Yijia Liu
FreeDriveRF: Monocular RGB Dynamic NeRF without Poses for Autonomous Driving via Point-Level Dynamic-Static Decoupling
May 14, 2025Abstract:Dynamic scene reconstruction for autonomous driving enables vehicles to perceive and interpret complex scene changes more precisely. Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have recently shown promising capability in scene modeling. However, many existing methods rely heavily on accurate poses inputs and multi-sensor data, leading to increased system complexity. To address this, we propose FreeDriveRF, which reconstructs dynamic driving scenes using only sequential RGB images without requiring poses inputs. We innovatively decouple dynamic and static parts at the early sampling level using semantic supervision, mitigating image blurring and artifacts. To overcome the challenges posed by object motion and occlusion in monocular camera, we introduce a warped ray-guided dynamic object rendering consistency loss, utilizing optical flow to better constrain the dynamic modeling process. Additionally, we incorporate estimated dynamic flow to constrain the pose optimization process, improving the stability and accuracy of unbounded scene reconstruction. Extensive experiments conducted on the KITTI and Waymo datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method in dynamic scene modeling for autonomous driving.
Implicit Generative Prior for Bayesian Neural Networks
Apr 27, 2024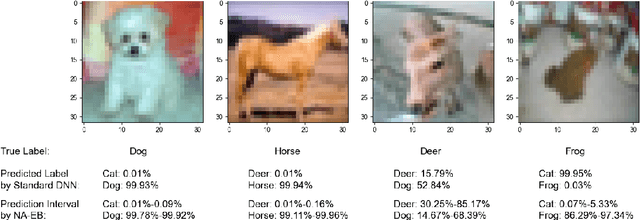
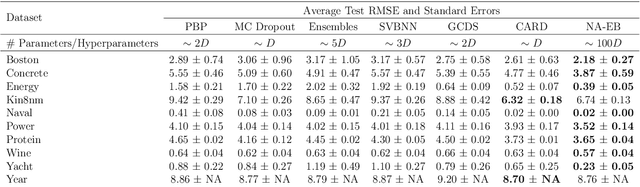
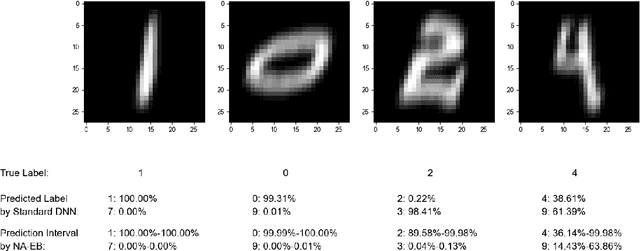
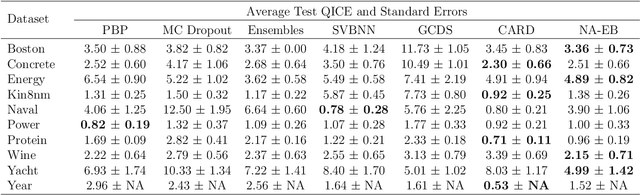
Abstract:Predictive uncertainty quantification is crucial for reliable decision-making in various applied domains. Bayesian neural networks offer a powerful framework for this task. However, defining meaningful priors and ensuring computational efficiency remain significant challenges, especially for complex real-world applications. This paper addresses these challenges by proposing a novel neural adaptive empirical Bayes (NA-EB) framework. NA-EB leverages a class of implicit generative priors derived from low-dimensional distributions. This allows for efficient handling of complex data structures and effective capture of underlying relationships in real-world datasets. The proposed NA-EB framework combines variational inference with a gradient ascent algorithm. This enables simultaneous hyperparameter selection and approximation of the posterior distribution, leading to improved computational efficiency. We establish the theoretical foundation of the framework through posterior and classification consistency. We demonstrate the practical applications of our framework through extensive evaluations on a variety of tasks, including the two-spiral problem, regression, 10 UCI datasets, and image classification tasks on both MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets. The results of our experiments highlight the superiority of our proposed framework over existing methods, such as sparse variational Bayesian and generative models, in terms of prediction accuracy and uncertainty quantification.
Improving Biomedical Pretrained Language Models with Knowledge
Apr 21, 2021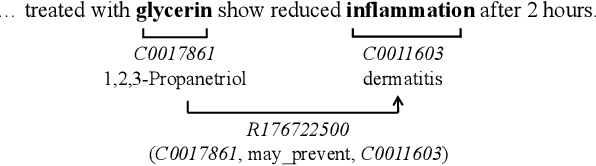

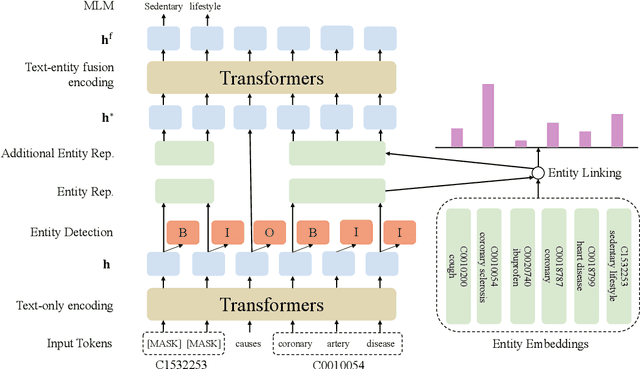
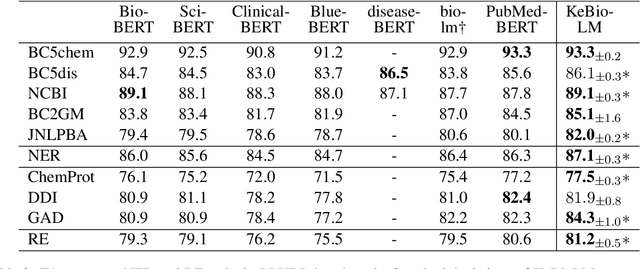
Abstract:Pretrained language models have shown success in many natural language processing tasks. Many works explore incorporating knowledge into language models. In the biomedical domain, experts have taken decades of effort on building large-scale knowledge bases. For example, the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) contains millions of entities with their synonyms and defines hundreds of relations among entities. Leveraging this knowledge can benefit a variety of downstream tasks such as named entity recognition and relation extraction. To this end, we propose KeBioLM, a biomedical pretrained language model that explicitly leverages knowledge from the UMLS knowledge bases. Specifically, we extract entities from PubMed abstracts and link them to UMLS. We then train a knowledge-aware language model that firstly applies a text-only encoding layer to learn entity representation and applies a text-entity fusion encoding to aggregate entity representation. Besides, we add two training objectives as entity detection and entity linking. Experiments on the named entity recognition and relation extraction from the BLURB benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Further analysis on a collected probing dataset shows that our model has better ability to model medical knowledge.
Lattice-BERT: Leveraging Multi-Granularity Representations in Chinese Pre-trained Language Models
Apr 15, 2021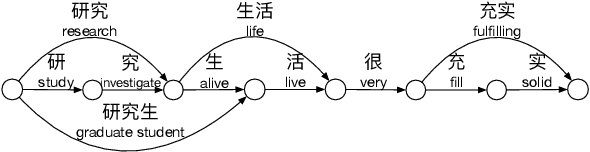


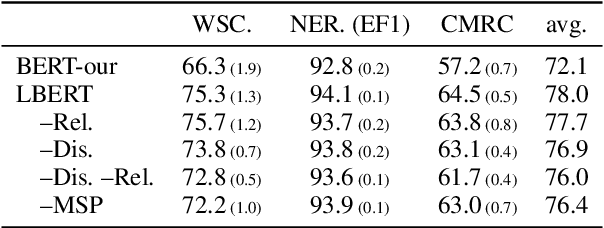
Abstract:Chinese pre-trained language models usually process text as a sequence of characters, while ignoring more coarse granularity, e.g., words. In this work, we propose a novel pre-training paradigm for Chinese -- Lattice-BERT, which explicitly incorporates word representations along with characters, thus can model a sentence in a multi-granularity manner. Specifically, we construct a lattice graph from the characters and words in a sentence and feed all these text units into transformers. We design a lattice position attention mechanism to exploit the lattice structures in self-attention layers. We further propose a masked segment prediction task to push the model to learn from rich but redundant information inherent in lattices, while avoiding learning unexpected tricks. Experiments on 11 Chinese natural language understanding tasks show that our model can bring an average increase of 1.5% under the 12-layer setting, which achieves new state-of-the-art among base-size models on the CLUE benchmarks. Further analysis shows that Lattice-BERT can harness the lattice structures, and the improvement comes from the exploration of redundant information and multi-granularity representations. Our code will be available at https://github.com/alibaba/pretrained-language-models/LatticeBERT.
VECO: Variable Encoder-decoder Pre-training for Cross-lingual Understanding and Generation
Oct 30, 2020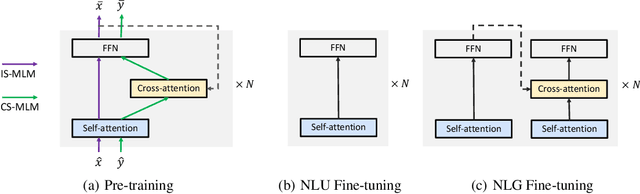



Abstract:Recent studies about learning multilingual representations have achieved significant performance gains across a wide range of downstream cross-lingual tasks. They train either an encoder-only Transformer mainly for understanding tasks, or an encoder-decoder Transformer specifically for generation tasks, ignoring the correlation between the two tasks and frameworks. In contrast, this paper presents a variable encoder-decoder (VECO) pre-training approach to unify the two mainstreams in both model architectures and pre-training tasks. VECO splits the standard Transformer block into several sub-modules trained with both inner-sequence and cross-sequence masked language modeling, and correspondingly reorganizes certain sub-modules for understanding and generation tasks during inference. Such a workflow not only ensures to train the most streamlined parameters necessary for two kinds of tasks, but also enables them to boost each other via sharing common sub-modules. As a result, VECO delivers new state-of-the-art results on various cross-lingual understanding tasks of the XTREME benchmark covering text classification, sequence labeling, question answering, and sentence retrieval. For generation tasks, VECO also outperforms all existing cross-lingual models and state-of-the-art Transformer variants on WMT14 English-to-German and English-to-French translation datasets, with gains of up to 1$\sim$2 BLEU.
Few-shot Slot Tagging with Collapsed Dependency Transfer and Label-enhanced Task-adaptive Projection Network
Jun 10, 2020
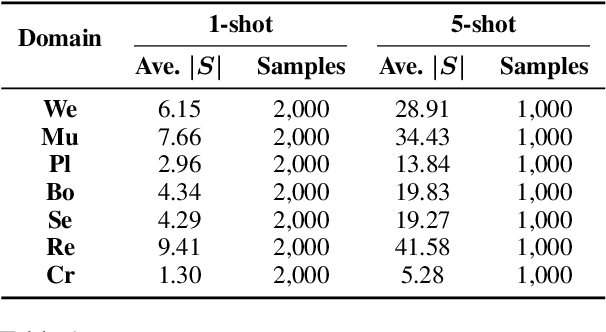

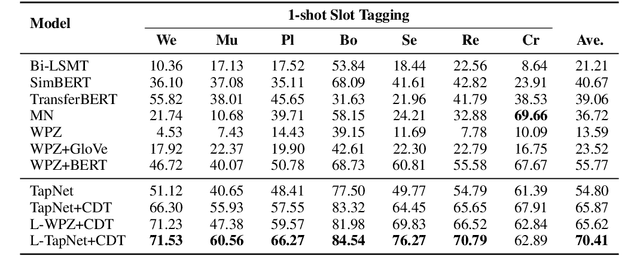
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the slot tagging with only a few labeled support sentences (a.k.a. few-shot). Few-shot slot tagging faces a unique challenge compared to the other few-shot classification problems as it calls for modeling the dependencies between labels. But it is hard to apply previously learned label dependencies to an unseen domain, due to the discrepancy of label sets. To tackle this, we introduce a collapsed dependency transfer mechanism into the conditional random field (CRF) to transfer abstract label dependency patterns as transition scores. In the few-shot setting, the emission score of CRF can be calculated as a word's similarity to the representation of each label. To calculate such similarity, we propose a Label-enhanced Task-Adaptive Projection Network (L-TapNet) based on the state-of-the-art few-shot classification model -- TapNet, by leveraging label name semantics in representing labels. Experimental results show that our model significantly outperforms the strongest few-shot learning baseline by 14.64 F1 scores in the one-shot setting.
Entity-Consistent End-to-end Task-Oriented Dialogue System with KB Retriever
Sep 18, 2019
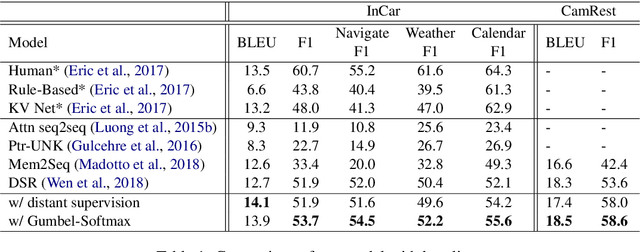
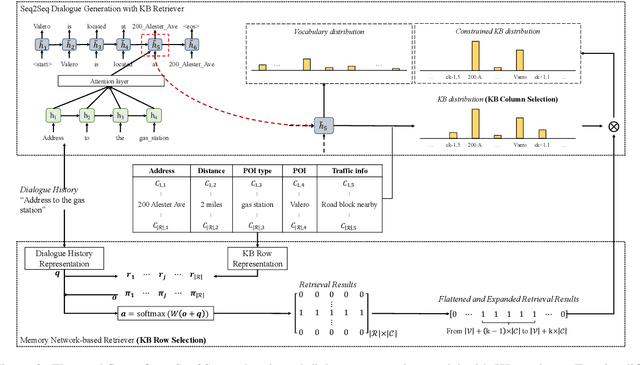
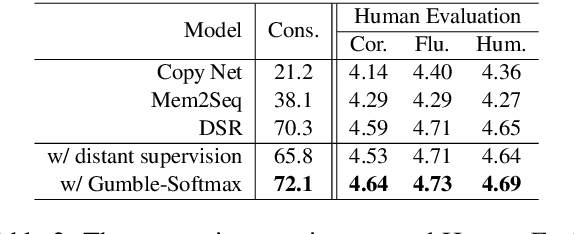
Abstract:Querying the knowledge base (KB) has long been a challenge in the end-to-end task-oriented dialogue system. Previous sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) dialogue generation work treats the KB query as an attention over the entire KB, without the guarantee that the generated entities are consistent with each other. In this paper, we propose a novel framework which queries the KB in two steps to improve the consistency of generated entities. In the first step, inspired by the observation that a response can usually be supported by a single KB row, we introduce a KB retrieval component which explicitly returns the most relevant KB row given a dialogue history. The retrieval result is further used to filter the irrelevant entities in a Seq2Seq response generation model to improve the consistency among the output entities. In the second step, we further perform the attention mechanism to address the most correlated KB column. Two methods are proposed to make the training feasible without labeled retrieval data, which include distant supervision and Gumbel-Softmax technique. Experiments on two publicly available task oriented dialog datasets show the effectiveness of our model by outperforming the baseline systems and producing entity-consistent responses.
Cross-Lingual BERT Transformation for Zero-Shot Dependency Parsing
Sep 15, 2019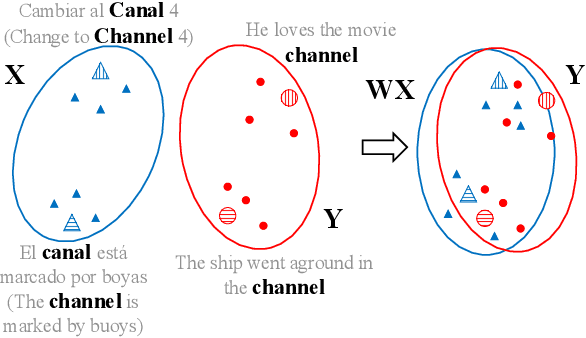
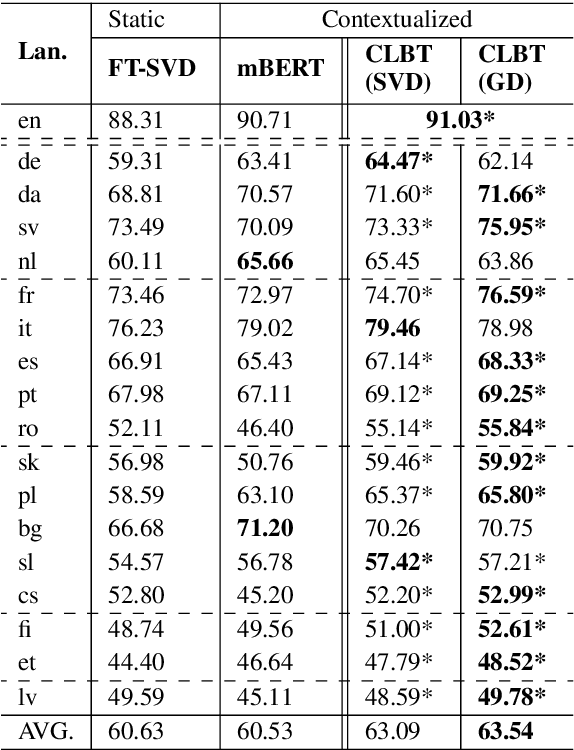
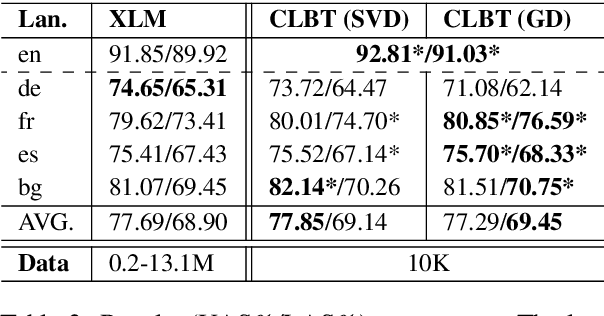
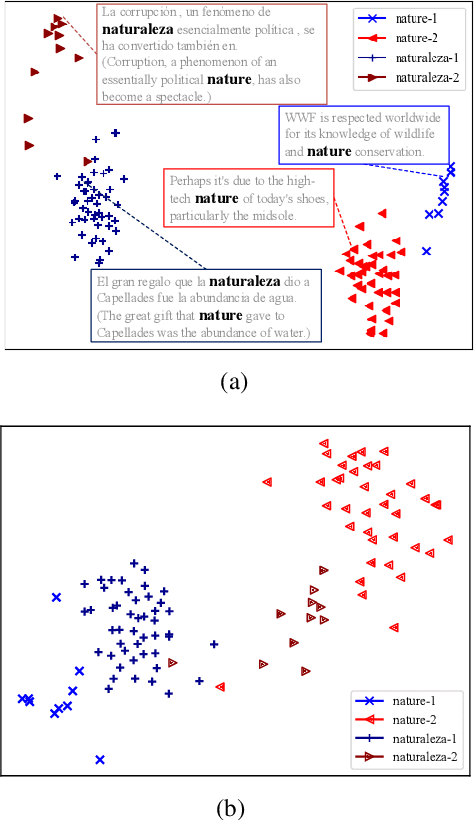
Abstract:This paper investigates the problem of learning cross-lingual representations in a contextual space. We propose Cross-Lingual BERT Transformation (CLBT), a simple and efficient approach to generate cross-lingual contextualized word embeddings based on publicly available pre-trained BERT models (Devlin et al., 2018). In this approach, a linear transformation is learned from contextual word alignments to align the contextualized embeddings independently trained in different languages. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach on zero-shot cross-lingual transfer parsing. Experiments show that our embeddings substantially outperform the previous state-of-the-art that uses static embeddings. We further compare our approach with XLM (Lample and Conneau, 2019), a recently proposed cross-lingual language model trained with massive parallel data, and achieve highly competitive results.
Few-Shot Sequence Labeling with Label Dependency Transfer
Jun 20, 2019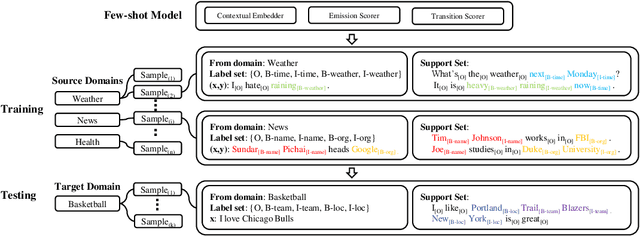
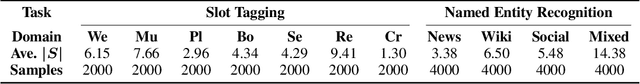
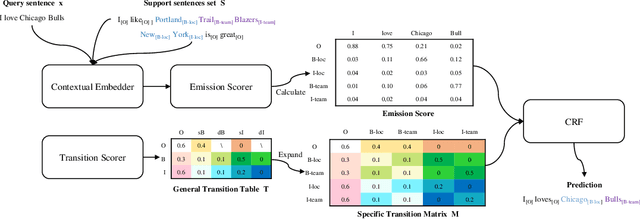
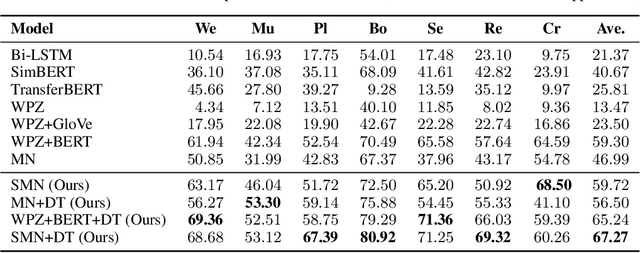
Abstract:Few-shot sequence labeling faces a unique challenge compared with the other fewshot classification problems, owing to the necessity for modeling the dependencies between labels. Different domains often have different label sets, which makes it difficult to directly utilize the label dependencies learned from one domain in another domain. In this paper, we introduce the dependency transfer mechanism that addresses such label-discrepancy problem. The dependency transfer mechanism learns the abstract label transition patterns from the source domains and generalizes such patterns in the target domain to benefit the prediction of a label sequence. We also develop the sequence matching network by adapting the matching network to sequence labeling case. Moreover, we propose a CRF-based few-shot sequence labeling framework to integrate both the dependency transfer mechanism and the sequence matching network. Experiments on slot tagging (ST) and named entity recognition (NER) datasets show that our model significantly outperforms the strongest few-shot learning baseline by 7.96 and 11.70 F1 scores respectively in the 1-shot setting.
An AMR Aligner Tuned by Transition-based Parser
Oct 08, 2018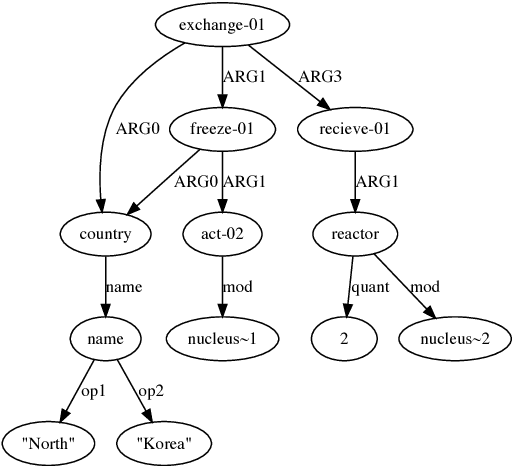
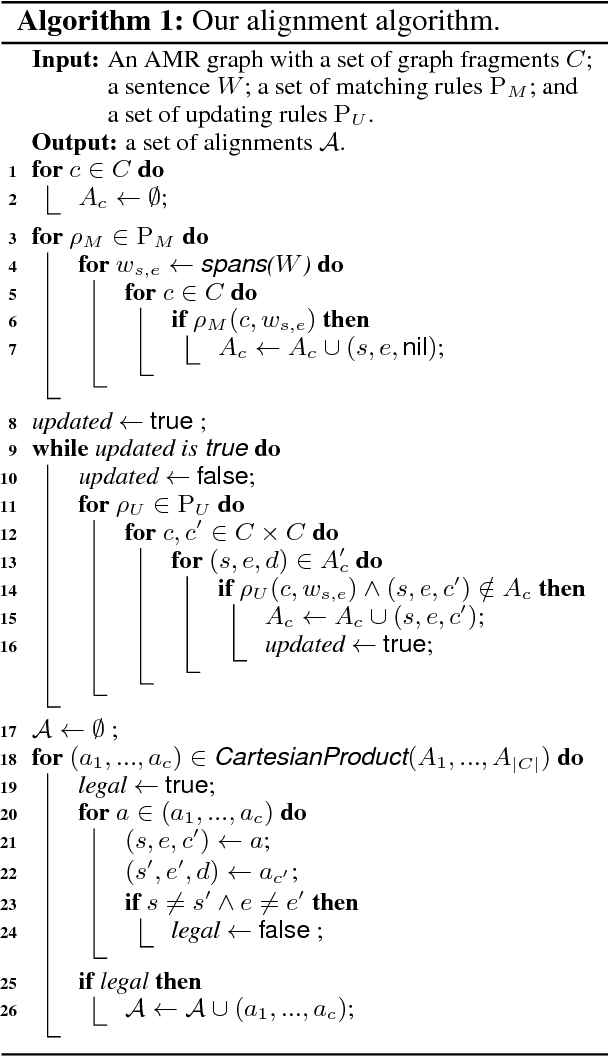
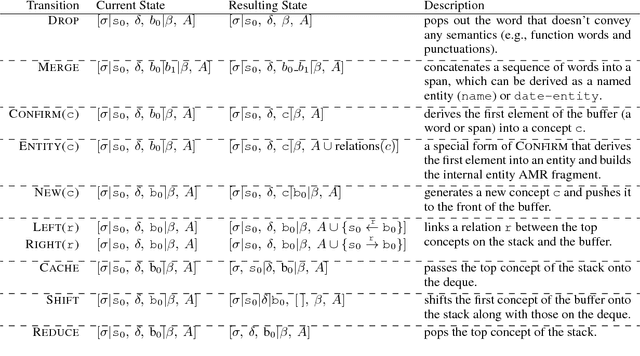
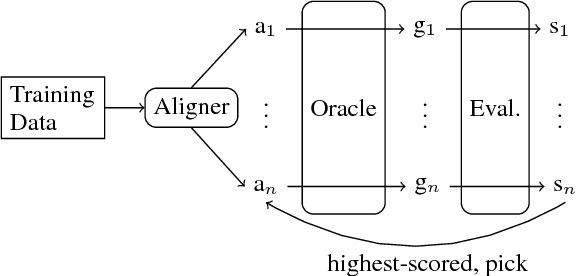
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new rich resource enhanced AMR aligner which produces multiple alignments and a new transition system for AMR parsing along with its oracle parser. Our aligner is further tuned by our oracle parser via picking the alignment that leads to the highest-scored achievable AMR graph. Experimental results show that our aligner outperforms the rule-based aligner in previous work by achieving higher alignment F1 score and consistently improving two open-sourced AMR parsers. Based on our aligner and transition system, we develop a transition-based AMR parser that parses a sentence into its AMR graph directly. An ensemble of our parsers with only words and POS tags as input leads to 68.4 Smatch F1 score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge