Shantanu Sharma
Federated Analytics: A survey
Feb 02, 2023

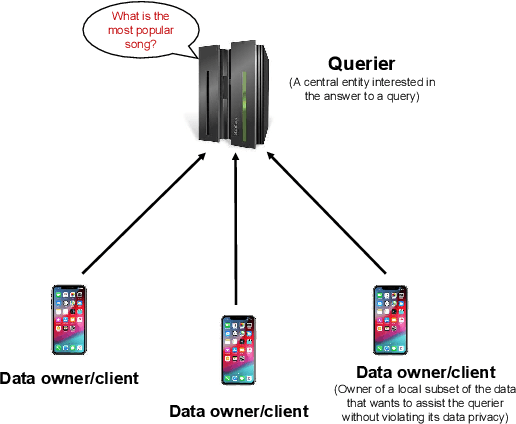

Abstract:Federated analytics (FA) is a privacy-preserving framework for computing data analytics over multiple remote parties (e.g., mobile devices) or silo-ed institutional entities (e.g., hospitals, banks) without sharing the data among parties. Motivated by the practical use cases of federated analytics, we follow a systematic discussion on federated analytics in this article. In particular, we discuss the unique characteristics of federated analytics and how it differs from federated learning. We also explore a wide range of FA queries and discuss various existing solutions and potential use case applications for different FA queries.
* To appear in APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing, Volume 12, Issue 1
Prism: Private Verifiable Set Computation over Multi-Owner Outsourced Databases
Apr 07, 2021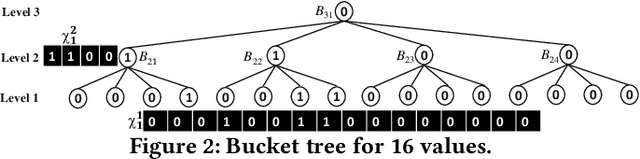
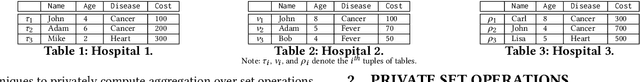
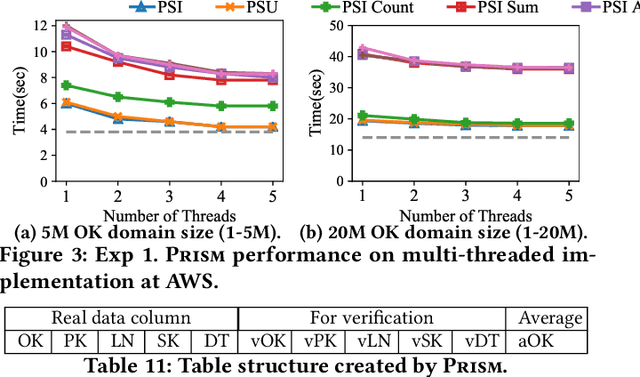
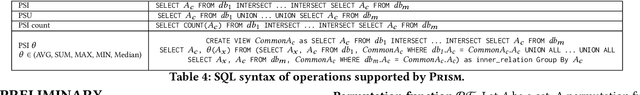
Abstract:This paper proposes Prism, a secret sharing based approach to compute private set operations (i.e., intersection and union), as well as aggregates over outsourced databases belonging to multiple owners. Prism enables data owners to pre-load the data onto non-colluding servers and exploits the additive and multiplicative properties of secret-shares to compute the above-listed operations in (at most) two rounds of communication between the servers (storing the secret-shares) and the querier, resulting in a very efficient implementation. Also, Prism does not require communication among the servers and supports result verification techniques for each operation to detect malicious adversaries. Experimental results show that Prism scales both in terms of the number of data owners and database sizes, to which prior approaches do not scale.
Concealer: SGX-based Secure, Volume Hiding, and Verifiable Processing of Spatial Time-Series Datasets
Feb 10, 2021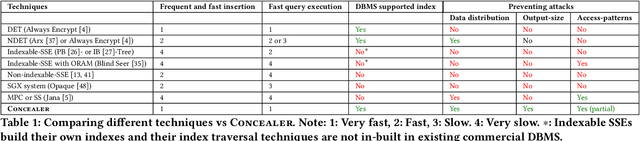
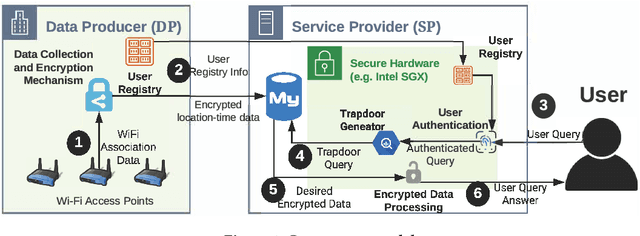

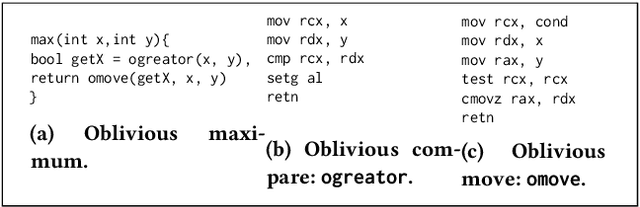
Abstract:This paper proposes a system, entitled Concealer that allows sharing time-varying spatial data (e.g., as produced by sensors) in encrypted form to an untrusted third-party service provider to provide location-based applications (involving aggregation queries over selected regions over time windows) to users. Concealer exploits carefully selected encryption techniques to use indexes supported by database systems and combines ways to add fake tuples in order to realize an efficient system that protects against leakage based on output-size. Thus, the design of Concealer overcomes two limitations of existing symmetric searchable encryption (SSE) techniques: (i) it avoids the need of specialized data structures that limit usability/practicality of SSE in large scale deployments, and (ii) it avoids information leakages based on the output-size, which may leak data distributions. Experimental results validate the efficiency of the proposed algorithms over a spatial time-series dataset (collected from a smart space) and TPC-H datasets, each of 136 Million rows, the size of which prior approaches have not scaled to.
Canopy: A Verifiable Privacy-Preserving Token Ring based Communication Protocol for Smart Homes
Apr 08, 2020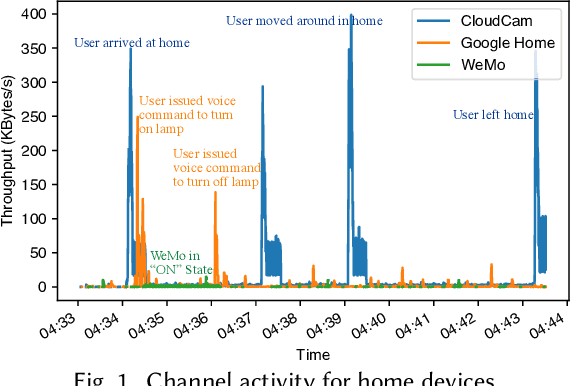
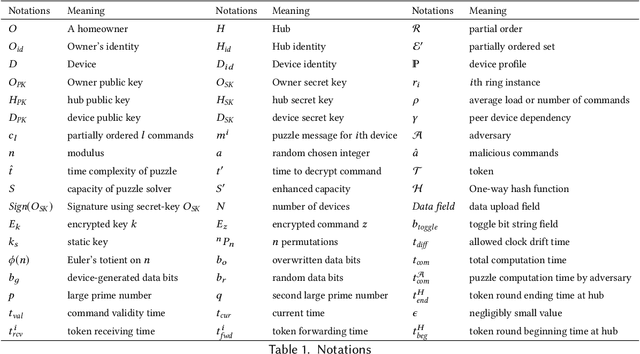
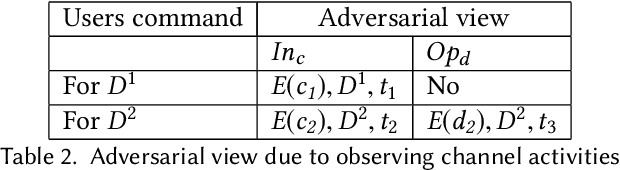
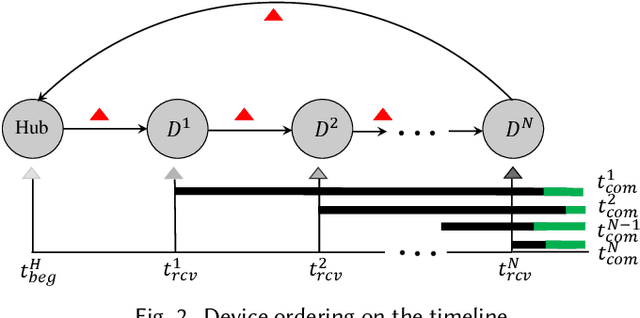
Abstract:This paper focuses on the new privacy challenges that arise in smart homes. Specifically, the paper focuses on inferring the user's activities -- which may, in turn, lead to the user's privacy -- via inferences through device activities and network traffic analysis. We develop techniques that are based on a cryptographically secure token circulation in a ring network consisting of smart home devices to prevent inferences from device activities, via device workflow, i.e., inferences from a coordinated sequence of devices' actuation. The solution hides the device activity and corresponding channel activities, and thus, preserve the individual's activities. We also extend our solution to deal with a large number of devices and devices that produce large-sized data by implementing parallel rings. Our experiments also evaluate the performance in terms of communication overheads of the proposed approach and the obtained privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge