Xingxu Yao
S4OD: Semi-Supervised learning for Single-Stage Object Detection
Apr 09, 2022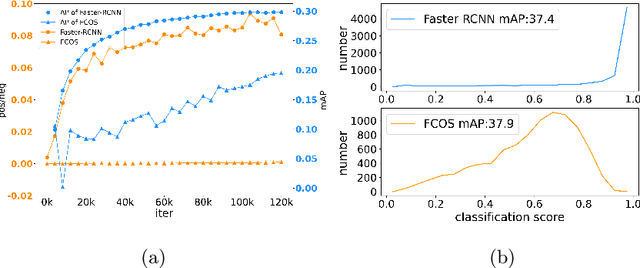
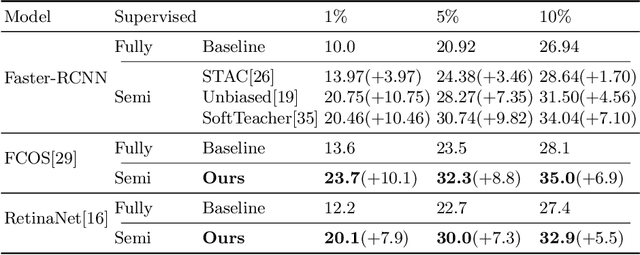
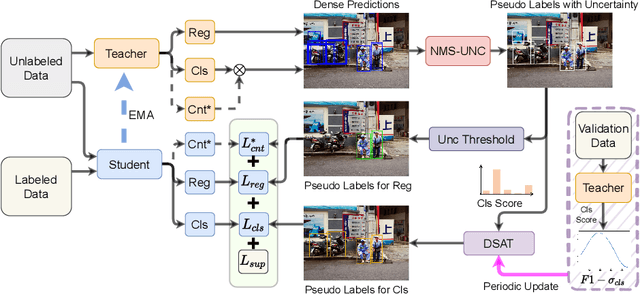
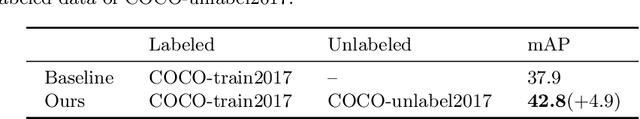
Abstract:Single-stage detectors suffer from extreme foreground-background class imbalance, while two-stage detectors do not. Therefore, in semi-supervised object detection, two-stage detectors can deliver remarkable performance by only selecting high-quality pseudo labels based on classification scores. However, directly applying this strategy to single-stage detectors would aggravate the class imbalance with fewer positive samples. Thus, single-stage detectors have to consider both quality and quantity of pseudo labels simultaneously. In this paper, we design a dynamic self-adaptive threshold (DSAT) strategy in classification branch, which can automatically select pseudo labels to achieve an optimal trade-off between quality and quantity. Besides, to assess the regression quality of pseudo labels in single-stage detectors, we propose a module to compute the regression uncertainty of boxes based on Non-Maximum Suppression. By leveraging only 10% labeled data from COCO, our method achieves 35.0% AP on anchor-free detector (FCOS) and 32.9% on anchor-based detector (RetinaNet).
2nd Place Solution for VisDA 2021 Challenge -- Universally Domain Adaptive Image Recognition
Oct 27, 2021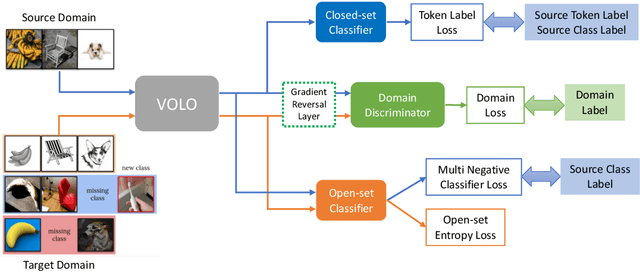
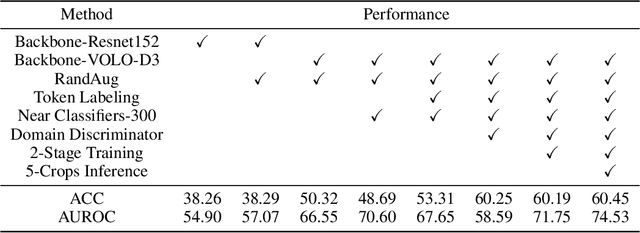
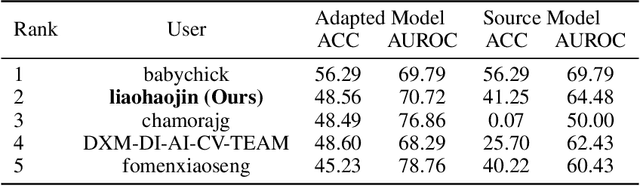
Abstract:The Visual Domain Adaptation (VisDA) 2021 Challenge calls for unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods that can deal with both input distribution shift and label set variance between the source and target domains. In this report, we introduce a universal domain adaptation (UniDA) method by aggregating several popular feature extraction and domain adaptation schemes. First, we utilize VOLO, a Transformer-based architecture with state-of-the-art performance in several visual tasks, as the backbone to extract effective feature representations. Second, we modify the open-set classifier of OVANet to recognize the unknown class with competitive accuracy and robustness. As shown in the leaderboard, our proposed UniDA method ranks the 2nd place with 48.56% ACC and 70.72% AUROC in the VisDA 2021 Challenge.
Affective Image Content Analysis: Two Decades Review and New Perspectives
Jun 30, 2021
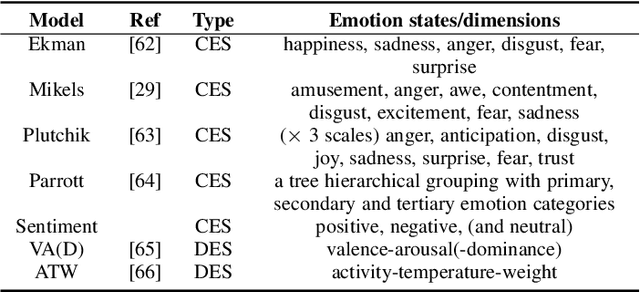
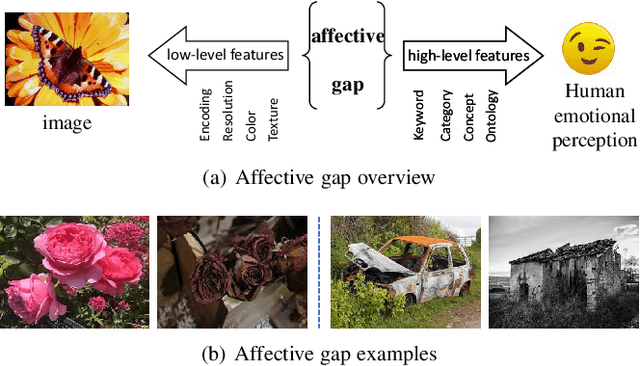

Abstract:Images can convey rich semantics and induce various emotions in viewers. Recently, with the rapid advancement of emotional intelligence and the explosive growth of visual data, extensive research efforts have been dedicated to affective image content analysis (AICA). In this survey, we will comprehensively review the development of AICA in the recent two decades, especially focusing on the state-of-the-art methods with respect to three main challenges -- the affective gap, perception subjectivity, and label noise and absence. We begin with an introduction to the key emotion representation models that have been widely employed in AICA and description of available datasets for performing evaluation with quantitative comparison of label noise and dataset bias. We then summarize and compare the representative approaches on (1) emotion feature extraction, including both handcrafted and deep features, (2) learning methods on dominant emotion recognition, personalized emotion prediction, emotion distribution learning, and learning from noisy data or few labels, and (3) AICA based applications. Finally, we discuss some challenges and promising research directions in the future, such as image content and context understanding, group emotion clustering, and viewer-image interaction.
Multi-Source Domain Adaptation for Object Detection
Jun 30, 2021



Abstract:To reduce annotation labor associated with object detection, an increasing number of studies focus on transferring the learned knowledge from a labeled source domain to another unlabeled target domain. However, existing methods assume that the labeled data are sampled from a single source domain, which ignores a more generalized scenario, where labeled data are from multiple source domains. For the more challenging task, we propose a unified Faster R-CNN based framework, termed Divide-and-Merge Spindle Network (DMSN), which can simultaneously enhance domain invariance and preserve discriminative power. Specifically, the framework contains multiple source subnets and a pseudo target subnet. First, we propose a hierarchical feature alignment strategy to conduct strong and weak alignments for low- and high-level features, respectively, considering their different effects for object detection. Second, we develop a novel pseudo subnet learning algorithm to approximate optimal parameters of pseudo target subset by weighted combination of parameters in different source subnets. Finally, a consistency regularization for region proposal network is proposed to facilitate each subnet to learn more abstract invariances. Extensive experiments on different adaptation scenarios demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model.
Computational Emotion Analysis From Images: Recent Advances and Future Directions
Mar 19, 2021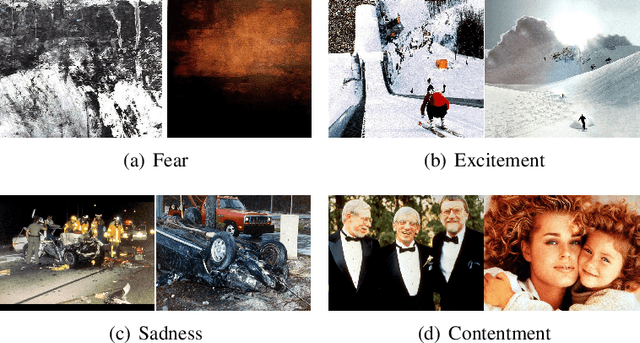
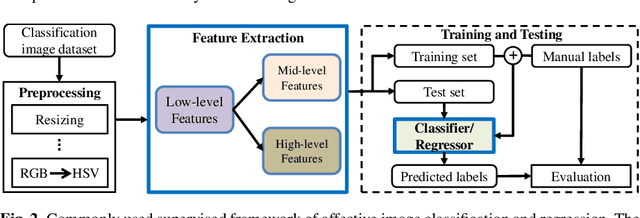
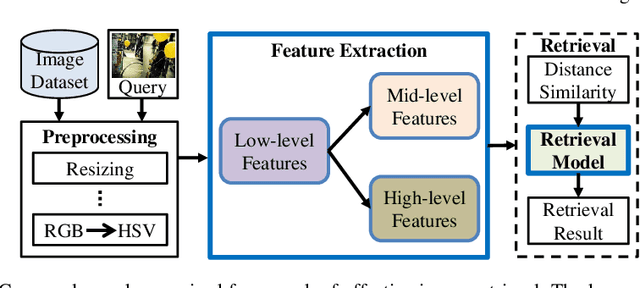
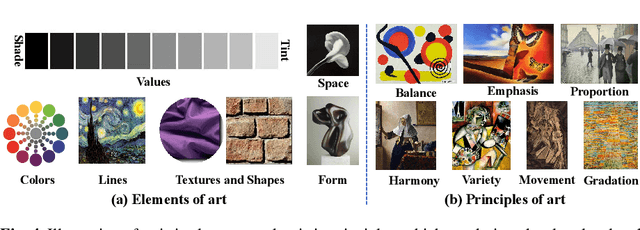
Abstract:Emotions are usually evoked in humans by images. Recently, extensive research efforts have been dedicated to understanding the emotions of images. In this chapter, we aim to introduce image emotion analysis (IEA) from a computational perspective with the focus on summarizing recent advances and suggesting future directions. We begin with commonly used emotion representation models from psychology. We then define the key computational problems that the researchers have been trying to solve and provide supervised frameworks that are generally used for different IEA tasks. After the introduction of major challenges in IEA, we present some representative methods on emotion feature extraction, supervised classifier learning, and domain adaptation. Furthermore, we introduce available datasets for evaluation and summarize some main results. Finally, we discuss some open questions and future directions that researchers can pursue.
Emotion-Based End-to-End Matching Between Image and Music in Valence-Arousal Space
Aug 22, 2020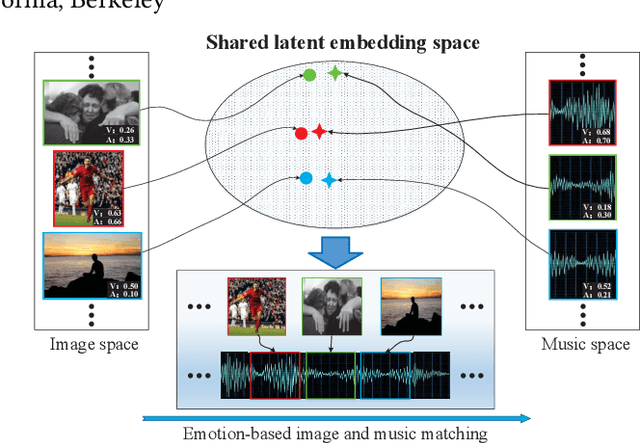
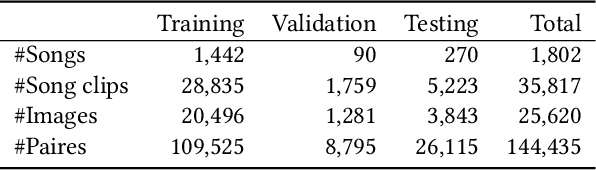
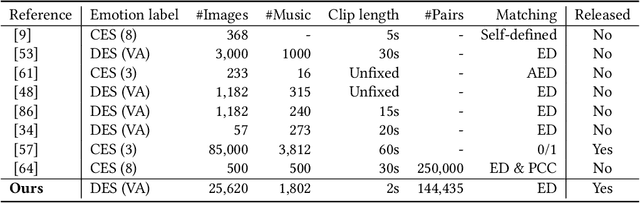
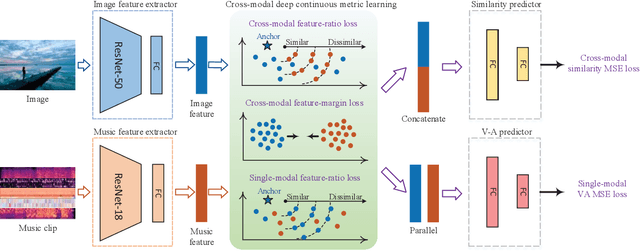
Abstract:Both images and music can convey rich semantics and are widely used to induce specific emotions. Matching images and music with similar emotions might help to make emotion perceptions more vivid and stronger. Existing emotion-based image and music matching methods either employ limited categorical emotion states which cannot well reflect the complexity and subtlety of emotions, or train the matching model using an impractical multi-stage pipeline. In this paper, we study end-to-end matching between image and music based on emotions in the continuous valence-arousal (VA) space. First, we construct a large-scale dataset, termed Image-Music-Emotion-Matching-Net (IMEMNet), with over 140K image-music pairs. Second, we propose cross-modal deep continuous metric learning (CDCML) to learn a shared latent embedding space which preserves the cross-modal similarity relationship in the continuous matching space. Finally, we refine the embedding space by further preserving the single-modal emotion relationship in the VA spaces of both images and music. The metric learning in the embedding space and task regression in the label space are jointly optimized for both cross-modal matching and single-modal VA prediction. The extensive experiments conducted on IMEMNet demonstrate the superiority of CDCML for emotion-based image and music matching as compared to the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge