Yuning Wang
Learning from Demonstrations via Capability-Aware Goal Sampling
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Despite its promise, imitation learning often fails in long-horizon environments where perfect replication of demonstrations is unrealistic and small errors can accumulate catastrophically. We introduce Cago (Capability-Aware Goal Sampling), a novel learning-from-demonstrations method that mitigates the brittle dependence on expert trajectories for direct imitation. Unlike prior methods that rely on demonstrations only for policy initialization or reward shaping, Cago dynamically tracks the agent's competence along expert trajectories and uses this signal to select intermediate steps--goals that are just beyond the agent's current reach--to guide learning. This results in an adaptive curriculum that enables steady progress toward solving the full task. Empirical results demonstrate that Cago significantly improves sample efficiency and final performance across a range of sparse-reward, goal-conditioned tasks, consistently outperforming existing learning from-demonstrations baselines.
* 39th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025)
CTS-CBS: A New Approach for Multi-Agent Collaborative Task Sequencing and Path Finding
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses a generalization problem of Multi-Agent Pathfinding (MAPF), called Collaborative Task Sequencing - Multi-Agent Pathfinding (CTS-MAPF), where agents must plan collision-free paths and visit a series of intermediate task locations in a specific order before reaching their final destinations. To address this problem, we propose a new approach, Collaborative Task Sequencing - Conflict-Based Search (CTS-CBS), which conducts a two-level search. In the high level, it generates a search forest, where each tree corresponds to a joint task sequence derived from the jTSP solution. In the low level, CTS-CBS performs constrained single-agent path planning to generate paths for each agent while adhering to high-level constraints. We also provide heoretical guarantees of its completeness and optimality (or sub-optimality with a bounded parameter). To evaluate the performance of CTS-CBS, we create two datasets, CTS-MAPF and MG-MAPF, and conduct comprehensive experiments. The results show that CTS-CBS adaptations for MG-MAPF outperform baseline algorithms in terms of success rate (up to 20 times larger) and runtime (up to 100 times faster), with less than a 10% sacrifice in solution quality. Furthermore, CTS-CBS offers flexibility by allowing users to adjust the sub-optimality bound omega to balance between solution quality and efficiency. Finally, practical robot tests demonstrate the algorithm's applicability in real-world scenarios.
PreGSU-A Generalized Traffic Scene Understanding Model for Autonomous Driving based on Pre-trained Graph Attention Network
Apr 16, 2024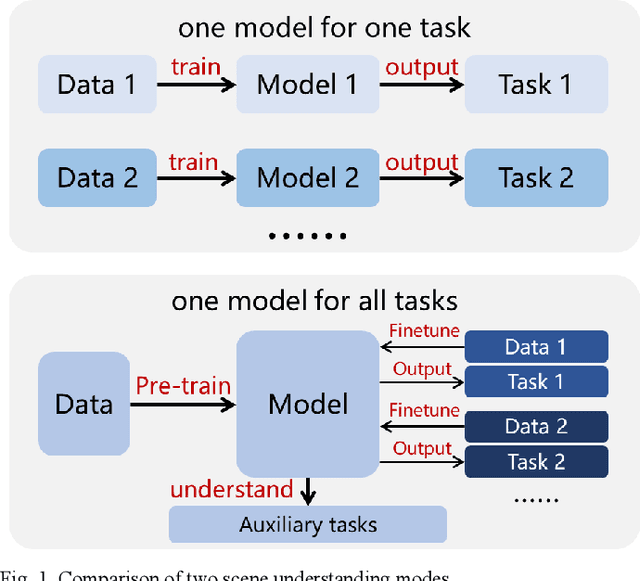
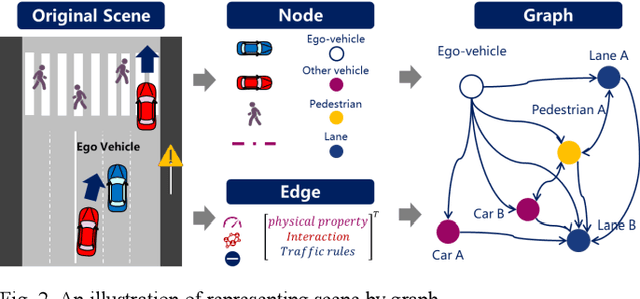
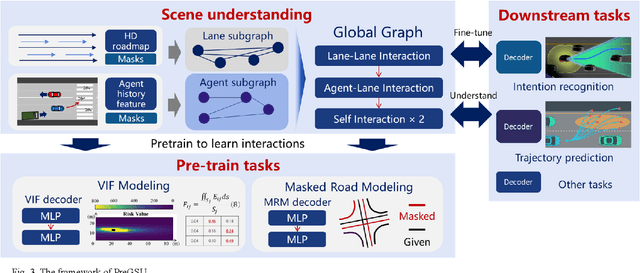
Abstract:Scene understanding, defined as learning, extraction, and representation of interactions among traffic elements, is one of the critical challenges toward high-level autonomous driving (AD). Current scene understanding methods mainly focus on one concrete single task, such as trajectory prediction and risk level evaluation. Although they perform well on specific metrics, the generalization ability is insufficient to adapt to the real traffic complexity and downstream demand diversity. In this study, we propose PreGSU, a generalized pre-trained scene understanding model based on graph attention network to learn the universal interaction and reasoning of traffic scenes to support various downstream tasks. After the feature engineering and sub-graph module, all elements are embedded as nodes to form a dynamic weighted graph. Then, four graph attention layers are applied to learn the relationships among agents and lanes. In the pre-train phase, the understanding model is trained on two self-supervised tasks: Virtual Interaction Force (VIF) modeling and Masked Road Modeling (MRM). Based on the artificial potential field theory, VIF modeling enables PreGSU to capture the agent-to-agent interactions while MRM extracts agent-to-road connections. In the fine-tuning process, the pre-trained parameters are loaded to derive detailed understanding outputs. We conduct validation experiments on two downstream tasks, i.e., trajectory prediction in urban scenario, and intention recognition in highway scenario, to verify the generalized ability and understanding ability. Results show that compared with the baselines, PreGSU achieves better accuracy on both tasks, indicating the potential to be generalized to various scenes and targets. Ablation study shows the effectiveness of pre-train task design.
Integrating Wearable Sensor Data and Self-reported Diaries for Personalized Affect Forecasting
Mar 23, 2024



Abstract:Emotional states, as indicators of affect, are pivotal to overall health, making their accurate prediction before onset crucial. Current studies are primarily centered on immediate short-term affect detection using data from wearable and mobile devices. These studies typically focus on objective sensory measures, often neglecting other forms of self-reported information like diaries and notes. In this paper, we propose a multimodal deep learning model for affect status forecasting. This model combines a transformer encoder with a pre-trained language model, facilitating the integrated analysis of objective metrics and self-reported diaries. To validate our model, we conduct a longitudinal study, enrolling college students and monitoring them over a year, to collect an extensive dataset including physiological, environmental, sleep, metabolic, and physical activity parameters, alongside open-ended textual diaries provided by the participants. Our results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves predictive accuracy of 82.50% for positive affect and 82.76% for negative affect, a full week in advance. The effectiveness of our model is further elevated by its explainability.
A Risk-aware Planning Framework of UGVs in Off-Road Environment
Feb 04, 2024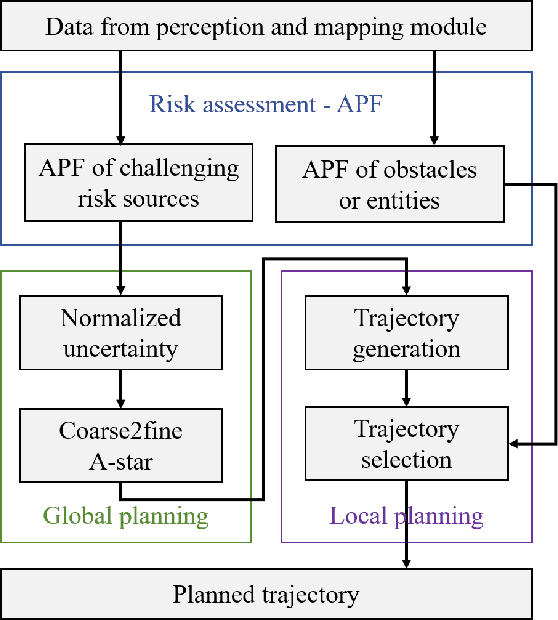
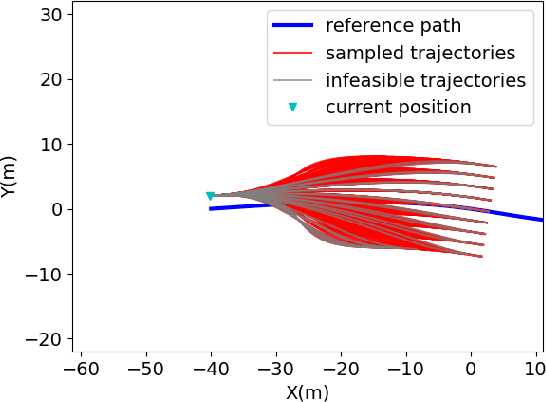
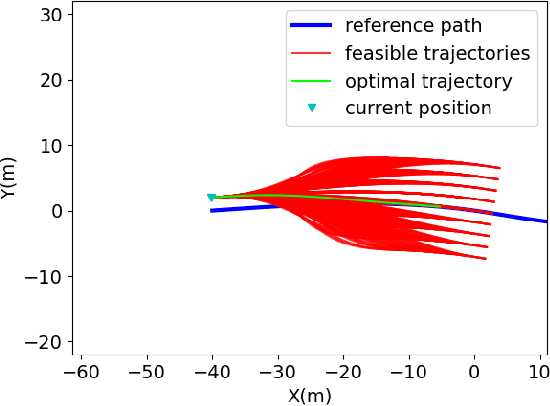
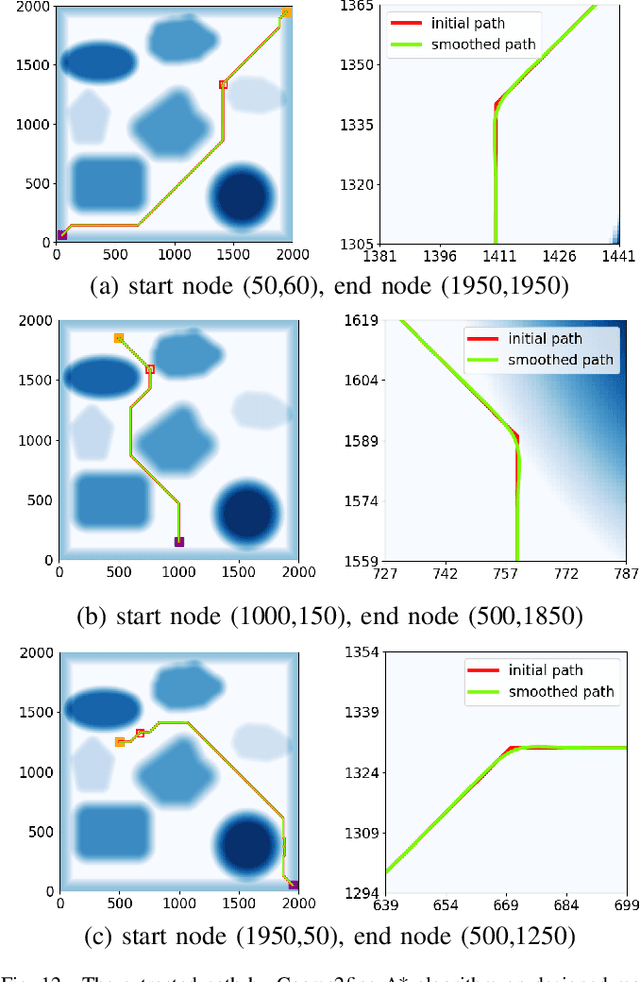
Abstract:Planning module is an essential component of intelligent vehicle study. In this paper, we address the risk-aware planning problem of UGVs through a global-local planning framework which seamlessly integrates risk assessment methods. In particular, a global planning algorithm named Coarse2fine A* is proposed, which incorporates a potential field approach to enhance the safety of the planning results while ensuring the efficiency of the algorithm. A deterministic sampling method for local planning is leveraged and modified to suit off-road environment. It also integrates a risk assessment model to emphasize the avoidance of local risks. The performance of the algorithm is demonstrated through simulation experiments by comparing it with baseline algorithms, where the results of Coarse2fine A* are shown to be approximately 30% safer than those of the baseline algorithms. The practicality and effectiveness of the proposed planning framework are validated by deploying it on a real-world system consisting of a control center and a practical UGV platform.
Easy attention: A simple self-attention mechanism for Transformers
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:To improve the robustness of transformer neural networks used for temporal-dynamics prediction of chaotic systems, we propose a novel attention mechanism called easy attention. Due to the fact that self attention only makes usage of the inner product of queries and keys, it is demonstrated that the keys, queries and softmax are not necessary for obtaining the attention score required to capture long-term dependencies in temporal sequences. Through implementing singular-value decomposition (SVD) on the softmax attention score, we further observe that the self attention compresses contribution from both queries and keys in the spanned space of the attention score. Therefore, our proposed easy-attention method directly treats the attention scores as learnable parameters. This approach produces excellent results when reconstructing and predicting the temporal dynamics of chaotic systems exhibiting more robustness and less complexity than the self attention or the widely-used long short-term memory (LSTM) network. Our results show great potential for applications in more complex high-dimensional dynamical systems.
A Deep-Learning Method Using Auto-encoder and Generative Adversarial Network for Anomaly Detection on Ancient Stone Stele Surfaces
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Accurate detection of natural deterioration and man-made damage on the surfaces of ancient stele in the first instance is essential for their preventive conservation. Existing methods for cultural heritage preservation are not able to achieve this goal perfectly due to the difficulty of balancing accuracy, efficiency, timeliness, and cost. This paper presents a deep-learning method to automatically detect above mentioned emergencies on ancient stone stele in real time, employing autoencoder (AE) and generative adversarial network (GAN). The proposed method overcomes the limitations of existing methods by requiring no extensive anomaly samples while enabling comprehensive detection of unpredictable anomalies. the method includes stages of monitoring, data acquisition, pre-processing, model structuring, and post-processing. Taking the Longmen Grottoes' stone steles as a case study, an unsupervised learning model based on AE and GAN architectures is proposed and validated with a reconstruction accuracy of 99.74\%. The method's evaluation revealed the proficient detection of seven artificially designed anomalies and demonstrated precision and reliability without false alarms. This research provides novel ideas and possibilities for the application of deep learning in the field of cultural heritage.
A Survey on Datasets for Decision-making of Autonomous Vehicle
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AV) are expected to reshape future transportation systems, and decision-making is one of the critical modules toward high-level automated driving. To overcome those complicated scenarios that rule-based methods could not cope with well, data-driven decision-making approaches have aroused more and more focus. The datasets to be used in developing data-driven methods dramatically influences the performance of decision-making, hence it is necessary to have a comprehensive insight into the existing datasets. From the aspects of collection sources, driving data can be divided into vehicle, environment, and driver related data. This study compares the state-of-the-art datasets of these three categories and summarizes their features including sensors used, annotation, and driving scenarios. Based on the characteristics of the datasets, this survey also concludes the potential applications of datasets on various aspects of AV decision-making, assisting researchers to find appropriate ones to support their own research. The future trends of AV dataset development are summarized.
Enhancing Mapless Trajectory Prediction through Knowledge Distillation
Jun 25, 2023

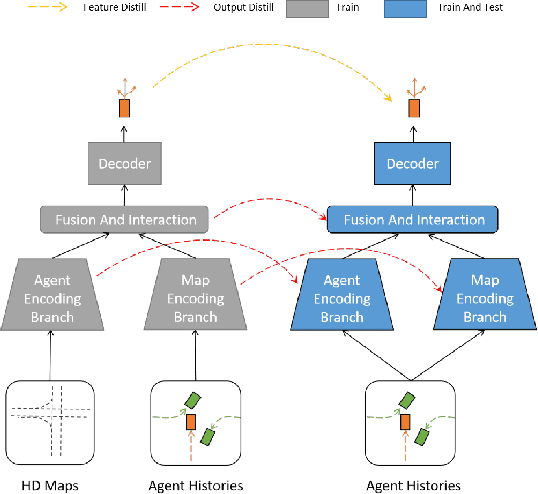

Abstract:Scene information plays a crucial role in trajectory forecasting systems for autonomous driving by providing semantic clues and constraints on potential future paths of traffic agents. Prevalent trajectory prediction techniques often take high-definition maps (HD maps) as part of the inputs to provide scene knowledge. Although HD maps offer accurate road information, they may suffer from the high cost of annotation or restrictions of law that limits their widespread use. Therefore, those methods are still expected to generate reliable prediction results in mapless scenarios. In this paper, we tackle the problem of improving the consistency of multi-modal prediction trajectories and the real road topology when map information is unavailable during the test phase. Specifically, we achieve this by training a map-based prediction teacher network on the annotated samples and transferring the knowledge to a student mapless prediction network using a two-fold knowledge distillation framework. Our solution is generalizable for common trajectory prediction networks and does not bring extra computation burden. Experimental results show that our method stably improves prediction performance in mapless mode on many widely used state-of-the-art trajectory prediction baselines, compensating for the gaps caused by the absence of HD maps. Qualitative visualization results demonstrate that our approach helps infer unseen map information.
$β$-Variational autoencoders and transformers for reduced-order modelling of fluid flows
Apr 07, 2023Abstract:Variational autoencoder (VAE) architectures have the potential to develop reduced-order models (ROMs) for chaotic fluid flows. We propose a method for learning compact and near-orthogonal ROMs using a combination of a $\beta$-VAE and a transformer, tested on numerical data from a two-dimensional viscous flow in both periodic and chaotic regimes. The $\beta$-VAE is trained to learn a compact latent representation of the flow velocity, and the transformer is trained to predict the temporal dynamics in latent space. Using the $\beta$-VAE to learn disentangled representations in latent-space, we obtain a more interpretable flow model with features that resemble those observed in the proper orthogonal decomposition, but with a more efficient representation. Using Poincar\'e maps, the results show that our method can capture the underlying dynamics of the flow outperforming other prediction models. The proposed method has potential applications in other fields such as weather forecasting, structural dynamics or biomedical engineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge