Wenxin Yu
An End-to-End Real-World Camera Imaging Pipeline
Nov 16, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in neural camera imaging pipelines have demonstrated notable progress. Nevertheless, the real-world imaging pipeline still faces challenges including the lack of joint optimization in system components, computational redundancies, and optical distortions such as lens shading.In light of this, we propose an end-to-end camera imaging pipeline (RealCamNet) to enhance real-world camera imaging performance. Our methodology diverges from conventional, fragmented multi-stage image signal processing towards end-to-end architecture. This architecture facilitates joint optimization across the full pipeline and the restoration of coordinate-biased distortions. RealCamNet is designed for high-quality conversion from RAW to RGB and compact image compression. Specifically, we deeply analyze coordinate-dependent optical distortions, e.g., vignetting and dark shading, and design a novel Coordinate-Aware Distortion Restoration (CADR) module to restore coordinate-biased distortions. Furthermore, we propose a Coordinate-Independent Mapping Compression (CIMC) module to implement tone mapping and redundant information compression. Existing datasets suffer from misalignment and overly idealized conditions, making them inadequate for training real-world imaging pipelines. Therefore, we collected a real-world imaging dataset. Experiment results show that RealCamNet achieves the best rate-distortion performance with lower inference latency.
Beyond Feature Mapping GAP: Integrating Real HDRTV Priors for Superior SDRTV-to-HDRTV Conversion
Nov 16, 2024



Abstract:The rise of HDR-WCG display devices has highlighted the need to convert SDRTV to HDRTV, as most video sources are still in SDR. Existing methods primarily focus on designing neural networks to learn a single-style mapping from SDRTV to HDRTV. However, the limited information in SDRTV and the diversity of styles in real-world conversions render this process an ill-posed problem, thereby constraining the performance and generalization of these methods. Inspired by generative approaches, we propose a novel method for SDRTV to HDRTV conversion guided by real HDRTV priors. Despite the limited information in SDRTV, introducing real HDRTV as reference priors significantly constrains the solution space of the originally high-dimensional ill-posed problem. This shift transforms the task from solving an unreferenced prediction problem to making a referenced selection, thereby markedly enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the conversion process. Specifically, our approach comprises two stages: the first stage employs a Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network to capture HDRTV priors, while the second stage matches these priors to the input SDRTV content to recover realistic HDRTV outputs. We evaluate our method on public datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness with significant improvements in both objective and subjective metrics across real and synthetic datasets.
Learn from Balance: Rectifying Knowledge Transfer for Long-Tailed Scenarios
Sep 12, 2024
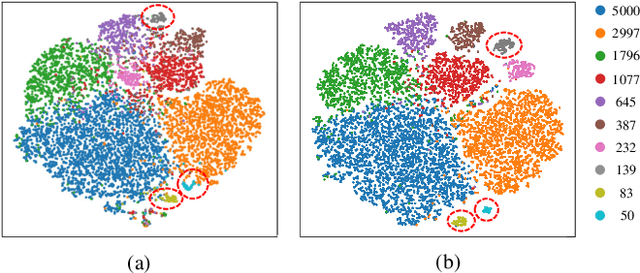

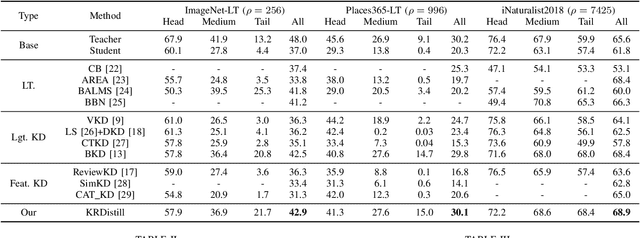
Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) transfers knowledge from a large pre-trained teacher network to a compact and efficient student network, making it suitable for deployment on resource-limited media terminals. However, traditional KD methods require balanced data to ensure robust training, which is often unavailable in practical applications. In such scenarios, a few head categories occupy a substantial proportion of examples. This imbalance biases the trained teacher network towards the head categories, resulting in severe performance degradation on the less represented tail categories for both the teacher and student networks. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called Knowledge Rectification Distillation (KRDistill) to address the imbalanced knowledge inherited in the teacher network through the incorporation of the balanced category priors. Furthermore, we rectify the biased predictions produced by the teacher network, particularly focusing on the tail categories. Consequently, the teacher network can provide balanced and accurate knowledge to train a reliable student network. Intensive experiments conducted on various long-tailed datasets demonstrate that our KRDistill can effectively train reliable student networks in realistic scenarios of data imbalance.
Beyond Alignment: Blind Video Face Restoration via Parsing-Guided Temporal-Coherent Transformer
Apr 21, 2024



Abstract:Multiple complex degradations are coupled in low-quality video faces in the real world. Therefore, blind video face restoration is a highly challenging ill-posed problem, requiring not only hallucinating high-fidelity details but also enhancing temporal coherence across diverse pose variations. Restoring each frame independently in a naive manner inevitably introduces temporal incoherence and artifacts from pose changes and keypoint localization errors. To address this, we propose the first blind video face restoration approach with a novel parsing-guided temporal-coherent transformer (PGTFormer) without pre-alignment. PGTFormer leverages semantic parsing guidance to select optimal face priors for generating temporally coherent artifact-free results. Specifically, we pre-train a temporal-spatial vector quantized auto-encoder on high-quality video face datasets to extract expressive context-rich priors. Then, the temporal parse-guided codebook predictor (TPCP) restores faces in different poses based on face parsing context cues without performing face pre-alignment. This strategy reduces artifacts and mitigates jitter caused by cumulative errors from face pre-alignment. Finally, the temporal fidelity regulator (TFR) enhances fidelity through temporal feature interaction and improves video temporal consistency. Extensive experiments on face videos show that our method outperforms previous face restoration baselines. The code will be released on \href{https://github.com/kepengxu/PGTFormer}{https://github.com/kepengxu/PGTFormer}.
Salient Object Detection via Bounding-box Supervision
May 11, 2022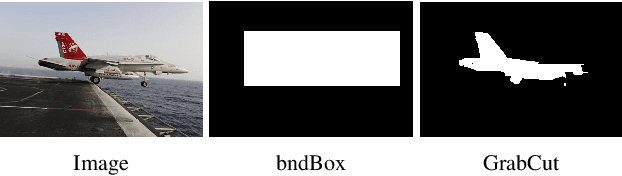
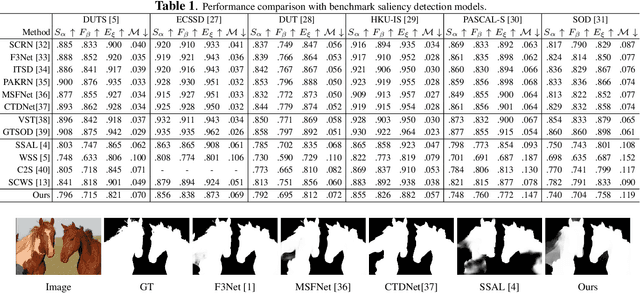
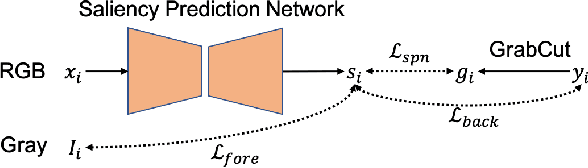
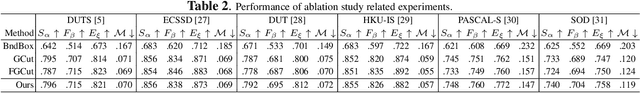
Abstract:The success of fully supervised saliency detection models depends on a large number of pixel-wise labeling. In this paper, we work on bounding-box based weakly-supervised saliency detection to relieve the labeling effort. Given the bounding box annotation, we observe that pixels inside the bounding box may contain extensive labeling noise. However, as a large amount of background is excluded, the foreground bounding box region contains a less complex background, making it possible to perform handcrafted features-based saliency detection with only the cropped foreground region. As the conventional handcrafted features are not representative enough, leading to noisy saliency maps, we further introduce structure-aware self-supervised loss to regularize the structure of the prediction. Further, we claim that pixels outside the bounding box should be background, thus partial cross-entropy loss function can be used to accurately localize the accurate background region. Experimental results on six benchmark RGB saliency datasets illustrate the effectiveness of our model.
A Survey on Semi-parametric Machine Learning Technique for Time Series Forecasting
Apr 02, 2021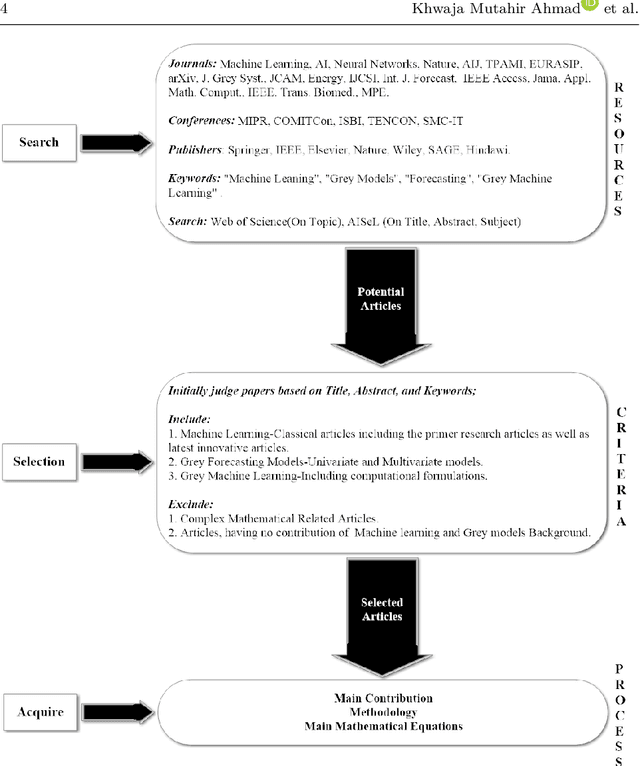
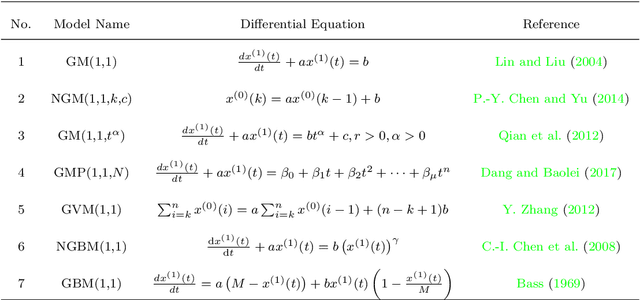
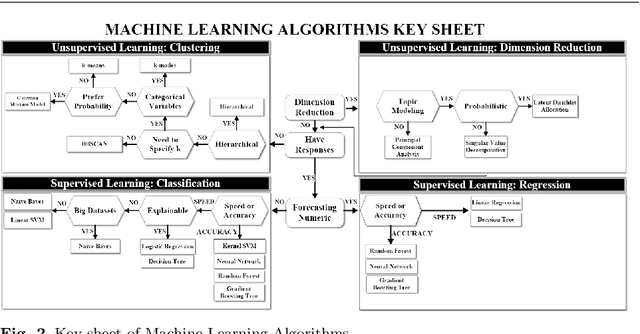
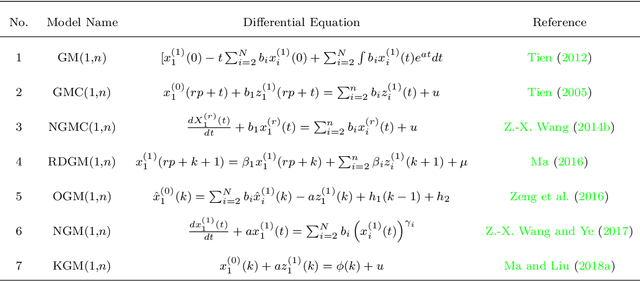
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has recently shown its capabilities for almost every field of life. Machine Learning, which is a subset of AI, is a `HOT' topic for researchers. Machine Learning outperforms other classical forecasting techniques in almost all-natural applications. It is a crucial part of modern research. As per this statement, Modern Machine Learning algorithms are hungry for big data. Due to the small datasets, the researchers may not prefer to use Machine Learning algorithms. To tackle this issue, the main purpose of this survey is to illustrate, demonstrate related studies for significance of a semi-parametric Machine Learning framework called Grey Machine Learning (GML). This kind of framework is capable of handling large datasets as well as small datasets for time series forecasting likely outcomes. This survey presents a comprehensive overview of the existing semi-parametric machine learning techniques for time series forecasting. In this paper, a primer survey on the GML framework is provided for researchers. To allow an in-depth understanding for the readers, a brief description of Machine Learning, as well as various forms of conventional grey forecasting models are discussed. Moreover, a brief description on the importance of GML framework is presented.
Revisiting the Loss Weight Adjustment in Object Detection
Mar 18, 2021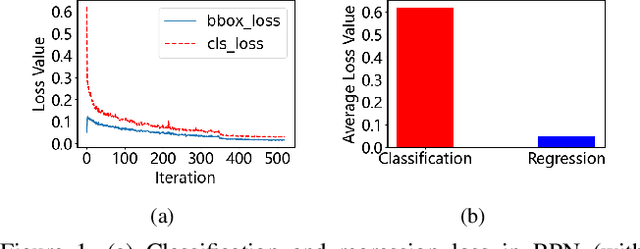
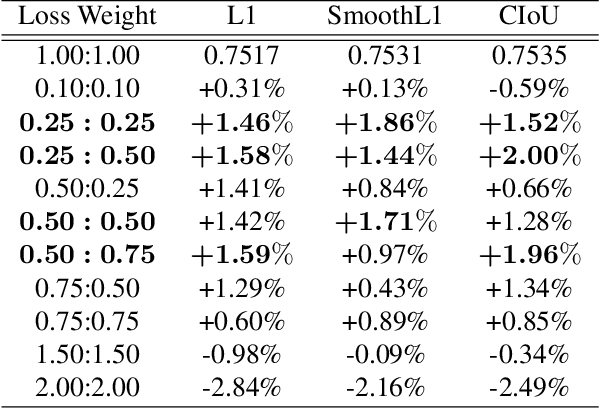
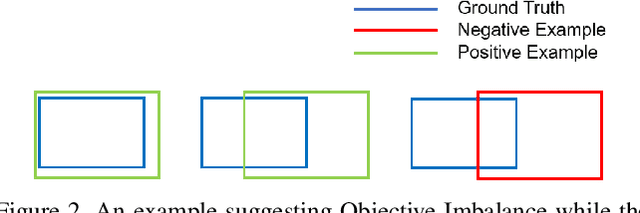
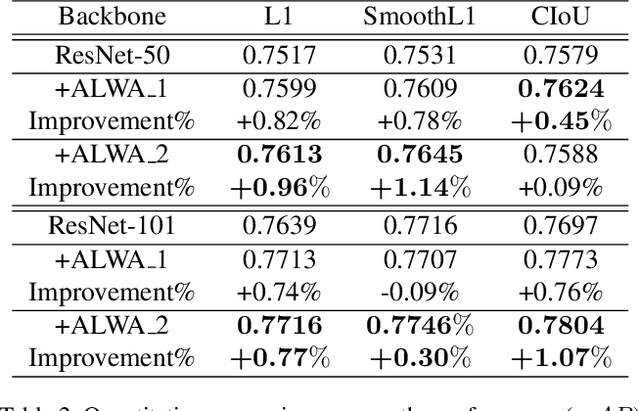
Abstract:By definition, object detection requires a multi-task loss in order to solve classification and regression tasks simultaneously. However, loss weight tends to be set manually in actuality. Therefore, a very practical problem that has not been studied so far arises: how to quickly find the loss weight that fits the current loss functions. In addition, when we choose different regression loss functions, whether the loss weight need to be adjusted and if so, how should it be adjusted still is a problem demanding prompt solution. In this paper, through experiments and theoretical analysis of prediction box shifting, we firstly find out three important conclusions about optimal loss weight allocation strategy, including (1) the classification loss curve decays faster than regression loss curve; (2) loss weight is less than 1; (3) the gap between classification and regression loss weight should not be too large. Then, based on the above conclusions, we propose an Adaptive Loss Weight Adjustment(ALWA) to solve the above two problems by dynamically adjusting the loss weight in the training process, according to statistical characteristics of loss values. By incorporating ALWA into both one-stage and two-stage object detectors, we show a consistent improvement on their performance using L1, SmoothL1 and CIoU loss, performance measures on popular object detection benchmarks including PASCAL VOC and MS COCO. The code is available at https://github.com/ywx-hub/ALWA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge