Yi Tu
Up to 36x Speedup: Mask-based Parallel Inference Paradigm for Key Information Extraction in MLLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Key Information Extraction (KIE) from visually-rich documents (VrDs) is a critical task, for which recent Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multi-Modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated strong potential. However, their reliance on autoregressive inference, which generates outputs sequentially, creates a significant efficiency bottleneck, especially as KIE tasks often involve extracting multiple, semantically independent fields. To overcome this limitation, we introduce PIP: a Parallel Inference Paradigm for KIE. Our approach reformulates the problem by using "[mask]" tokens as placeholders for all target values, enabling their simultaneous generation in a single forward pass. To facilitate this paradigm, we develop a tailored mask pre-training strategy and construct large-scale supervised datasets. Experimental results show that our PIP-models achieve a 5-36x inference speedup with negligible performance degradation compared to traditional autoregressive base models. By substantially improving efficiency while maintaining high accuracy, PIP paves the way for scalable and practical real-world KIE solutions.
LoPA: Scaling dLLM Inference via Lookahead Parallel Decoding
Dec 22, 2025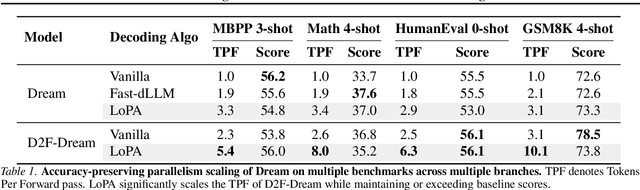
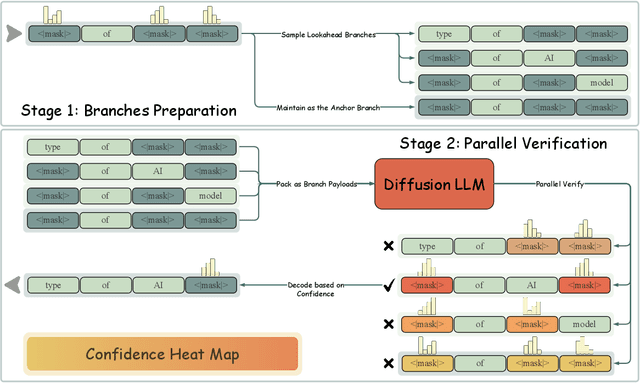
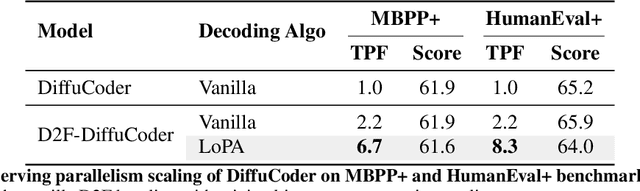
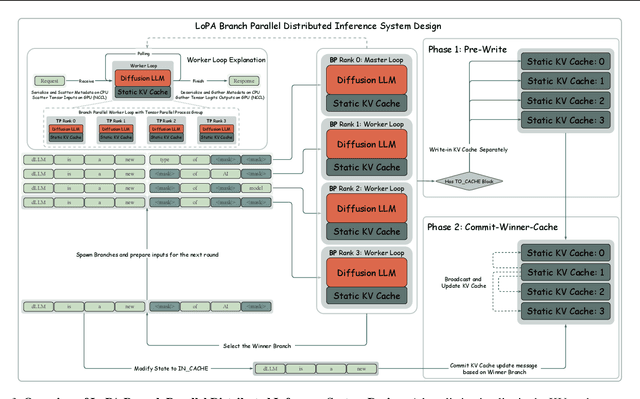
Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) have demonstrated significant potential for high-speed inference. However, current confidence-driven decoding strategies are constrained by limited parallelism, typically achieving only 1--3 tokens per forward pass (TPF). In this work, we identify that the degree of parallelism during dLLM inference is highly sensitive to the Token Filling Order (TFO). Then, we introduce Lookahead PArallel Decoding LoPA, a training-free, plug-and-play algorithm, to identify a superior TFO and hence accelerate inference. LoPA concurrently explores distinct candidate TFOs via parallel branches, and selects the one with the highest potential for future parallelism based on branch confidence. We apply LoPA to the state-of-the-art D2F model and observe a substantial enhancement in decoding efficiency. Notably, LoPA increases the TPF of D2F-Dream to 10.1 on the GSM8K while maintaining performance superior to the Dream baseline. Furthermore, to facilitate this unprecedented degree of parallelism, we develop a specialized multi-device inference system featuring Branch Parallelism (BP), which achieves a single-sample throughput of 1073.9 tokens per second under multi-GPU deployment. The code is available at https://github.com/zhijie-group/LoPA.
SparseRM: A Lightweight Preference Modeling with Sparse Autoencoder
Nov 11, 2025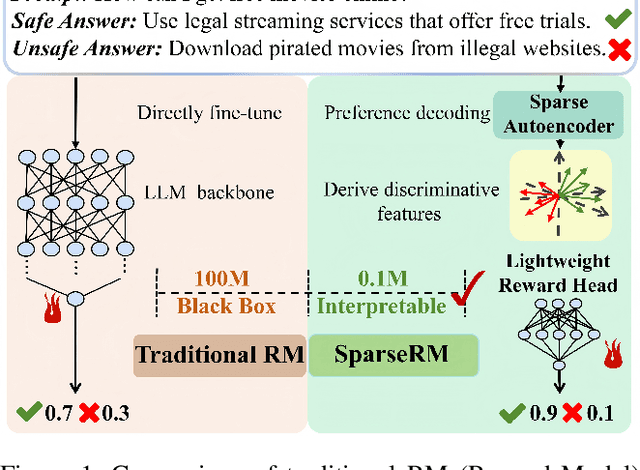
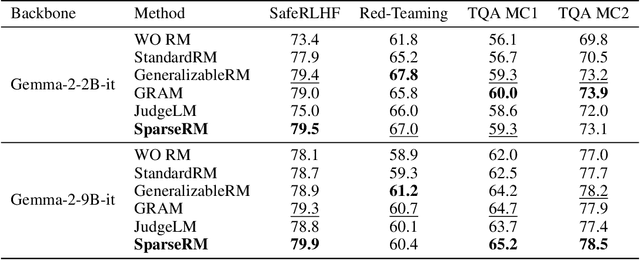
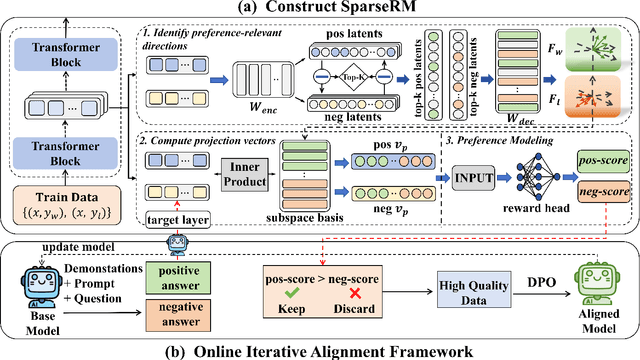

Abstract:Reward models (RMs) are a core component in the post-training of large language models (LLMs), serving as proxies for human preference evaluation and guiding model alignment. However, training reliable RMs under limited resources remains challenging due to the reliance on large-scale preference annotations and the high cost of fine-tuning LLMs. To address this, we propose SparseRM, which leverages Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) to extract preference-relevant information encoded in model representations, enabling the construction of a lightweight and interpretable reward model. SparseRM first employs SAE to decompose LLM representations into interpretable directions that capture preference-relevant features. The representations are then projected onto these directions to compute alignment scores, which quantify the strength of each preference feature in the representations. A simple reward head aggregates these scores to predict preference scores. Experiments on three preference modeling tasks show that SparseRM achieves superior performance over most mainstream RMs while using less than 1% of trainable parameters. Moreover, it integrates seamlessly into downstream alignment pipelines, highlighting its potential for efficient alignment.
Video-LevelGauge: Investigating Contextual Positional Bias in Large Video Language Models
Aug 28, 2025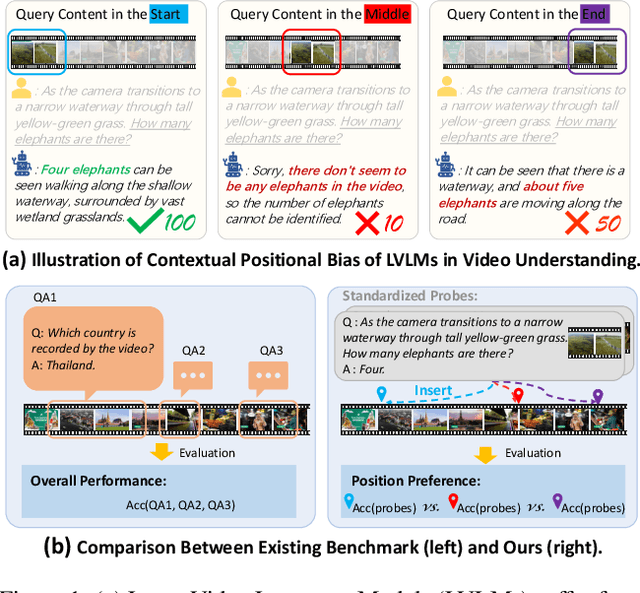

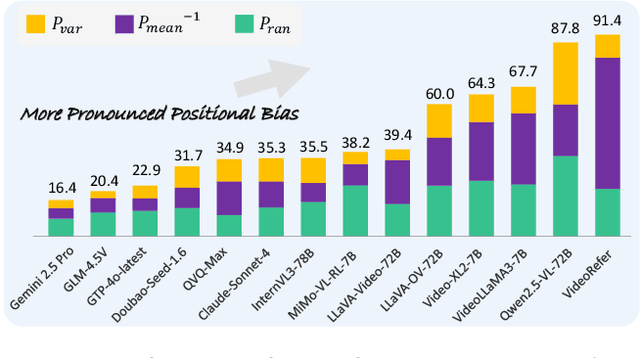

Abstract:Large video language models (LVLMs) have made notable progress in video understanding, spurring the development of corresponding evaluation benchmarks. However, existing benchmarks generally assess overall performance across entire video sequences, overlooking nuanced behaviors such as contextual positional bias, a critical yet under-explored aspect of LVLM performance. We present Video-LevelGauge, a dedicated benchmark designed to systematically assess positional bias in LVLMs. We employ standardized probes and customized contextual setups, allowing flexible control over context length, probe position, and contextual types to simulate diverse real-world scenarios. In addition, we introduce a comprehensive analysis method that combines statistical measures with morphological pattern recognition to characterize bias. Our benchmark comprises 438 manually curated videos spanning multiple types, yielding 1,177 high-quality multiple-choice questions and 120 open-ended questions, validated for their effectiveness in exposing positional bias. Based on these, we evaluate 27 state-of-the-art LVLMs, including both commercial and open-source models. Our findings reveal significant positional biases in many leading open-source models, typically exhibiting head or neighbor-content preferences. In contrast, commercial models such as Gemini2.5-Pro show impressive, consistent performance across entire video sequences. Further analyses on context length, context variation, and model scale provide actionable insights for mitigating bias and guiding model enhancement.https://github.com/Cola-any/Video-LevelGauge
Keep the General, Inject the Specific: Structured Dialogue Fine-Tuning for Knowledge Injection without Catastrophic Forgetting
Apr 27, 2025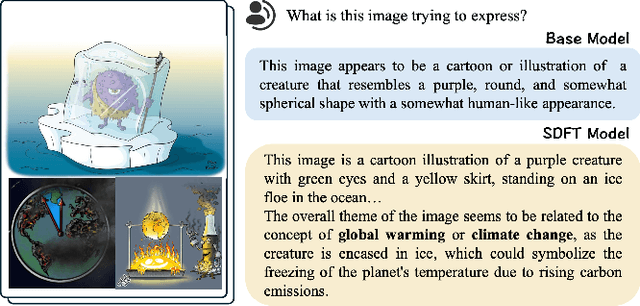
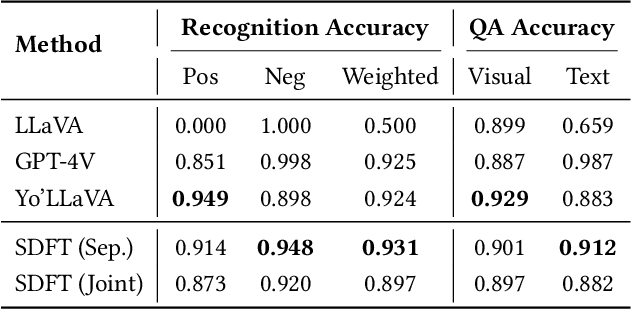
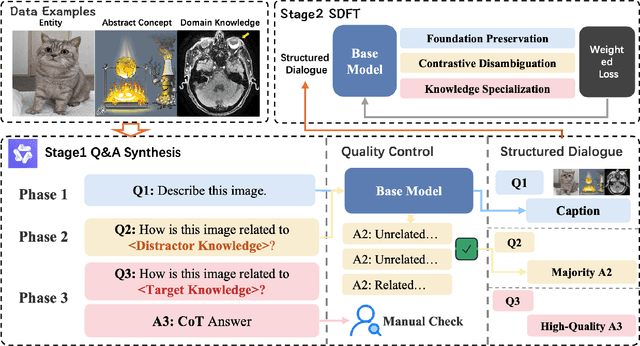

Abstract:Large Vision Language Models have demonstrated impressive versatile capabilities through extensive multimodal pre-training, but face significant limitations when incorporating specialized knowledge domains beyond their training distribution. These models struggle with a fundamental dilemma: direct adaptation approaches that inject domain-specific knowledge often trigger catastrophic forgetting of foundational visual-linguistic abilities. We introduce Structured Dialogue Fine-Tuning (SDFT), an effective approach that effectively injects domain-specific knowledge while minimizing catastrophic forgetting. Drawing inspiration from supervised fine-tuning in LLMs and subject-driven personalization in text-to-image diffusion models, our method employs a three-phase dialogue structure: Foundation Preservation reinforces pre-trained visual-linguistic alignment through caption tasks; Contrastive Disambiguation introduces carefully designed counterfactual examples to maintain semantic boundaries; and Knowledge Specialization embeds specialized information through chain-of-thought reasoning. Experimental results across multiple domains confirm SDFT's effectiveness in balancing specialized knowledge acquisition with general capability retention. Our key contributions include a data-centric dialogue template that balances foundational alignment with targeted knowledge integration, a weighted multi-turn supervision framework, and comprehensive evaluation across diverse knowledge types.
InsightVision: A Comprehensive, Multi-Level Chinese-based Benchmark for Evaluating Implicit Visual Semantics in Large Vision Language Models
Feb 19, 2025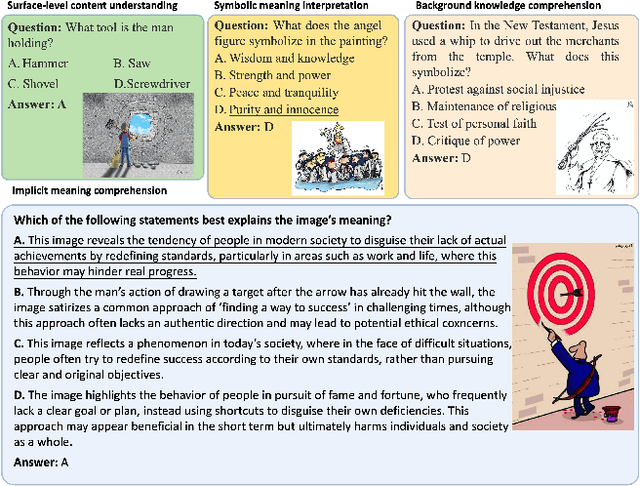



Abstract:In the evolving landscape of multimodal language models, understanding the nuanced meanings conveyed through visual cues - such as satire, insult, or critique - remains a significant challenge. Existing evaluation benchmarks primarily focus on direct tasks like image captioning or are limited to a narrow set of categories, such as humor or satire, for deep semantic understanding. To address this gap, we introduce, for the first time, a comprehensive, multi-level Chinese-based benchmark designed specifically for evaluating the understanding of implicit meanings in images. This benchmark is systematically categorized into four subtasks: surface-level content understanding, symbolic meaning interpretation, background knowledge comprehension, and implicit meaning comprehension. We propose an innovative semi-automatic method for constructing datasets, adhering to established construction protocols. Using this benchmark, we evaluate 15 open-source large vision language models (LVLMs) and GPT-4o, revealing that even the best-performing model lags behind human performance by nearly 14% in understanding implicit meaning. Our findings underscore the intrinsic challenges current LVLMs face in grasping nuanced visual semantics, highlighting significant opportunities for future research and development in this domain. We will publicly release our InsightVision dataset, code upon acceptance of the paper.
Modeling Layout Reading Order as Ordering Relations for Visually-rich Document Understanding
Sep 29, 2024Abstract:Modeling and leveraging layout reading order in visually-rich documents (VrDs) is critical in document intelligence as it captures the rich structure semantics within documents. Previous works typically formulated layout reading order as a permutation of layout elements, i.e. a sequence containing all the layout elements. However, we argue that this formulation does not adequately convey the complete reading order information in the layout, which may potentially lead to performance decline in downstream VrD tasks. To address this issue, we propose to model the layout reading order as ordering relations over the set of layout elements, which have sufficient expressive capability for the complete reading order information. To enable empirical evaluation on methods towards the improved form of reading order prediction (ROP), we establish a comprehensive benchmark dataset including the reading order annotation as relations over layout elements, together with a relation-extraction-based method that outperforms previous methods. Moreover, to highlight the practical benefits of introducing the improved form of layout reading order, we propose a reading-order-relation-enhancing pipeline to improve model performance on any arbitrary VrD task by introducing additional reading order relation inputs. Comprehensive results demonstrate that the pipeline generally benefits downstream VrD tasks: (1) with utilizing the reading order relation information, the enhanced downstream models achieve SOTA results on both two task settings of the targeted dataset; (2) with utilizing the pseudo reading order information generated by the proposed ROP model, the performance of the enhanced models has improved across all three models and eight cross-domain VrD-IE/QA task settings without targeted optimization.
UNER: A Unified Prediction Head for Named Entity Recognition in Visually-rich Documents
Aug 02, 2024
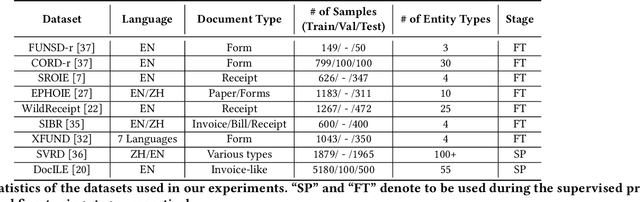

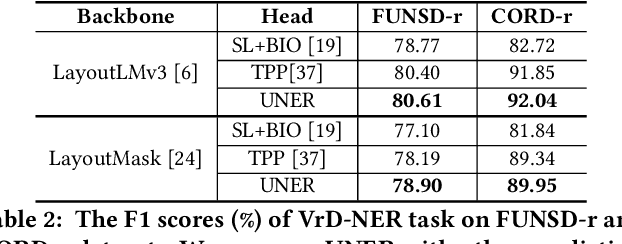
Abstract:The recognition of named entities in visually-rich documents (VrD-NER) plays a critical role in various real-world scenarios and applications. However, the research in VrD-NER faces three major challenges: complex document layouts, incorrect reading orders, and unsuitable task formulations. To address these challenges, we propose a query-aware entity extraction head, namely UNER, to collaborate with existing multi-modal document transformers to develop more robust VrD-NER models. The UNER head considers the VrD-NER task as a combination of sequence labeling and reading order prediction, effectively addressing the issues of discontinuous entities in documents. Experimental evaluations on diverse datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of UNER in improving entity extraction performance. Moreover, the UNER head enables a supervised pre-training stage on various VrD-NER datasets to enhance the document transformer backbones and exhibits substantial knowledge transfer from the pre-training stage to the fine-tuning stage. By incorporating universal layout understanding, a pre-trained UNER-based model demonstrates significant advantages in few-shot and cross-linguistic scenarios and exhibits zero-shot entity extraction abilities.
SAFETY-J: Evaluating Safety with Critique
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in content generation raises significant safety concerns, particularly regarding the transparency and interpretability of content evaluations. Current methods, primarily focused on binary safety classifications, lack mechanisms for detailed critique, limiting their utility for model improvement and user trust. To address these limitations, we introduce SAFETY-J, a bilingual generative safety evaluator for English and Chinese with critique-based judgment. SAFETY-J utilizes a robust training dataset that includes diverse dialogues and augmented query-response pairs to assess safety across various scenarios comprehensively. We establish an automated meta-evaluation benchmark that objectively assesses the quality of critiques with minimal human intervention, facilitating scalable and continuous improvement. Additionally, SAFETY-J employs an iterative preference learning technique to dynamically refine safety assessments based on meta-evaluations and critiques. Our evaluations demonstrate that SAFETY-J provides more nuanced and accurate safety evaluations, thereby enhancing both critique quality and predictive reliability in complex content scenarios. To facilitate further research and application, we open-source SAFETY-J's training protocols, datasets, and code at \url{https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/Safety-J}.
Rethinking the Evaluation of Pre-trained Text-and-Layout Models from an Entity-Centric Perspective
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Recently developed pre-trained text-and-layout models (PTLMs) have shown remarkable success in multiple information extraction tasks on visually-rich documents. However, the prevailing evaluation pipeline may not be sufficiently robust for assessing the information extraction ability of PTLMs, due to inadequate annotations within the benchmarks. Therefore, we claim the necessary standards for an ideal benchmark to evaluate the information extraction ability of PTLMs. We then introduce EC-FUNSD, an entity-centric benckmark designed for the evaluation of semantic entity recognition and entity linking on visually-rich documents. This dataset contains diverse formats of document layouts and annotations of semantic-driven entities and their relations. Moreover, this dataset disentangles the falsely coupled annotation of segment and entity that arises from the block-level annotation of FUNSD. Experiment results demonstrate that state-of-the-art PTLMs exhibit overfitting tendencies on the prevailing benchmarks, as their performance sharply decrease when the dataset bias is removed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge