Xubin Zheng
GROVER: Graph-guided Representation of Omics and Vision with Expert Regulation for Adaptive Spatial Multi-omics Fusion
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Effectively modeling multimodal spatial omics data is critical for understanding tissue complexity and underlying biological mechanisms. While spatial transcriptomics, proteomics, and epigenomics capture molecular features, they lack pathological morphological context. Integrating these omics with histopathological images is therefore essential for comprehensive disease tissue analysis. However, substantial heterogeneity across omics, imaging, and spatial modalities poses significant challenges. Naive fusion of semantically distinct sources often leads to ambiguous representations. Additionally, the resolution mismatch between high-resolution histology images and lower-resolution sequencing spots complicates spatial alignment. Biological perturbations during sample preparation further distort modality-specific signals, hindering accurate integration. To address these challenges, we propose Graph-guided Representation of Omics and Vision with Expert Regulation for Adaptive Spatial Multi-omics Fusion (GROVER), a novel framework for adaptive integration of spatial multi-omics data. GROVER leverages a Graph Convolutional Network encoder based on Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks to capture the nonlinear dependencies between each modality and its associated spatial structure, thereby producing expressive, modality-specific embeddings. To align these representations, we introduce a spot-feature-pair contrastive learning strategy that explicitly optimizes the correspondence across modalities at each spot. Furthermore, we design a dynamic expert routing mechanism that adaptively selects informative modalities for each spot while suppressing noisy or low-quality inputs. Experiments on real-world spatial omics datasets demonstrate that GROVER outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, providing a robust and reliable solution for multimodal integration.
Pan-infection Foundation Framework Enables Multiple Pathogen Prediction
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:Host-response-based diagnostics can improve the accuracy of diagnosing bacterial and viral infections, thereby reducing inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions. However, the existing cohorts with limited sample size and coarse infections types are unable to support the exploration of an accurate and generalizable diagnostic model. Here, we curate the largest infection host-response transcriptome data, including 11,247 samples across 89 blood transcriptome datasets from 13 countries and 21 platforms. We build a diagnostic model for pathogen prediction starting from a pan-infection model as foundation (AUC = 0.97) based on the pan-infection dataset. Then, we utilize knowledge distillation to efficiently transfer the insights from this "teacher" model to four lightweight pathogen "student" models, i.e., staphylococcal infection (AUC = 0.99), streptococcal infection (AUC = 0.94), HIV infection (AUC = 0.93), and RSV infection (AUC = 0.94), as well as a sepsis "student" model (AUC = 0.99). The proposed knowledge distillation framework not only facilitates the diagnosis of pathogens using pan-infection data, but also enables an across-disease study from pan-infection to sepsis. Moreover, the framework enables high-degree lightweight design of diagnostic models, which is expected to be adaptively deployed in clinical settings.
Single-View Graph Contrastive Learning with Soft Neighborhood Awareness
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Most graph contrastive learning (GCL) methods heavily rely on cross-view contrast, thus facing several concomitant challenges, such as the complexity of designing effective augmentations, the potential for information loss between views, and increased computational costs. To mitigate reliance on cross-view contrasts, we propose \ttt{SIGNA}, a novel single-view graph contrastive learning framework. Regarding the inconsistency between structural connection and semantic similarity of neighborhoods, we resort to soft neighborhood awareness for GCL. Specifically, we leverage dropout to obtain structurally-related yet randomly-noised embedding pairs for neighbors, which serve as potential positive samples. At each epoch, the role of partial neighbors is switched from positive to negative, leading to probabilistic neighborhood contrastive learning effect. Furthermore, we propose a normalized Jensen-Shannon divergence estimator for a better effect of contrastive learning. Surprisingly, experiments on diverse node-level tasks demonstrate that our simple single-view GCL framework consistently outperforms existing methods by margins of up to 21.74% (PPI). In particular, with soft neighborhood awareness, SIGNA can adopt MLPs instead of complicated GCNs as the encoder to generate representations in transductive learning tasks, thus speeding up its inference process by 109 times to 331 times. The source code is available at https://github.com/sunisfighting/SIGNA.
scFusionTTT: Single-cell transcriptomics and proteomics fusion with Test-Time Training layers
Oct 17, 2024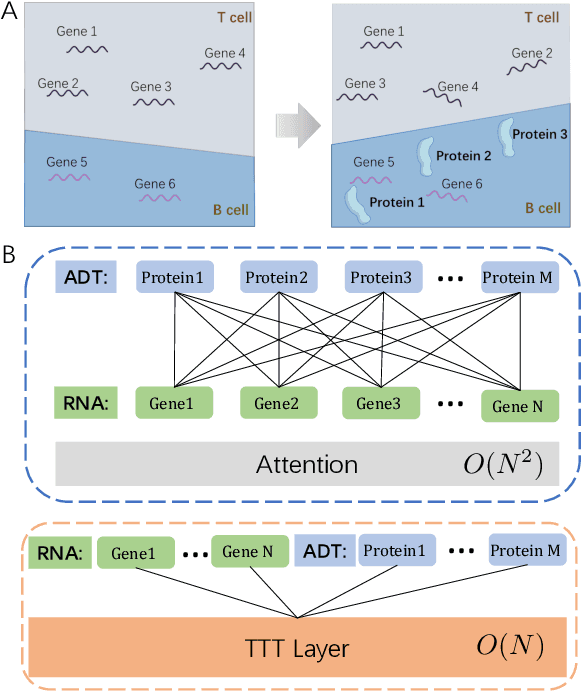
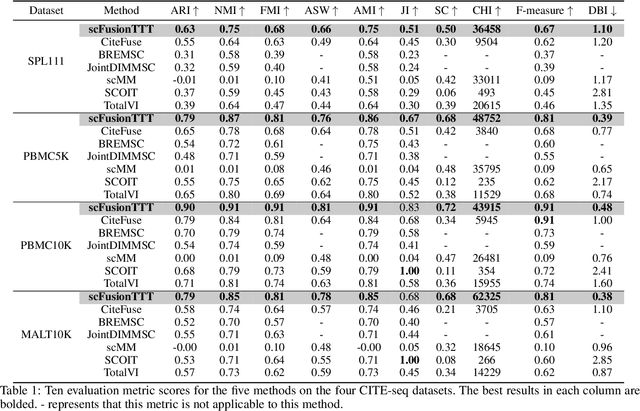
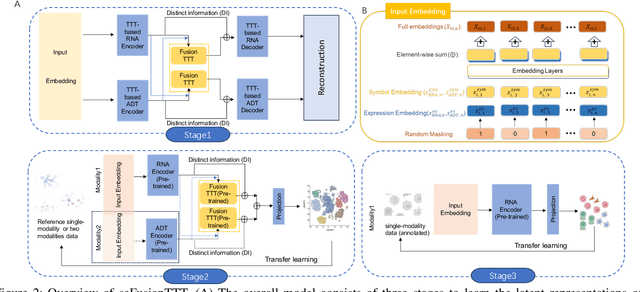
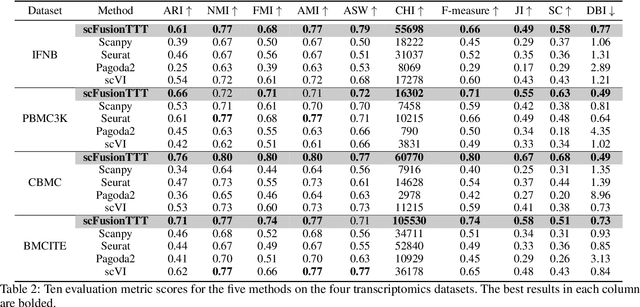
Abstract:Single-cell multi-omics (scMulti-omics) refers to the paired multimodal data, such as Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by Sequencing (CITE-seq), where the regulation of each cell was measured from different modalities, i.e. genes and proteins. scMulti-omics can reveal heterogeneity inside tumors and understand the distinct genetic properties of diverse cell types, which is crucial to targeted therapy. Currently, deep learning methods based on attention structures in the bioinformatics area face two challenges. The first challenge is the vast number of genes in a single cell. Traditional attention-based modules struggled to effectively leverage all gene information due to their limited capacity for long-context learning and high-complexity computing. The second challenge is that genes in the human genome are ordered and influence each other's expression. Most of the methods ignored this sequential information. The recently introduced Test-Time Training (TTT) layer is a novel sequence modeling approach, particularly suitable for handling long contexts like genomics data because TTT layer is a linear complexity sequence modeling structure and is better suited to data with sequential relationships. In this paper, we propose scFusionTTT, a novel method for Single-Cell multimodal omics Fusion with TTT-based masked autoencoder. Of note, we combine the order information of genes and proteins in the human genome with the TTT layer, fuse multimodal omics, and enhance unimodal omics analysis. Finally, the model employs a three-stage training strategy, which yielded the best performance across most metrics in four multimodal omics datasets and four unimodal omics datasets, demonstrating the superior performance of our model. The dataset and code will be available on https://github.com/DM0815/scFusionTTT.
Learn from Balance: Rectifying Knowledge Transfer for Long-Tailed Scenarios
Sep 12, 2024
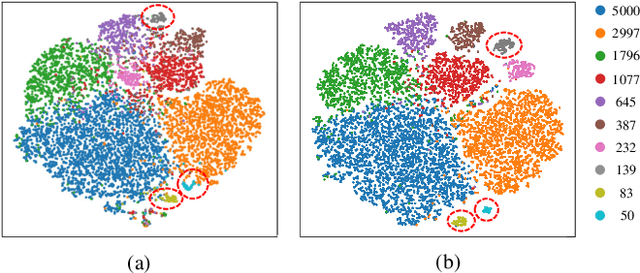

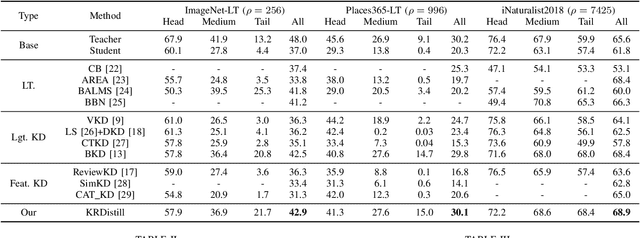
Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) transfers knowledge from a large pre-trained teacher network to a compact and efficient student network, making it suitable for deployment on resource-limited media terminals. However, traditional KD methods require balanced data to ensure robust training, which is often unavailable in practical applications. In such scenarios, a few head categories occupy a substantial proportion of examples. This imbalance biases the trained teacher network towards the head categories, resulting in severe performance degradation on the less represented tail categories for both the teacher and student networks. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called Knowledge Rectification Distillation (KRDistill) to address the imbalanced knowledge inherited in the teacher network through the incorporation of the balanced category priors. Furthermore, we rectify the biased predictions produced by the teacher network, particularly focusing on the tail categories. Consequently, the teacher network can provide balanced and accurate knowledge to train a reliable student network. Intensive experiments conducted on various long-tailed datasets demonstrate that our KRDistill can effectively train reliable student networks in realistic scenarios of data imbalance.
FusionMamba: Dynamic Feature Enhancement for Multimodal Image Fusion with Mamba
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Multi-modal image fusion aims to combine information from different modes to create a single image with comprehensive information and detailed textures. However, fusion models based on convolutional neural networks encounter limitations in capturing global image features due to their focus on local convolution operations. Transformer-based models, while excelling in global feature modeling, confront computational challenges stemming from their quadratic complexity. Recently, the Selective Structured State Space Model has exhibited significant potential for long-range dependency modeling with linear complexity, offering a promising avenue to address the aforementioned dilemma. In this paper, we propose FusionMamba, a novel dynamic feature enhancement method for multimodal image fusion with Mamba. Specifically, we devise an improved efficient Mamba model for image fusion, integrating efficient visual state space model with dynamic convolution and channel attention. This refined model not only upholds the performance of Mamba and global modeling capability but also diminishes channel redundancy while enhancing local enhancement capability. Additionally, we devise a dynamic feature fusion module (DFFM) comprising two dynamic feature enhancement modules (DFEM) and a cross modality fusion mamba module (CMFM). The former serves for dynamic texture enhancement and dynamic difference perception, whereas the latter enhances correlation features between modes and suppresses redundant intermodal information. FusionMamba has yielded state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across various multimodal medical image fusion tasks (CT-MRI, PET-MRI, SPECT-MRI), infrared and visible image fusion task (IR-VIS) and multimodal biomedical image fusion dataset (GFP-PC), which is proved that our model has generalization ability. The code for FusionMamba is available at https://github.com/millieXie/FusionMamba.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge