Yuanyuan Gao
Visionary: The World Model Carrier Built on WebGPU-Powered Gaussian Splatting Platform
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Neural rendering, particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has evolved rapidly and become a key component for building world models. However, existing viewer solutions remain fragmented, heavy, or constrained by legacy pipelines, resulting in high deployment friction and limited support for dynamic content and generative models. In this work, we present Visionary, an open, web-native platform for real-time various Gaussian Splatting and meshes rendering. Built on an efficient WebGPU renderer with per-frame ONNX inference, Visionary enables dynamic neural processing while maintaining a lightweight, "click-to-run" browser experience. It introduces a standardized Gaussian Generator contract, which not only supports standard 3DGS rendering but also allows plug-and-play algorithms to generate or update Gaussians each frame. Such inference also enables us to apply feedforward generative post-processing. The platform further offers a plug in three.js library with a concise TypeScript API for seamless integration into existing web applications. Experiments show that, under identical 3DGS assets, Visionary achieves superior rendering efficiency compared to current Web viewers due to GPU-based primitive sorting. It already supports multiple variants, including MLP-based 3DGS, 4DGS, neural avatars, and style transformation or enhancement networks. By unifying inference and rendering directly in the browser, Visionary significantly lowers the barrier to reproduction, comparison, and deployment of 3DGS-family methods, serving as a unified World Model Carrier for both reconstructive and generative paradigms.
CityGS-X: A Scalable Architecture for Efficient and Geometrically Accurate Large-Scale Scene Reconstruction
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Despite its significant achievements in large-scale scene reconstruction, 3D Gaussian Splatting still faces substantial challenges, including slow processing, high computational costs, and limited geometric accuracy. These core issues arise from its inherently unstructured design and the absence of efficient parallelization. To overcome these challenges simultaneously, we introduce CityGS-X, a scalable architecture built on a novel parallelized hybrid hierarchical 3D representation (PH^2-3D). As an early attempt, CityGS-X abandons the cumbersome merge-and-partition process and instead adopts a newly-designed batch-level multi-task rendering process. This architecture enables efficient multi-GPU rendering through dynamic Level-of-Detail voxel allocations, significantly improving scalability and performance. Through extensive experiments, CityGS-X consistently outperforms existing methods in terms of faster training times, larger rendering capacities, and more accurate geometric details in large-scale scenes. Notably, CityGS-X can train and render a scene with 5,000+ images in just 5 hours using only 4 * 4090 GPUs, a task that would make other alternative methods encounter Out-Of-Memory (OOM) issues and fail completely. This implies that CityGS-X is far beyond the capacity of other existing methods.
CoSurfGS:Collaborative 3D Surface Gaussian Splatting with Distributed Learning for Large Scene Reconstruction
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive performance in scene reconstruction. However, most existing GS-based surface reconstruction methods focus on 3D objects or limited scenes. Directly applying these methods to large-scale scene reconstruction will pose challenges such as high memory costs, excessive time consumption, and lack of geometric detail, which makes it difficult to implement in practical applications. To address these issues, we propose a multi-agent collaborative fast 3DGS surface reconstruction framework based on distributed learning for large-scale surface reconstruction. Specifically, we develop local model compression (LMC) and model aggregation schemes (MAS) to achieve high-quality surface representation of large scenes while reducing GPU memory consumption. Extensive experiments on Urban3d, MegaNeRF, and BlendedMVS demonstrate that our proposed method can achieve fast and scalable high-fidelity surface reconstruction and photorealistic rendering. Our project page is available at \url{https://gyy456.github.io/CoSurfGS}.
DGTR: Distributed Gaussian Turbo-Reconstruction for Sparse-View Vast Scenes
Nov 20, 2024
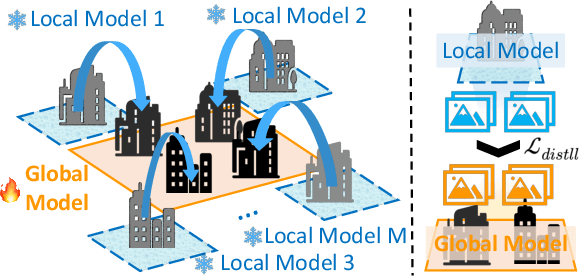


Abstract:Novel-view synthesis (NVS) approaches play a critical role in vast scene reconstruction. However, these methods rely heavily on dense image inputs and prolonged training times, making them unsuitable where computational resources are limited. Additionally, few-shot methods often struggle with poor reconstruction quality in vast environments. This paper presents DGTR, a novel distributed framework for efficient Gaussian reconstruction for sparse-view vast scenes. Our approach divides the scene into regions, processed independently by drones with sparse image inputs. Using a feed-forward Gaussian model, we predict high-quality Gaussian primitives, followed by a global alignment algorithm to ensure geometric consistency. Synthetic views and depth priors are incorporated to further enhance training, while a distillation-based model aggregation mechanism enables efficient reconstruction. Our method achieves high-quality large-scale scene reconstruction and novel-view synthesis in significantly reduced training times, outperforming existing approaches in both speed and scalability. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework on vast aerial scenes, achieving high-quality results within minutes. Code will released on our [https://3d-aigc.github.io/DGTR].
GGRt: Towards Pose-free Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting in Real-time
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents GGRt, a novel approach to generalizable novel view synthesis that alleviates the need for real camera poses, complexity in processing high-resolution images, and lengthy optimization processes, thus facilitating stronger applicability of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) in real-world scenarios. Specifically, we design a novel joint learning framework that consists of an Iterative Pose Optimization Network (IPO-Net) and a Generalizable 3D-Gaussians (G-3DG) model. With the joint learning mechanism, the proposed framework can inherently estimate robust relative pose information from the image observations and thus primarily alleviate the requirement of real camera poses. Moreover, we implement a deferred back-propagation mechanism that enables high-resolution training and inference, overcoming the resolution constraints of previous methods. To enhance the speed and efficiency, we further introduce a progressive Gaussian cache module that dynamically adjusts during training and inference. As the first pose-free generalizable 3D-GS framework, GGRt achieves inference at $\ge$ 5 FPS and real-time rendering at $\ge$ 100 FPS. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that our method outperforms existing NeRF-based pose-free techniques in terms of inference speed and effectiveness. It can also approach the real pose-based 3D-GS methods. Our contributions provide a significant leap forward for the integration of computer vision and computer graphics into practical applications, offering state-of-the-art results on LLFF, KITTI, and Waymo Open datasets and enabling real-time rendering for immersive experiences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge