Yahya H. Ezzeldin
Federated Orthogonal Training: Mitigating Global Catastrophic Forgetting in Continual Federated Learning
Sep 03, 2023



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has gained significant attraction due to its ability to enable privacy-preserving training over decentralized data. Current literature in FL mostly focuses on single-task learning. However, over time, new tasks may appear in the clients and the global model should learn these tasks without forgetting previous tasks. This real-world scenario is known as Continual Federated Learning (CFL). The main challenge of CFL is Global Catastrophic Forgetting, which corresponds to the fact that when the global model is trained on new tasks, its performance on old tasks decreases. There have been a few recent works on CFL to propose methods that aim to address the global catastrophic forgetting problem. However, these works either have unrealistic assumptions on the availability of past data samples or violate the privacy principles of FL. We propose a novel method, Federated Orthogonal Training (FOT), to overcome these drawbacks and address the global catastrophic forgetting in CFL. Our algorithm extracts the global input subspace of each layer for old tasks and modifies the aggregated updates of new tasks such that they are orthogonal to the global principal subspace of old tasks for each layer. This decreases the interference between tasks, which is the main cause for forgetting. We empirically show that FOT outperforms state-of-the-art continual learning methods in the CFL setting, achieving an average accuracy gain of up to 15% with 27% lower forgetting while only incurring a minimal computation and communication cost.
SLoRA: Federated Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning of Language Models
Aug 12, 2023



Abstract:Transfer learning via fine-tuning pre-trained transformer models has gained significant success in delivering state-of-the-art results across various NLP tasks. In the absence of centralized data, Federated Learning (FL) can benefit from distributed and private data of the FL edge clients for fine-tuning. However, due to the limited communication, computation, and storage capabilities of edge devices and the huge sizes of popular transformer models, efficient fine-tuning is crucial to make federated training feasible. This work explores the opportunities and challenges associated with applying parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods in different FL settings for language tasks. Specifically, our investigation reveals that as the data across users becomes more diverse, the gap between fully fine-tuning the model and employing PEFT methods widens. To bridge this performance gap, we propose a method called SLoRA, which overcomes the key limitations of LoRA in high heterogeneous data scenarios through a novel data-driven initialization technique. Our experimental results demonstrate that SLoRA achieves performance comparable to full fine-tuning, with significant sparse updates with approximately $\sim 1\%$ density while reducing training time by up to $90\%$.
The Resource Problem of Using Linear Layer Leakage Attack in Federated Learning
Mar 27, 2023



Abstract:Secure aggregation promises a heightened level of privacy in federated learning, maintaining that a server only has access to a decrypted aggregate update. Within this setting, linear layer leakage methods are the only data reconstruction attacks able to scale and achieve a high leakage rate regardless of the number of clients or batch size. This is done through increasing the size of an injected fully-connected (FC) layer. However, this results in a resource overhead which grows larger with an increasing number of clients. We show that this resource overhead is caused by an incorrect perspective in all prior work that treats an attack on an aggregate update in the same way as an individual update with a larger batch size. Instead, by attacking the update from the perspective that aggregation is combining multiple individual updates, this allows the application of sparsity to alleviate resource overhead. We show that the use of sparsity can decrease the model size overhead by over 327$\times$ and the computation time by 3.34$\times$ compared to SOTA while maintaining equivalent total leakage rate, 77% even with $1000$ clients in aggregation.
Secure Aggregation in Federated Learning is not Private: Leaking User Data at Large Scale through Model Modification
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:Security and privacy are important concerns in machine learning. End user devices often contain a wealth of data and this information is sensitive and should not be shared with servers or enterprises. As a result, federated learning was introduced to enable machine learning over large decentralized datasets while promising privacy by eliminating the need for data sharing. However, prior work has shown that shared gradients often contain private information and attackers can gain knowledge either through malicious modification of the architecture and parameters or by using optimization to approximate user data from the shared gradients. Despite this, most attacks have so far been limited in scale of number of clients, especially failing when client gradients are aggregated together using secure model aggregation. The attacks that still function are strongly limited in the number of clients attacked, amount of training samples they leak, or number of iterations they take to be trained. In this work, we introduce MANDRAKE, an attack that overcomes previous limitations to directly leak large amounts of client data even under secure aggregation across large numbers of clients. Furthermore, we break the anonymity of aggregation as the leaked data is identifiable and directly tied back to the clients they come from. We show that by sending clients customized convolutional parameters, the weight gradients of data points between clients will remain separate through aggregation. With an aggregation across many clients, prior work could only leak less than 1% of images. With the same number of non-zero parameters, and using only a single training iteration, MANDRAKE leaks 70-80% of data samples.
Federated Analytics: A survey
Feb 02, 2023

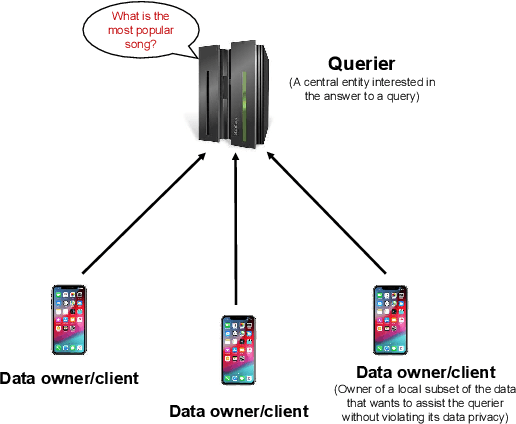

Abstract:Federated analytics (FA) is a privacy-preserving framework for computing data analytics over multiple remote parties (e.g., mobile devices) or silo-ed institutional entities (e.g., hospitals, banks) without sharing the data among parties. Motivated by the practical use cases of federated analytics, we follow a systematic discussion on federated analytics in this article. In particular, we discuss the unique characteristics of federated analytics and how it differs from federated learning. We also explore a wide range of FA queries and discuss various existing solutions and potential use case applications for different FA queries.
* To appear in APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing, Volume 12, Issue 1
How Much Privacy Does Federated Learning with Secure Aggregation Guarantee?
Aug 03, 2022



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has attracted growing interest for enabling privacy-preserving machine learning on data stored at multiple users while avoiding moving the data off-device. However, while data never leaves users' devices, privacy still cannot be guaranteed since significant computations on users' training data are shared in the form of trained local models. These local models have recently been shown to pose a substantial privacy threat through different privacy attacks such as model inversion attacks. As a remedy, Secure Aggregation (SA) has been developed as a framework to preserve privacy in FL, by guaranteeing the server can only learn the global aggregated model update but not the individual model updates. While SA ensures no additional information is leaked about the individual model update beyond the aggregated model update, there are no formal guarantees on how much privacy FL with SA can actually offer; as information about the individual dataset can still potentially leak through the aggregated model computed at the server. In this work, we perform a first analysis of the formal privacy guarantees for FL with SA. Specifically, we use Mutual Information (MI) as a quantification metric and derive upper bounds on how much information about each user's dataset can leak through the aggregated model update. When using the FedSGD aggregation algorithm, our theoretical bounds show that the amount of privacy leakage reduces linearly with the number of users participating in FL with SA. To validate our theoretical bounds, we use an MI Neural Estimator to empirically evaluate the privacy leakage under different FL setups on both the MNIST and CIFAR10 datasets. Our experiments verify our theoretical bounds for FedSGD, which show a reduction in privacy leakage as the number of users and local batch size grow, and an increase in privacy leakage with the number of training rounds.
FairFed: Enabling Group Fairness in Federated Learning
Oct 02, 2021



Abstract:As machine learning becomes increasingly incorporated in crucial decision-making scenarios such as healthcare, recruitment, and loan assessment, there have been increasing concerns about the privacy and fairness of such systems. Federated learning has been viewed as a promising solution for collaboratively learning machine learning models among multiple parties while maintaining the privacy of their local data. However, federated learning also poses new challenges in mitigating the potential bias against certain populations (e.g., demographic groups), which typically requires centralized access to the sensitive information (e.g., race, gender) of each data point. Motivated by the importance and challenges of group fairness in federated learning, in this work, we propose FairFed, a novel algorithm to enhance group fairness via a fairness-aware aggregation method, aiming to provide fair model performance across different sensitive groups (e.g., racial, gender groups) while maintaining high utility. The formulation can potentially provide more flexibility in the customized local debiasing strategies for each client. When running federated training on two widely investigated fairness datasets, Adult and COMPAS, our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art fair federated learning frameworks under a high heterogeneous sensitive attribute distribution.
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Scheduling in mmWave Networks
Aug 01, 2021



Abstract:We consider a source that wishes to communicate with a destination at a desired rate, over a mmWave network where links are subject to blockage and nodes to failure (e.g., in a hostile military environment). To achieve resilience to link and node failures, we here explore a state-of-the-art Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) deep reinforcement learning algorithm, that adapts the information flow through the network, without using knowledge of the link capacities or network topology. Numerical evaluations show that our algorithm can achieve the desired rate even in dynamic environments and it is robust against blockage.
Quantizing data for distributed learning
Dec 14, 2020



Abstract:We consider machine learning applications that train a model by leveraging data distributed over a network, where communication constraints can create a performance bottleneck. A number of recent approaches are proposing to overcome this bottleneck through compression of gradient updates. However, as models become larger, so does the size of the gradient updates. In this paper, we propose an alternate approach, that quantizes data instead of gradients, and can support learning over applications where the size of gradient updates is prohibitive. Our approach combines aspects of: (1) sample selection; (2) dataset quantization; and (3) gradient compensation. We analyze the convergence of the proposed approach for smooth convex and non-convex objective functions and show that we can achieve order optimal convergence rates with communication that mostly depends on the data rather than the model (gradient) dimension. We use our proposed algorithm to train ResNet models on the CIFAR-10 and ImageNet datasets, and show that we can achieve an order of magnitude savings over gradient compression methods.
On Distributed Quantization for Classification
Nov 01, 2019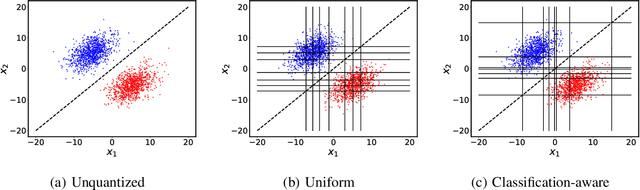
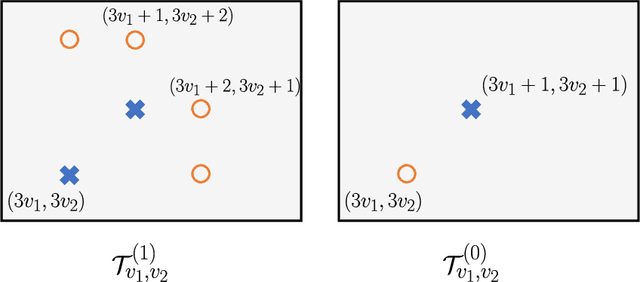
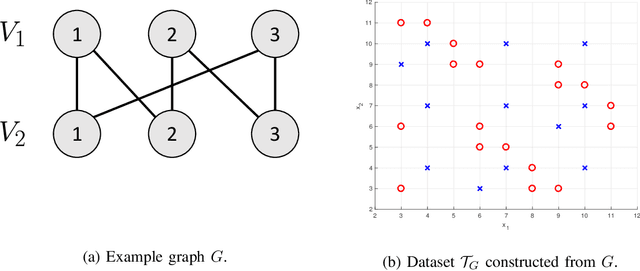
Abstract:We consider the problem of distributed feature quantization, where the goal is to enable a pretrained classifier at a central node to carry out its classification on features that are gathered from distributed nodes through communication constrained channels. We propose the design of distributed quantization schemes specifically tailored to the classification task: unlike quantization schemes that help the central node reconstruct the original signal as accurately as possible, our focus is not reconstruction accuracy, but instead correct classification. Our work does not make any apriori distributional assumptions on the data, but instead uses training data for the quantizer design. Our main contributions include: we prove NP-hardness of finding optimal quantizers in the general case; we design an optimal scheme for a special case; we propose quantization algorithms, that leverage discrete neural representations and training data, and can be designed in polynomial-time for any number of features, any number of classes, and arbitrary division of features across the distributed nodes. We find that tailoring the quantizers to the classification task can offer significant savings: as compared to alternatives, we can achieve more than a factor of two reduction in terms of the number of bits communicated, for the same classification accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge