Yiyang Liu
On-the-Fly VLA Adaptation via Test-Time Reinforcement Learning
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action models have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for general-purpose robot learning, enabling agents to map visual observations and natural-language instructions into executable robotic actions. Though popular, they are primarily trained via supervised fine-tuning or training-time reinforcement learning, requiring explicit fine-tuning phases, human interventions, or controlled data collection. Consequently, existing methods remain unsuitable for challenging simulated- or physical-world deployments, where robots must respond autonomously and flexibly to evolving environments. To address this limitation, we introduce a Test-Time Reinforcement Learning for VLAs (TT-VLA), a framework that enables on-the-fly policy adaptation during inference. TT-VLA formulates a dense reward mechanism that leverages step-by-step task-progress signals to refine action policies during test time while preserving the SFT/RL-trained priors, making it an effective supplement to current VLA models. Empirical results show that our approach enhances overall adaptability, stability, and task success in dynamic, previously unseen scenarios under simulated and real-world settings. We believe TT-VLA offers a principled step toward self-improving, deployment-ready VLAs.
A Topic Modeling Analysis of Stigma Dimensions, Social, and Related Behavioral Circumstances in Clinical Notes Among Patients with HIV
Jun 10, 2025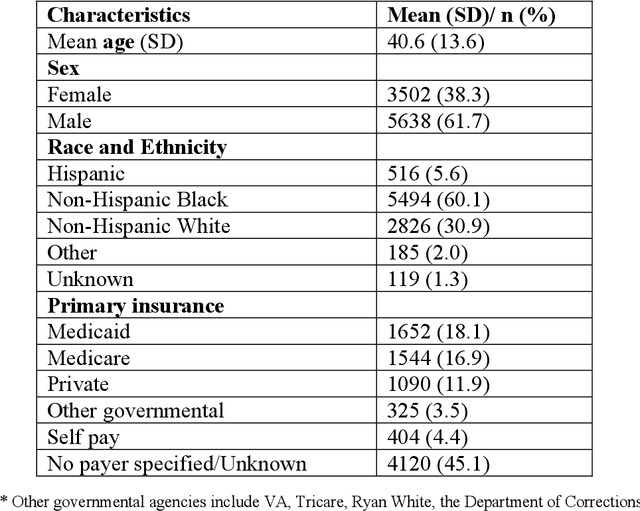
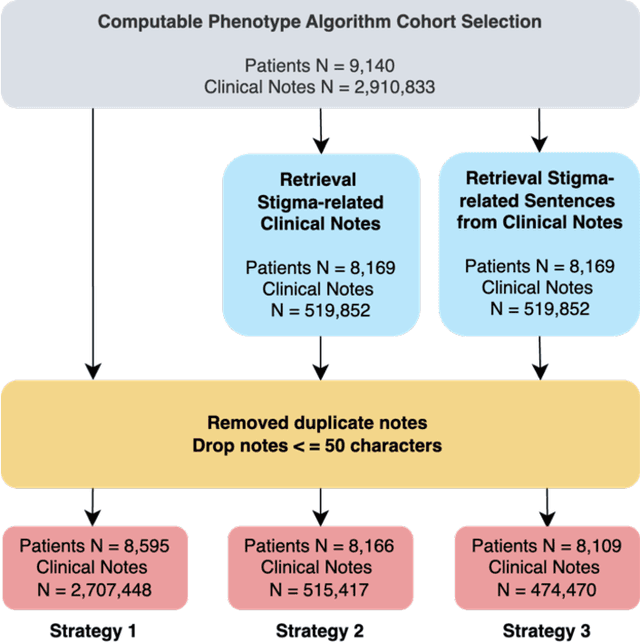
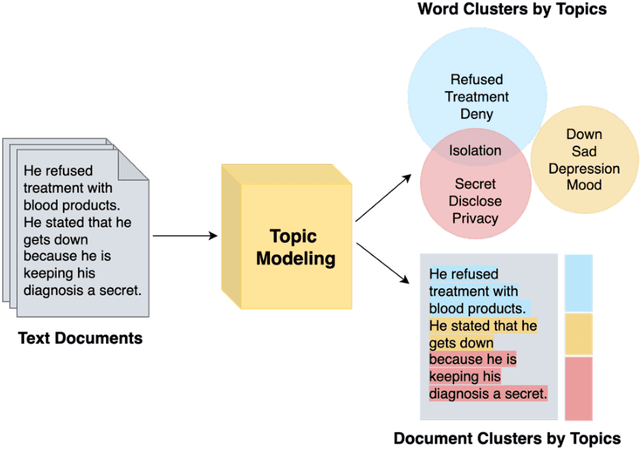
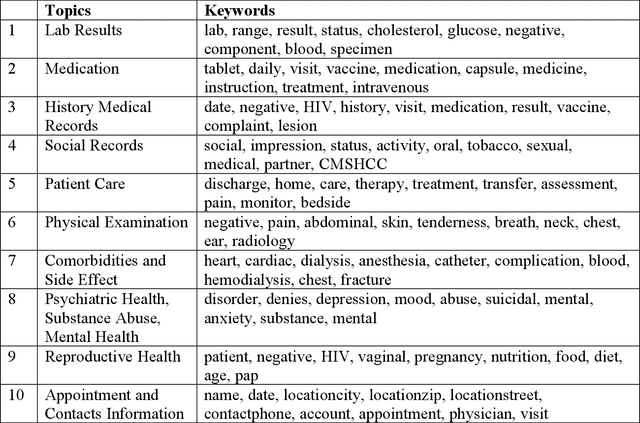
Abstract:Objective: To characterize stigma dimensions, social, and related behavioral circumstances in people living with HIV (PLWHs) seeking care, using natural language processing methods applied to a large collection of electronic health record (EHR) clinical notes from a large integrated health system in the southeast United States. Methods: We identified 9,140 cohort of PLWHs from the UF Health IDR and performed topic modeling analysis using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) to uncover stigma dimensions, social, and related behavioral circumstances. Domain experts created a seed list of HIV-related stigma keywords, then applied a snowball strategy to iteratively review notes for additional terms until saturation was reached. To identify more target topics, we tested three keyword-based filtering strategies. Domain experts manually reviewed the detected topics using the prevalent terms and key discussion topics. Word frequency analysis was used to highlight the prevalent terms associated with each topic. In addition, we conducted topic variation analysis among subgroups to examine differences across age and sex-specific demographics. Results and Conclusion: Topic modeling on sentences containing at least one keyword uncovered a wide range of topic themes associated with HIV-related stigma, social, and related behaviors circumstances, including "Mental Health Concern and Stigma", "Social Support and Engagement", "Limited Healthcare Access and Severe Illness", "Treatment Refusal and Isolation" and so on. Topic variation analysis across age subgroups revealed differences. Extracting and understanding the HIV-related stigma dimensions, social, and related behavioral circumstances from EHR clinical notes enables scalable, time-efficient assessment, overcoming the limitations of traditional questionnaires and improving patient outcomes.
Metadata-Enhanced Speech Emotion Recognition: Augmented Residual Integration and Co-Attention in Two-Stage Fine-Tuning
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) involves analyzing vocal expressions to determine the emotional state of speakers, where the comprehensive and thorough utilization of audio information is paramount. Therefore, we propose a novel approach on self-supervised learning (SSL) models that employs all available auxiliary information -- specifically metadata -- to enhance performance. Through a two-stage fine-tuning method in multi-task learning, we introduce the Augmented Residual Integration (ARI) module, which enhances transformer layers in encoder of SSL models. The module efficiently preserves acoustic features across all different levels, thereby significantly improving the performance of metadata-related auxiliary tasks that require various levels of features. Moreover, the Co-attention module is incorporated due to its complementary nature with ARI, enabling the model to effectively utilize multidimensional information and contextual relationships from metadata-related auxiliary tasks. Under pre-trained base models and speaker-independent setup, our approach consistently surpasses state-of-the-art (SOTA) models on multiple SSL encoders for the IEMOCAP dataset.
MixCut:A Data Augmentation Method for Facial Expression Recognition
May 17, 2024Abstract:In the facial expression recognition task, researchers always get low accuracy of expression classification due to a small amount of training samples. In order to solve this kind of problem, we proposes a new data augmentation method named MixCut. In this method, we firstly interpolate the two original training samples at the pixel level in a random ratio to generate new samples. Then, pixel removal is performed in random square regions on the new samples to generate the final training samples. We evaluated the MixCut method on Fer2013Plus and RAF-DB. With MixCut, we achieved 85.63% accuracy in eight-label classification on Fer2013Plus and 87.88% accuracy in seven-label classification on RAF-DB, effectively improving the classification accuracy of facial expression image recognition. Meanwhile, on Fer2013Plus, MixCut achieved performance improvements of +0.59%, +0.36%, and +0.39% compared to the other three data augmentation methods: CutOut, Mixup, and CutMix, respectively. MixCut improves classification accuracy on RAF-DB by +0.22%, +0.65%, and +0.5% over these three data augmentation methods.
A survey on fairness of large language models in e-commerce: progress, application, and challenge
May 15, 2024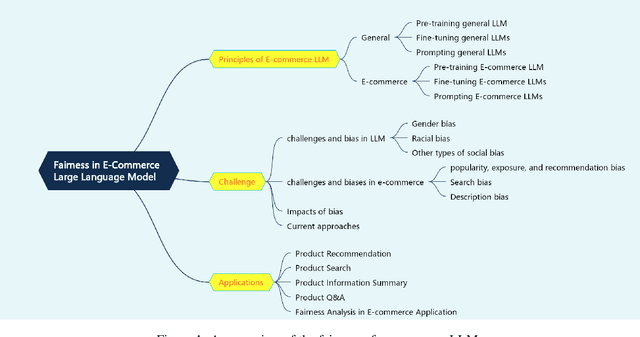
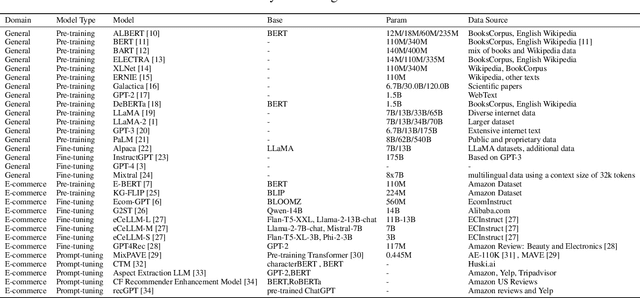
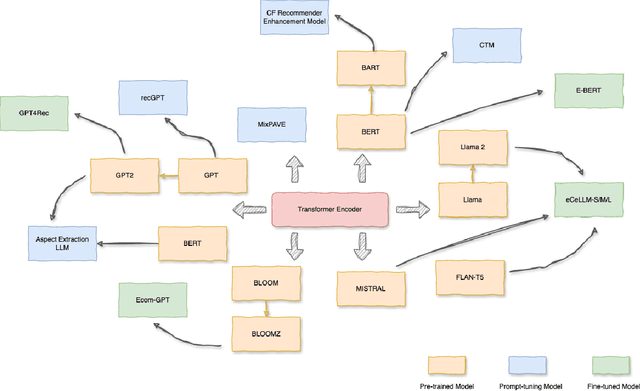
Abstract:This survey explores the fairness of large language models (LLMs) in e-commerce, examining their progress, applications, and the challenges they face. LLMs have become pivotal in the e-commerce domain, offering innovative solutions and enhancing customer experiences. This work presents a comprehensive survey on the applications and challenges of LLMs in e-commerce. The paper begins by introducing the key principles underlying the use of LLMs in e-commerce, detailing the processes of pretraining, fine-tuning, and prompting that tailor these models to specific needs. It then explores the varied applications of LLMs in e-commerce, including product reviews, where they synthesize and analyze customer feedback; product recommendations, where they leverage consumer data to suggest relevant items; product information translation, enhancing global accessibility; and product question and answer sections, where they automate customer support. The paper critically addresses the fairness challenges in e-commerce, highlighting how biases in training data and algorithms can lead to unfair outcomes, such as reinforcing stereotypes or discriminating against certain groups. These issues not only undermine consumer trust, but also raise ethical and legal concerns. Finally, the work outlines future research directions, emphasizing the need for more equitable and transparent LLMs in e-commerce. It advocates for ongoing efforts to mitigate biases and improve the fairness of these systems, ensuring they serve diverse global markets effectively and ethically. Through this comprehensive analysis, the survey provides a holistic view of the current landscape of LLMs in e-commerce, offering insights into their potential and limitations, and guiding future endeavors in creating fairer and more inclusive e-commerce environments.
LLM-Powered Test Case Generation for Detecting Tricky Bugs
Apr 16, 2024
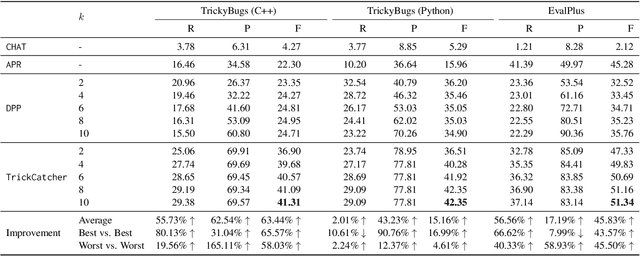

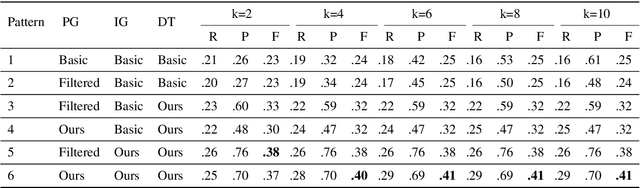
Abstract:Conventional automated test generation tools struggle to generate test oracles and tricky bug-revealing test inputs. Large Language Models (LLMs) can be prompted to produce test inputs and oracles for a program directly, but the precision of the tests can be very low for complex scenarios (only 6.3% based on our experiments). To fill this gap, this paper proposes AID, which combines LLMs with differential testing to generate fault-revealing test inputs and oracles targeting plausibly correct programs (i.e., programs that have passed all the existing tests). In particular, AID selects test inputs that yield diverse outputs on a set of program variants generated by LLMs, then constructs the test oracle based on the outputs. We evaluate AID on two large-scale datasets with tricky bugs: TrickyBugs and EvalPlus, and compare it with three state-of-the-art baselines. The evaluation results show that the recall, precision, and F1 score of AID outperform the state-of-the-art by up to 1.80x, 2.65x, and 1.66x, respectively.
Hint-dynamic Knowledge Distillation
Nov 30, 2022


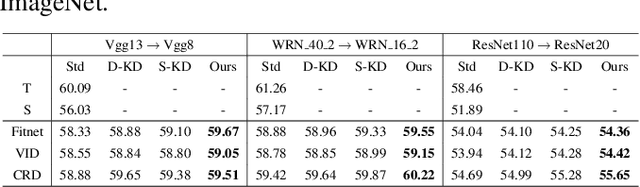
Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) transfers the knowledge from a high-capacity teacher model to promote a smaller student model. Existing efforts guide the distillation by matching their prediction logits, feature embedding, etc., while leaving how to efficiently utilize them in junction less explored. In this paper, we propose Hint-dynamic Knowledge Distillation, dubbed HKD, which excavates the knowledge from the teacher' s hints in a dynamic scheme. The guidance effect from the knowledge hints usually varies in different instances and learning stages, which motivates us to customize a specific hint-learning manner for each instance adaptively. Specifically, a meta-weight network is introduced to generate the instance-wise weight coefficients about knowledge hints in the perception of the dynamical learning progress of the student model. We further present a weight ensembling strategy to eliminate the potential bias of coefficient estimation by exploiting the historical statics. Experiments on standard benchmarks of CIFAR-100 and Tiny-ImageNet manifest that the proposed HKD well boost the effect of knowledge distillation tasks.
Recognizing Nested Entities from Flat Supervision: A New NER Subtask, Feasibility and Challenges
Nov 01, 2022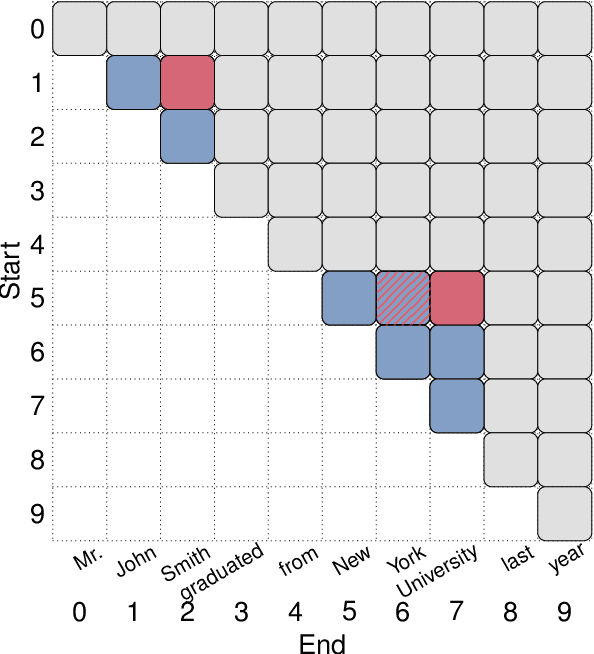
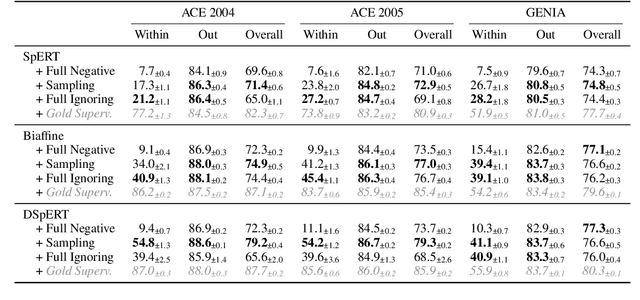
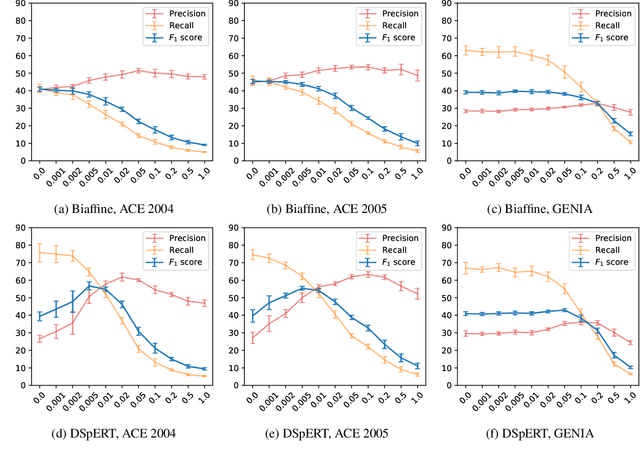
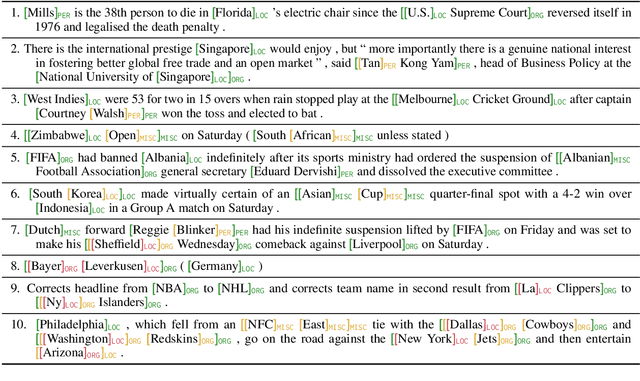
Abstract:Many recent named entity recognition (NER) studies criticize flat NER for its non-overlapping assumption, and switch to investigating nested NER. However, existing nested NER models heavily rely on training data annotated with nested entities, while labeling such data is costly. This study proposes a new subtask, nested-from-flat NER, which corresponds to a realistic application scenario: given data annotated with flat entities only, one may still desire the trained model capable of recognizing nested entities. To address this task, we train span-based models and deliberately ignore the spans nested inside labeled entities, since these spans are possibly unlabeled entities. With nested entities removed from the training data, our model achieves 54.8%, 54.2% and 41.1% F1 scores on the subset of spans within entities on ACE 2004, ACE 2005 and GENIA, respectively. This suggests the effectiveness of our approach and the feasibility of the task. In addition, the model's performance on flat entities is entirely unaffected. We further manually annotate the nested entities in the test set of CoNLL 2003, creating a nested-from-flat NER benchmark. Analysis results show that the main challenges stem from the data and annotation inconsistencies between the flat and nested entities.
Deep Span Representations for Named Entity Recognition
Oct 09, 2022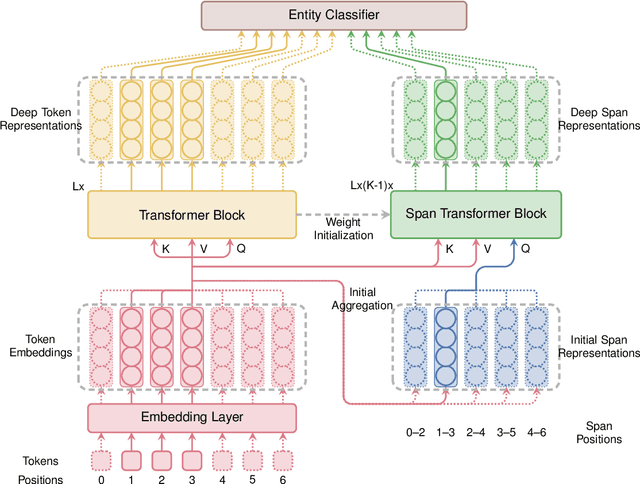
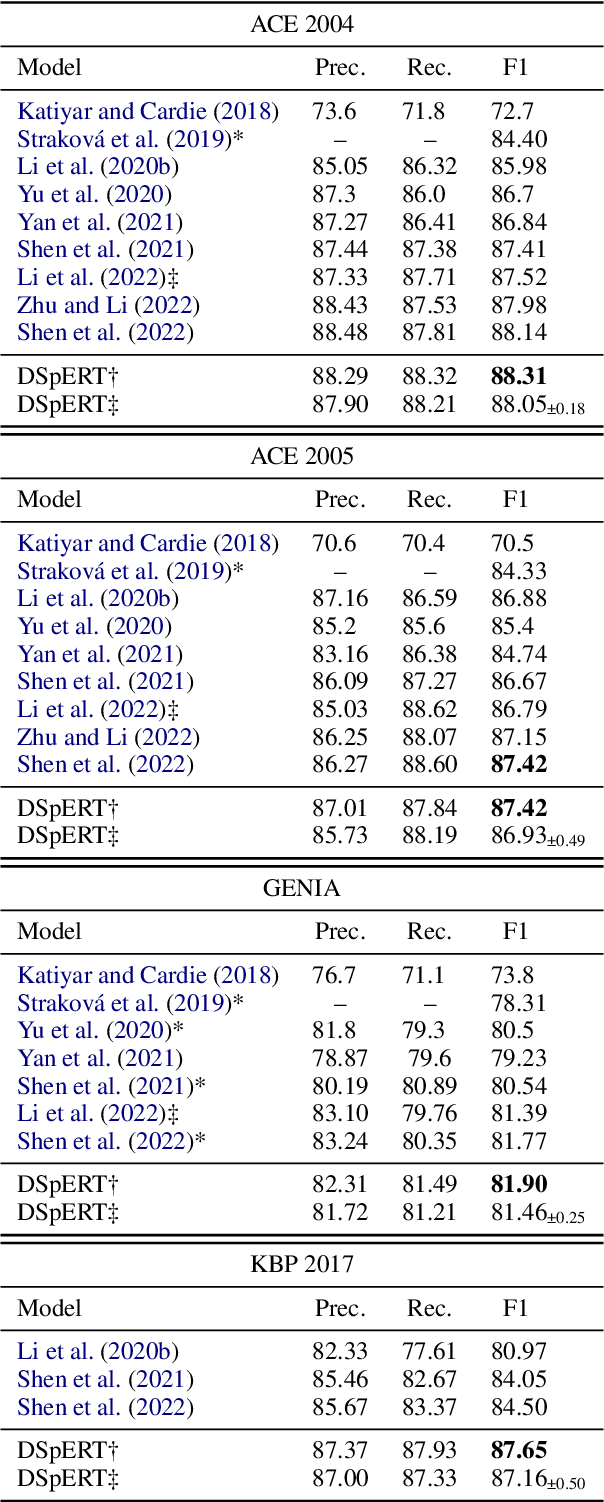

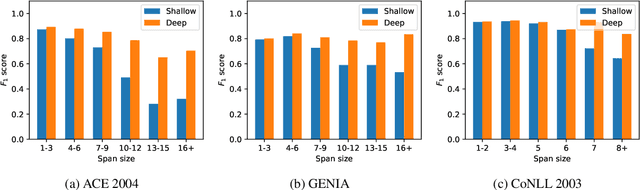
Abstract:Span-based models are one of the most straightforward methods for named entity recognition (NER). Existing span-based NER systems shallowly aggregate the token representations to span representations. However, this typically results in significant ineffectiveness for long-span entities, a coupling between the representations of overlapping spans, and ultimately a performance degradation. In this study, we propose DSpERT (Deep Span Encoder Representations from Transformers), which comprises a standard Transformer and a span Transformer. The latter uses low-layered span representations as queries, and aggregates the token representations as keys and values, layer by layer from bottom to top. Thus, DSpERT produces span representations of deep semantics. With weight initialization from pretrained language models, DSpERT achieves performance higher than or competitive with recent state-of-the-art systems on eight NER benchmarks. Experimental results verify the importance of the depth for span representations, and show that DSpERT performs particularly well on long-span entities and nested structures. Further, the deep span representations are well structured and easily separable in the feature space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge