Yihan Xu
EcoFlight: Finding Low-Energy Paths Through Obstacles for Autonomous Sensing Drones
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Obstacle avoidance path planning for uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), or drones, is rarely addressed in most flight path planning schemes, despite obstacles being a realistic condition. Obstacle avoidance can also be energy-intensive, making it a critical factor in efficient point-to-point drone flights. To address these gaps, we propose EcoFlight, an energy-efficient pathfinding algorithm that determines the lowest-energy route in 3D space with obstacles. The algorithm models energy consumption based on the drone propulsion system and flight dynamics. We conduct extensive evaluations, comparing EcoFlight with direct-flight and shortest-distance schemes. The simulation results across various obstacle densities show that EcoFlight consistently finds paths with lower energy consumption than comparable algorithms, particularly in high-density environments. We also demonstrate that a suitable flying speed can further enhance energy savings.
* Autonomous drone, A* algorithm, 3D environments, path planning, obstacle avoidance, energy efficiency, MIT Conference
Learning to Beamform for Cooperative Localization and Communication: A Link Heterogeneous GNN-Based Approach
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a key enabler for next-generation wireless networks, supporting advanced applications such as high-precision localization and environment reconstruction. Cooperative ISAC (CoISAC) further enhances these capabilities by enabling multiple base stations (BSs) to jointly optimize communication and sensing performance through coordination. However, CoISAC beamforming design faces significant challenges due to system heterogeneity, large-scale problem complexity, and sensitivity to parameter estimation errors. Traditional deep learning-based techniques fail to exploit the unique structural characteristics of CoISAC systems, thereby limiting their ability to enhance system performance. To address these challenges, we propose a Link-Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (LHGNN) for joint beamforming in CoISAC systems. Unlike conventional approaches, LHGNN models communication and sensing links as heterogeneous nodes and their interactions as edges, enabling the capture of the heterogeneous nature and intricate interactions of CoISAC systems. Furthermore, a graph attention mechanism is incorporated to dynamically adjust node and link importance, improving robustness to channel and position estimation errors. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed attention-enhanced LHGNN achieves superior communication rates while maintaining sensing accuracy under power constraints. The proposed method also exhibits strong robustness to communication channel and position estimation error.
MENTOR: Mixture-of-Experts Network with Task-Oriented Perturbation for Visual Reinforcement Learning
Oct 19, 2024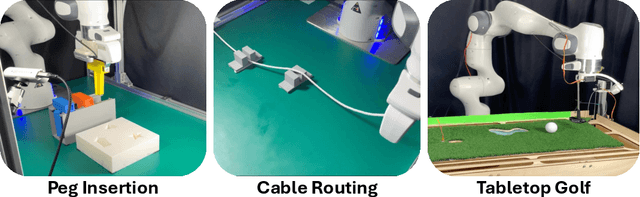
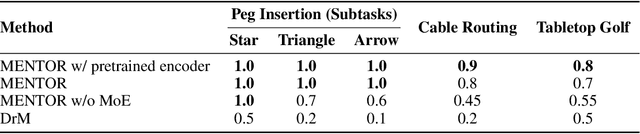
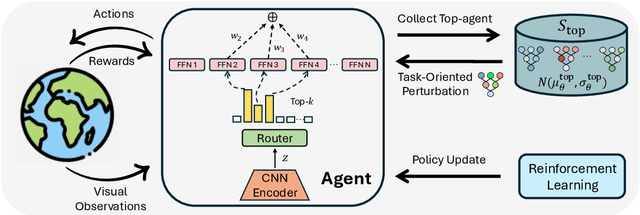
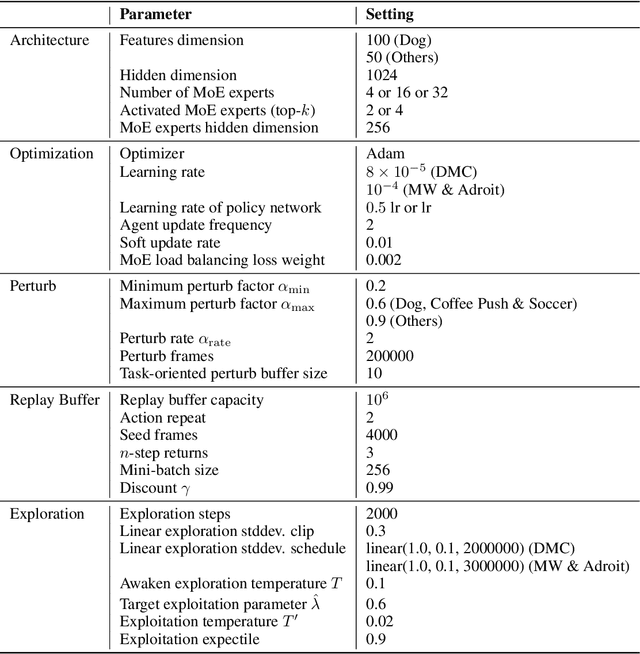
Abstract:Visual deep reinforcement learning (RL) enables robots to acquire skills from visual input for unstructured tasks. However, current algorithms suffer from low sample efficiency, limiting their practical applicability. In this work, we present MENTOR, a method that improves both the architecture and optimization of RL agents. Specifically, MENTOR replaces the standard multi-layer perceptron (MLP) with a mixture-of-experts (MoE) backbone, enhancing the agent's ability to handle complex tasks by leveraging modular expert learning to avoid gradient conflicts. Furthermore, MENTOR introduces a task-oriented perturbation mechanism, which heuristically samples perturbation candidates containing task-relevant information, leading to more targeted and effective optimization. MENTOR outperforms state-of-the-art methods across three simulation domains -- DeepMind Control Suite, Meta-World, and Adroit. Additionally, MENTOR achieves an average of 83% success rate on three challenging real-world robotic manipulation tasks including peg insertion, cable routing, and tabletop golf, which significantly surpasses the success rate of 32% from the current strongest model-free visual RL algorithm. These results underscore the importance of sample efficiency in advancing visual RL for real-world robotics. Experimental videos are available at https://suninghuang19.github.io/mentor_page.
Knowledge-Enhanced Facial Expression Recognition with Emotional-to-Neutral Transformation
Sep 13, 2024



Abstract:Existing facial expression recognition (FER) methods typically fine-tune a pre-trained visual encoder using discrete labels. However, this form of supervision limits to specify the emotional concept of different facial expressions. In this paper, we observe that the rich knowledge in text embeddings, generated by vision-language models, is a promising alternative for learning discriminative facial expression representations. Inspired by this, we propose a novel knowledge-enhanced FER method with an emotional-to-neutral transformation. Specifically, we formulate the FER problem as a process to match the similarity between a facial expression representation and text embeddings. Then, we transform the facial expression representation to a neutral representation by simulating the difference in text embeddings from textual facial expression to textual neutral. Finally, a self-contrast objective is introduced to pull the facial expression representation closer to the textual facial expression, while pushing it farther from the neutral representation. We conduct evaluation with diverse pre-trained visual encoders including ResNet-18 and Swin-T on four challenging facial expression datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art FER methods. The code will be publicly available.
Dynamic Adapter Meets Prompt Tuning: Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning for Point Cloud Analysis
Mar 03, 2024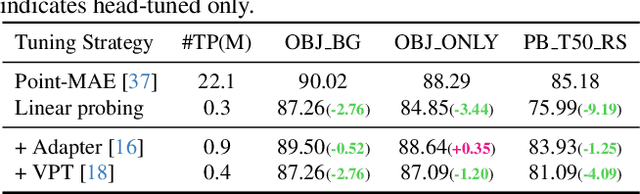
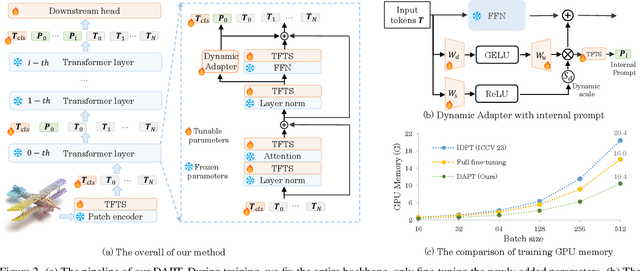
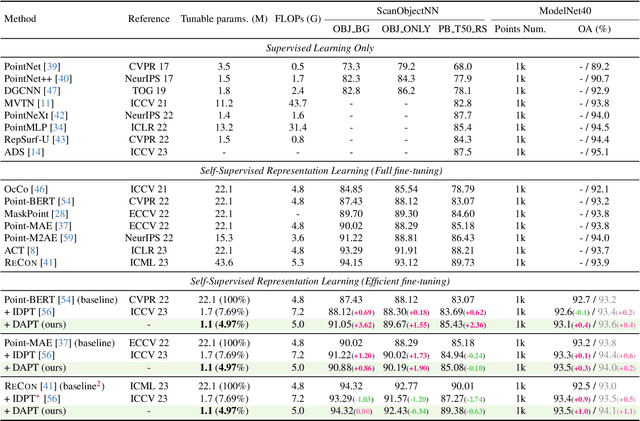
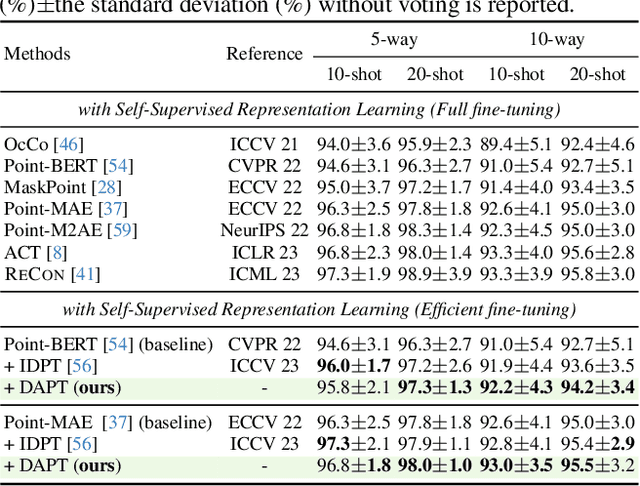
Abstract:Point cloud analysis has achieved outstanding performance by transferring point cloud pre-trained models. However, existing methods for model adaptation usually update all model parameters, i.e., full fine-tuning paradigm, which is inefficient as it relies on high computational costs (e.g., training GPU memory) and massive storage space. In this paper, we aim to study parameter-efficient transfer learning for point cloud analysis with an ideal trade-off between task performance and parameter efficiency. To achieve this goal, we freeze the parameters of the default pre-trained models and then propose the Dynamic Adapter, which generates a dynamic scale for each token, considering the token significance to the downstream task. We further seamlessly integrate Dynamic Adapter with Prompt Tuning (DAPT) by constructing Internal Prompts, capturing the instance-specific features for interaction. Extensive experiments conducted on five challenging datasets demonstrate that the proposed DAPT achieves superior performance compared to the full fine-tuning counterparts while significantly reducing the trainable parameters and training GPU memory by 95% and 35%, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/LMD0311/DAPT.
ESTISR: Adapting Efficient Scene Text Image Super-resolution for Real-Scenes
Jun 04, 2023



Abstract:While scene text image super-resolution (STISR) has yielded remarkable improvements in accurately recognizing scene text, prior methodologies have placed excessive emphasis on optimizing performance, rather than paying due attention to efficiency - a crucial factor in ensuring deployment of the STISR-STR pipeline. In this work, we propose a novel Efficient Scene Text Image Super-resolution (ESTISR) Network for resource-limited deployment platform. ESTISR's functionality primarily depends on two critical components: a CNN-based feature extractor and an efficient self-attention mechanism used for decoding low-resolution images. We designed a re-parameterized inverted residual block specifically suited for resource-limited circumstances as the feature extractor. Meanwhile, we proposed a novel self-attention mechanism, softmax shrinking, based on a kernel-based approach. This innovative technique offers linear complexity while also naturally incorporating discriminating low-level features into the self-attention structure. Extensive experiments on TextZoom show that ESTISR retains a high image restoration quality and improved STR accuracy of low-resolution images. Furthermore, ESTISR consistently outperforms current methods in terms of actual running time and peak memory consumption, while achieving a better trade-off between performance and efficiency.
Adaptive Multi-User Channel Estimation Based on Contrastive Feature Learning
Mar 06, 2023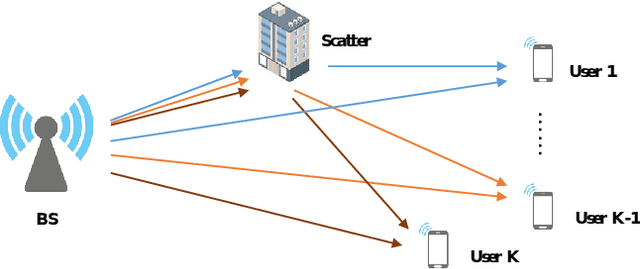
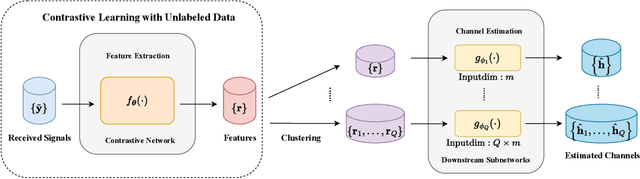
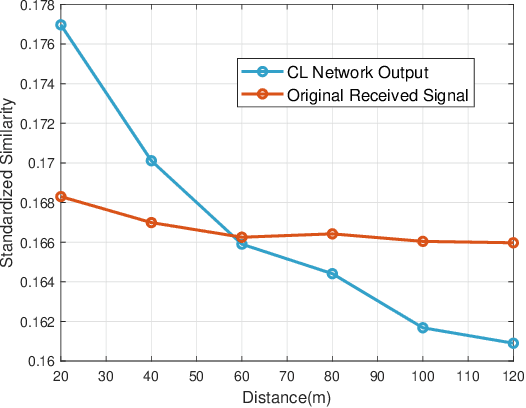
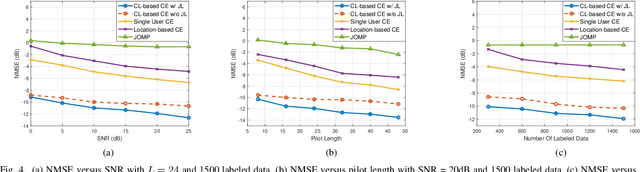
Abstract:Correlation exploitation is essential for efficient multi-user channel estimation (MUCE) in massive MIMO systems. However, the existing works either rely on presumed strong correlation or learn the correlation through large amount of labeled data, which are difficult to acquire in a real system. In this paper, we propose an adaptive MUCE algorithm based on contrastive feature learning. The contrastive learning (CL) is used to automatically learn the similarity within channels by extracting the channel state information (CSI) features based on location information. The similar features will be fed into the downstream network to explore the strong correlations among CSI features to improve the MUCE performance with a small number of labeled data. Simulation results show that the contrastive feature learning can enhance the overall MUCE performance with high training efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge