiently distills knowledge from pathology foundation models and demonstrates the ability to accurately predict cell-type compositions from histology images, without physically performing the costly spatial transcriptomics. Our method demonstrates competitive performance compared to existing methods such as Hist2Cell, while significantly reducing computational complexity.
Electromagnetic Wave Property Inspired Radio Environment Knowledge Construction and AI-based Verification for 6G Digital Twin Channel
Jun 02, 2024



Abstract:As the underlying foundation of a digital twin network (DTN), a digital twin channel (DTC) can accurately depict the process of radio propagation in the air interface to support the DTN-based 6G wireless network. Since radio propagation is affected by the environment, constructing the relationship between the environment and radio wave propagation is the key to improving the accuracy of DTC, and the construction method based on artificial intelligence (AI) is the most concentrated. However, in the existing methods, the environment information input into the neural network (NN) has many dimensions, and the correlation between the environment and the channel relationship is unclear, resulting in a highly complex relationship construction process. To solve this issue, in this paper, we propose a construction method of radio environment knowledge (REK) inspired by the electromagnetic wave property to quantify the contribution of radio propagation. Specifically, a range selection scheme for effective environment information based on random geometry is proposed to reduce the redundancy of environment information. We quantify the contribution of radio propagation reflection, diffraction and scatterer blockage using environment information and propose a flow chart of REK construction to replace the feature extraction process partially based on NN. To validate REK's effectiveness, we conduct a path loss prediction task based on a lightweight convolutional neural network (CNN) employing a simple two-layer convolutional structure. The results show that the accuracy of the range selection method reaches 90\%; the constructed REK maintains the prediction error of 0.3 and only needs 0.04 seconds of testing time, effectively reducing the network complexity.
Towards 6G Digital Twin Channel Using Radio Environment Knowledge Pool
Dec 16, 2023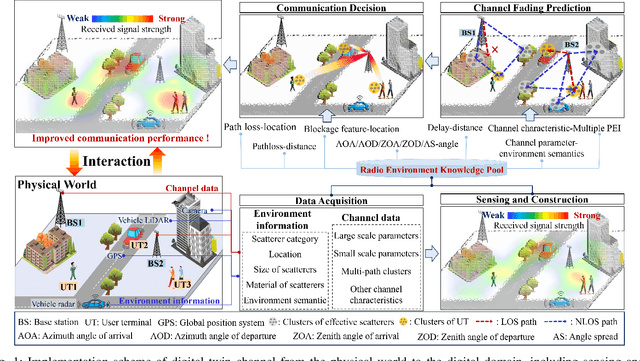
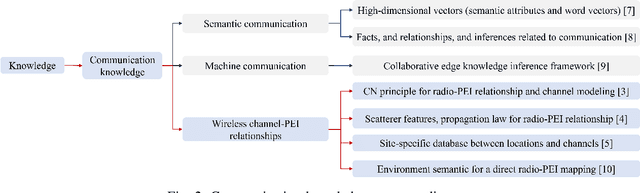
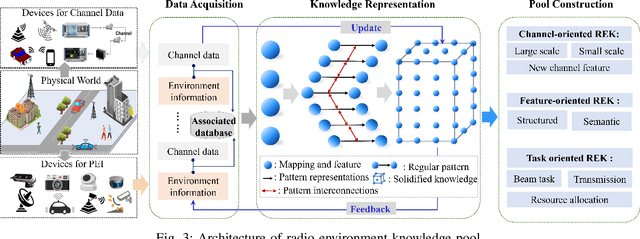
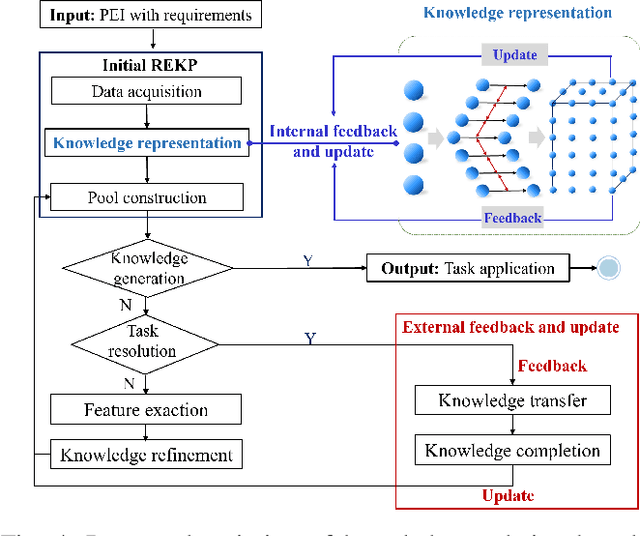
Abstract:DTC is a technical system that reflects the raw channel fading states and variations in a digital form at the virtual space, to actively adapt to novel communication techniques of the wireless communication system (WCS) at the physical or link level. To realize DTC, in this article, the concept and construction method of the radio environment knowledge pool (REKP) is proposed, which possesses the advantages of being controllable, interpretable, renewable, and generalized. Concretely, it is a collection that represents the regular pattern representations and interconnections between propagation environment information (PEI) and channel data. It also has the ability to update knowledge based on environment changes, human cognition, and technological developments. Firstly, the current state of knowledge-based research in the communication field and that for acquiring channel knowledge and achieving DTC are summarized. Secondly, how to construct and update REKP to conduct key communication tasks is given. Then, the typical cases with extensive numerical results are presented to demonstrate the great potential of REKP in enabling DTC. Finally, how to utilize REKP to address key challenges in implementing DTC and 6G WCS are discussed, including interpretability and generalization of DTC, and enhancing performance and reducing costs in the 6G WCS.
Cell Spatial Analysis in Crohn's Disease: Unveiling Local Cell Arrangement Pattern with Graph-based Signatures
Aug 20, 2023Abstract:Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory condition that affects segments of the gastrointestinal tract. CD activity is determined by histological findings, particularly the density of neutrophils observed on Hematoxylin and Eosin stains (H&E) imaging. However, understanding the broader morphometry and local cell arrangement beyond cell counting and tissue morphology remains challenging. To address this, we characterize six distinct cell types from H&E images and develop a novel approach for the local spatial signature of each cell. Specifically, we create a 10-cell neighborhood matrix, representing neighboring cell arrangements for each individual cell. Utilizing t-SNE for non-linear spatial projection in scatter-plot and Kernel Density Estimation contour-plot formats, our study examines patterns of differences in the cellular environment associated with the odds ratio of spatial patterns between active CD and control groups. This analysis is based on data collected at the two research institutes. The findings reveal heterogeneous nearest-neighbor patterns, signifying distinct tendencies of cell clustering, with a particular focus on the rectum region. These variations underscore the impact of data heterogeneity on cell spatial arrangements in CD patients. Moreover, the spatial distribution disparities between the two research sites highlight the significance of collaborative efforts among healthcare organizations. All research analysis pipeline tools are available at https://github.com/MASILab/cellNN.
Polycraft World AI Lab : An Extensible Platform for Evaluating Artificial Intelligence Agents
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:As artificial intelligence research advances, the platforms used to evaluate AI agents need to adapt and grow to continue to challenge them. We present the Polycraft World AI Lab (PAL), a task simulator with an API based on the Minecraft mod Polycraft World. Our platform is built to allow AI agents with different architectures to easily interact with the Minecraft world, train and be evaluated in multiple tasks. PAL enables the creation of tasks in a flexible manner as well as having the capability to manipulate any aspect of the task during an evaluation. All actions taken by AI agents and external actors (non-player-characters, NPCs) in the open-world environment are logged to streamline evaluation. Here we present two custom tasks on the PAL platform, one focused on multi-step planning and one focused on navigation, and evaluations of agents solving them. In summary, we report a versatile and extensible AI evaluation platform with a low barrier to entry for AI researchers to utilize.
How to Define the Propagation Environment Semantics and Its Application in Scatterer-Based Beam Prediction
Sep 17, 2022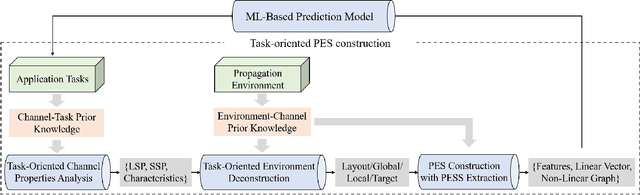
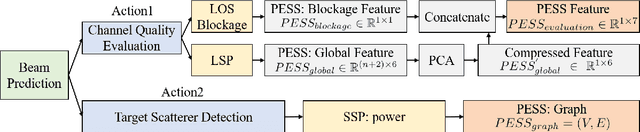
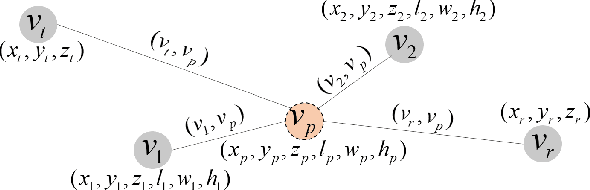
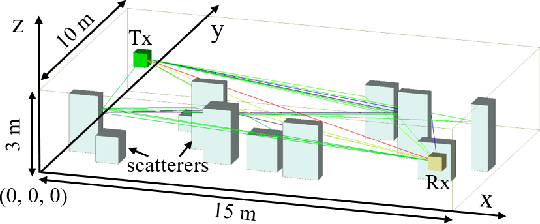
Abstract:In view of the propagation environment directly determining the channel fading, the application tasks can also be solved with the aid of the environment information. Inspired by task-oriented semantic communication and machine learning (ML) powered environment-channel mapping methods, this work aims to provide a new view of the environment from the semantic level, which defines the propagation environment semantics (PES) as a limited set of propagation environment semantic symbols (PESS) for diverse application tasks. The PESS is extracted oriented to the tasks with channel properties as a foundation. For method validation, the PES-aided beam prediction (PESaBP) is presented in non-line-of-sight (NLOS). The PESS of environment features and graphs are given for the semantic actions of channel quality evaluation and target scatterer detection of maximum power, which can obtain 0.92 and 0.9 precision, respectively, and save over 87% of time cost.
Implicit Saliency in Deep Neural Networks
Aug 04, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we show that existing recognition and localization deep architectures, that have not been exposed to eye tracking data or any saliency datasets, are capable of predicting the human visual saliency. We term this as implicit saliency in deep neural networks. We calculate this implicit saliency using expectancy-mismatch hypothesis in an unsupervised fashion. Our experiments show that extracting saliency in this fashion provides comparable performance when measured against the state-of-art supervised algorithms. Additionally, the robustness outperforms those algorithms when we add large noise to the input images. Also, we show that semantic features contribute more than low-level features for human visual saliency detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge