Yifang Zhang
Humanoids and Human Centered Mechatronics
Beyond Textual Context: Structural Graph Encoding with Adaptive Space Alignment to alleviate the hallucination of LLMs
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:Currently, the main approach for Large Language Models (LLMs) to tackle the hallucination issue is incorporating Knowledge Graphs(KGs).However, LLMs typically treat KGs as plain text, extracting only semantic information and limiting their use of the crucial structural aspects of KGs. Another challenge is the gap between the embedding spaces of KGs encoders and LLMs text embeddings, which hinders the effective integration of structured knowledge. To overcome these obstacles, we put forward the SSKG-LLM, an innovative model architecture that is designed to efficiently integrate both the Structural and Semantic information of KGs into the reasoning processes of LLMs. SSKG-LLM incorporates the Knowledge Graph Retrieval (KGR) module and the Knowledge Graph Encoding (KGE) module to preserve semantics while utilizing structure. Then, the Knowledge Graph Adaptation (KGA) module is incorporated to enable LLMs to understand KGs embeddings. We conduct extensive experiments and provide a detailed analysis to explore how incorporating the structural information of KGs can enhance the factual reasoning abilities of LLMs. Our code are available at https://github.com/yfangZhang/SSKG-LLM.
MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning: Datasets, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Outlook
Sep 17, 2025
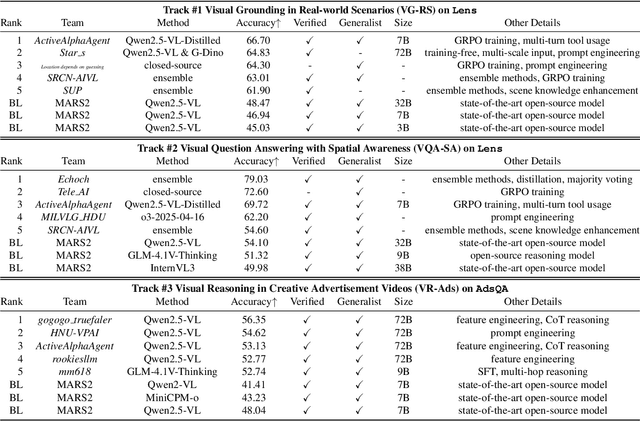

Abstract:This paper reviews the MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning. We aim to bring together different approaches in multimodal machine learning and LLMs via a large benchmark. We hope it better allows researchers to follow the state-of-the-art in this very dynamic area. Meanwhile, a growing number of testbeds have boosted the evolution of general-purpose large language models. Thus, this year's MARS2 focuses on real-world and specialized scenarios to broaden the multimodal reasoning applications of MLLMs. Our organizing team released two tailored datasets Lens and AdsQA as test sets, which support general reasoning in 12 daily scenarios and domain-specific reasoning in advertisement videos, respectively. We evaluated 40+ baselines that include both generalist MLLMs and task-specific models, and opened up three competition tracks, i.e., Visual Grounding in Real-world Scenarios (VG-RS), Visual Question Answering with Spatial Awareness (VQA-SA), and Visual Reasoning in Creative Advertisement Videos (VR-Ads). Finally, 76 teams from the renowned academic and industrial institutions have registered and 40+ valid submissions (out of 1200+) have been included in our ranking lists. Our datasets, code sets (40+ baselines and 15+ participants' methods), and rankings are publicly available on the MARS2 workshop website and our GitHub organization page https://github.com/mars2workshop/, where our updates and announcements of upcoming events will be continuously provided.
LENS: Multi-level Evaluation of Multimodal Reasoning with Large Language Models
May 21, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved significant advances in integrating visual and linguistic information, yet their ability to reason about complex and real-world scenarios remains limited. The existing benchmarks are usually constructed in the task-oriented manner without guarantee that different task samples come from the same data distribution, thus they often fall short in evaluating the synergistic effects of lower-level perceptual capabilities on higher-order reasoning. To lift this limitation, we contribute Lens, a multi-level benchmark with 3.4K contemporary images and 60K+ human-authored questions covering eight tasks and 12 daily scenarios, forming three progressive task tiers, i.e., perception, understanding, and reasoning. One feature is that each image is equipped with rich annotations for all tasks. Thus, this dataset intrinsically supports to evaluate MLLMs to handle image-invariable prompts, from basic perception to compositional reasoning. In addition, our images are manully collected from the social media, in which 53% were published later than Jan. 2025. We evaluate 15+ frontier MLLMs such as Qwen2.5-VL-72B, InternVL3-78B, GPT-4o and two reasoning models QVQ-72B-preview and Kimi-VL. These models are released later than Dec. 2024, and none of them achieve an accuracy greater than 60% in the reasoning tasks. Project page: https://github.com/Lens4MLLMs/lens. ICCV 2025 workshop page: https://lens4mllms.github.io/mars2-workshop-iccv2025/
Exo-muscle: A semi-rigid assistive device for the knee
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:In this work, we introduce the principle, design and mechatronics of Exo-Muscle, a novel assistive device for the knee joint. Different from the existing systems based on rigid exoskeleton structures or soft-tendon driven approaches, the proposed device leverages a new semi-rigid principle that explores the benefits of both rigid and soft systems. The use of a novel semi-rigid chain mechanism around the knee joint eliminates the presence of misalignment between the device and the knee joint center of rotation, while at the same time, it forms a well-defined route for the tendon. This results in more deterministic load compensation functionality compared to the fully soft systems. The proposed device can provide up to 38Nm assistive torque to the knee joint. In the experiment section, the device was successfully validated through a series of experiments demonstrating the capacity of the device to provide the target assistive functionality in the knee joint.
Towards Multi-view Graph Anomaly Detection with Similarity-Guided Contrastive Clustering
Sep 15, 2024Abstract:Anomaly detection on graphs plays an important role in many real-world applications. Usually, these data are composed of multiple types (e.g., user information and transaction records for financial data), thus exhibiting view heterogeneity. Therefore, it can be challenging to leverage such multi-view information and learn the graph's contextual information to identify rare anomalies. To tackle this problem, many deep learning-based methods utilize contrastive learning loss as a regularization term to learn good representations. However, many existing contrastive-based methods show that traditional contrastive learning losses fail to consider the semantic information (e.g., class membership information). In addition, we theoretically show that clustering-based contrastive learning also easily leads to a sub-optimal solution. To address these issues, in this paper, we proposed an autoencoder-based clustering framework regularized by a similarity-guided contrastive loss to detect anomalous nodes. Specifically, we build a similarity map to help the model learn robust representations without imposing a hard margin constraint between the positive and negative pairs. Theoretically, we show that the proposed similarity-guided loss is a variant of contrastive learning loss, and how it alleviates the issue of unreliable pseudo-labels with the connection to graph spectral clustering. Experimental results on several datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed framework.
LAiW: A Chinese Legal Large Language Models Benchmark
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:With the emergence of numerous legal LLMs, there is currently a lack of a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating their legal abilities. In this paper, we propose the first Chinese Legal LLMs benchmark based on legal capabilities. Through the collaborative efforts of legal and artificial intelligence experts, we divide the legal capabilities of LLMs into three levels: basic legal NLP capability, basic legal application capability, and complex legal application capability. We have completed the first phase of evaluation, which mainly focuses on the capability of basic legal NLP. The evaluation results show that although some legal LLMs have better performance than their backbones, there is still a gap compared to ChatGPT. Our benchmark can be found at URL.
Empowering Many, Biasing a Few: Generalist Credit Scoring through Large Language Models
Oct 01, 2023



Abstract:Credit and risk assessments are cornerstones of the financial landscape, impacting both individual futures and broader societal constructs. Existing credit scoring models often exhibit limitations stemming from knowledge myopia and task isolation. In response, we formulate three hypotheses and undertake an extensive case study to investigate LLMs' viability in credit assessment. Our empirical investigations unveil LLMs' ability to overcome the limitations inherent in conventional models. We introduce a novel benchmark curated for credit assessment purposes, fine-tune a specialized Credit and Risk Assessment Large Language Model (CALM), and rigorously examine the biases that LLMs may harbor. Our findings underscore LLMs' potential in revolutionizing credit assessment, showcasing their adaptability across diverse financial evaluations, and emphasizing the critical importance of impartial decision-making in the financial sector. Our datasets, models, and benchmarks are open-sourced for other researchers.
Reconstructing Graph Diffusion History from a Single Snapshot
Jun 04, 2023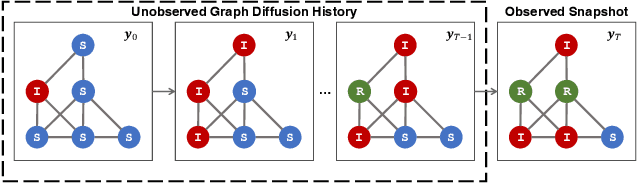
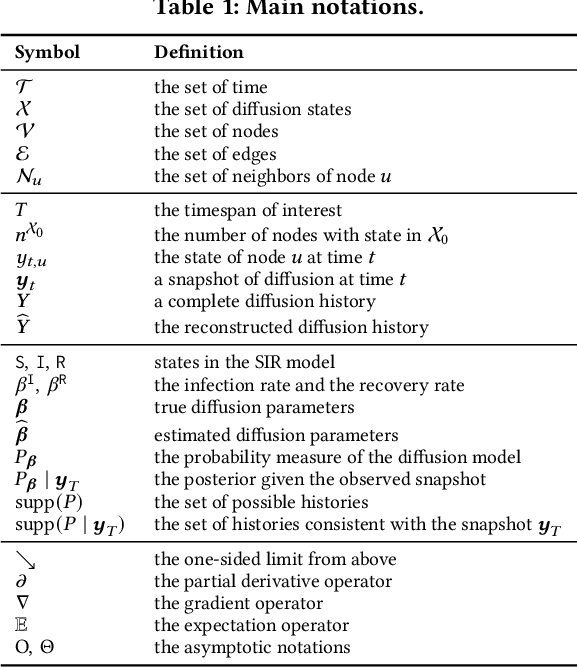
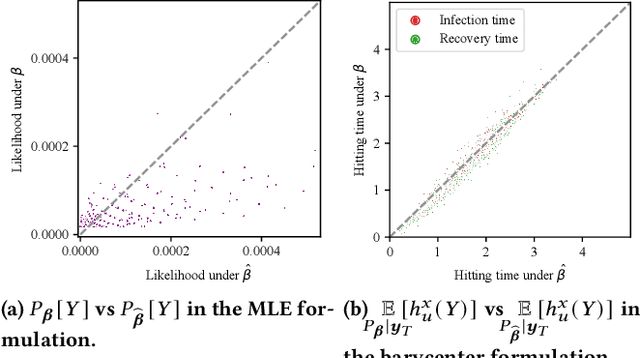
Abstract:Diffusion on graphs is ubiquitous with numerous high-impact applications. In these applications, complete diffusion histories play an essential role in terms of identifying dynamical patterns, reflecting on precaution actions, and forecasting intervention effects. Despite their importance, complete diffusion histories are rarely available and are highly challenging to reconstruct due to ill-posedness, explosive search space, and scarcity of training data. To date, few methods exist for diffusion history reconstruction. They are exclusively based on the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) formulation and require to know true diffusion parameters. In this paper, we study an even harder problem, namely reconstructing Diffusion history from A single SnapsHot} (DASH), where we seek to reconstruct the history from only the final snapshot without knowing true diffusion parameters. We start with theoretical analyses that reveal a fundamental limitation of the MLE formulation. We prove: (a) estimation error of diffusion parameters is unavoidable due to NP-hardness of diffusion parameter estimation, and (b) the MLE formulation is sensitive to estimation error of diffusion parameters. To overcome the inherent limitation of the MLE formulation, we propose a novel barycenter formulation: finding the barycenter of the posterior distribution of histories, which is provably stable against the estimation error of diffusion parameters. We further develop an effective solver named DIffusion hiTting Times with Optimal proposal (DITTO) by reducing the problem to estimating posterior expected hitting times via the Metropolis--Hastings Markov chain Monte Carlo method (M--H MCMC) and employing an unsupervised graph neural network to learn an optimal proposal to accelerate the convergence of M--H MCMC. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method.
An Adaptive Enhancement Based Hybrid CNN Model for Digital Dental X-ray Positions Classification
May 01, 2020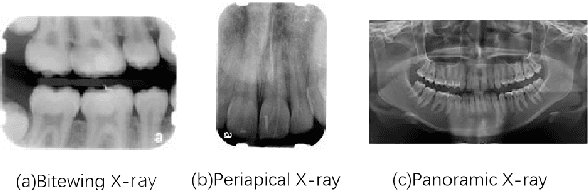
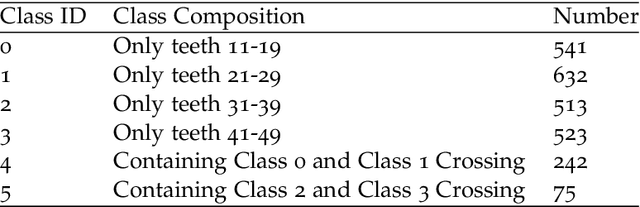
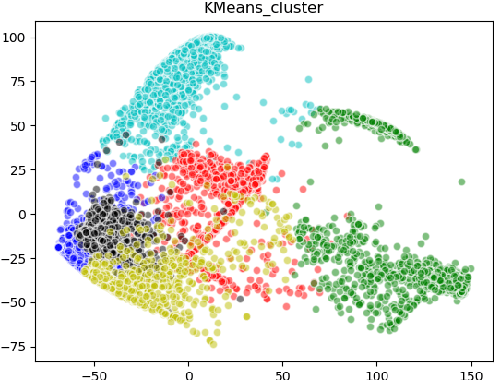
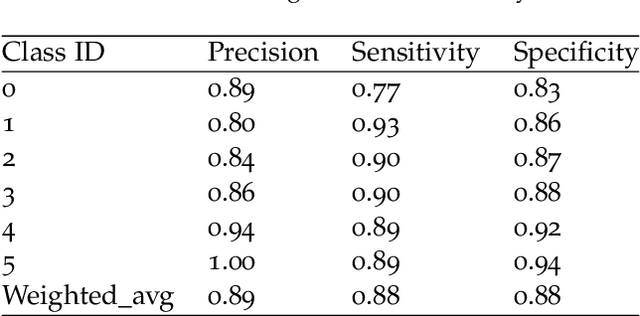
Abstract:Analysis of dental radiographs is an important part of the diagnostic process in daily clinical practice. Interpretation by an expert includes teeth detection and numbering. In this project, a novel solution based on adaptive histogram equalization and convolution neural network (CNN) is proposed, which automatically performs the task for dental x-rays. In order to improve the detection accuracy, we propose three pre-processing techniques to supplement the baseline CNN based on some prior domain knowledge. Firstly, image sharpening and median filtering are used to remove impulse noise, and the edge is enhanced to some extent. Next, adaptive histogram equalization is used to overcome the problem of excessive amplification noise of HE. Finally, a multi-CNN hybrid model is proposed to classify six different locations of dental slices. The results showed that the accuracy and specificity of the test set exceeded 90\%, and the AUC reached 0.97. In addition, four dentists were invited to manually annotate the test data set (independently) and then compare it with the labels obtained by our proposed algorithm. The results show that our method can effectively identify the X-ray location of teeth.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge