Xin-Qiang Cai
Positive-Unlabeled Reinforcement Learning Distillation for On-Premise Small Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Due to constraints on privacy, cost, and latency, on-premise deployment of small models is increasingly common. However, most practical pipelines stop at supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and fail to reach the reinforcement learning (RL) alignment stage. The main reason is that RL alignment typically requires either expensive human preference annotation or heavy reliance on high-quality reward models with large-scale API usage and ongoing engineering maintenance, both of which are ill-suited to on-premise settings. To bridge this gap, we propose a positive-unlabeled (PU) RL distillation method for on-premise small-model deployment. Without human-labeled preferences or a reward model, our method distills the teacher's preference-optimization capability from black-box generations into a locally trainable student. For each prompt, we query the teacher once to obtain an anchor response, locally sample multiple student candidates, and perform anchor-conditioned self-ranking to induce pairwise or listwise preferences, enabling a fully local training loop via direct preference optimization or group relative policy optimization. Theoretical analysis justifies that the induced preference signal by our method is order-consistent and concentrates on near-optimal candidates, supporting its stability for preference optimization. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves consistently strong performance under a low-cost setting.
PIG-Nav: Key Insights for Pretrained Image Goal Navigation Models
Jul 23, 2025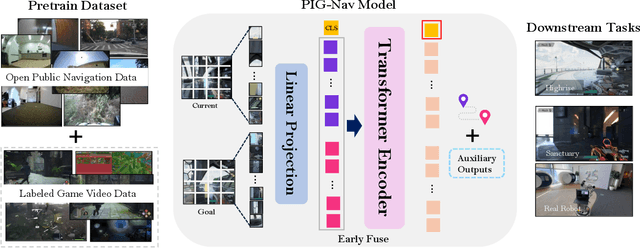
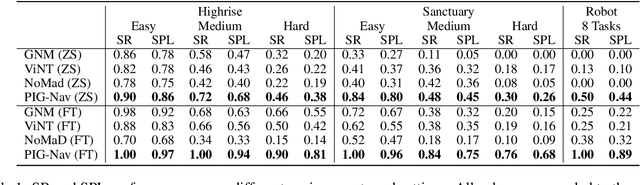
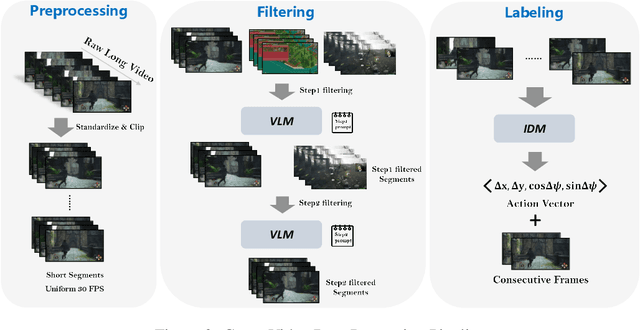
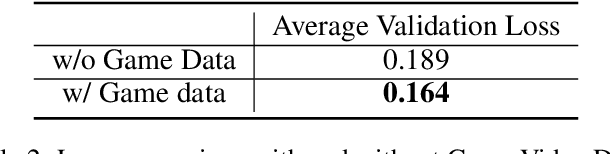
Abstract:Recent studies have explored pretrained (foundation) models for vision-based robotic navigation, aiming to achieve generalizable navigation and positive transfer across diverse environments while enhancing zero-shot performance in unseen settings. In this work, we introduce PIG-Nav (Pretrained Image-Goal Navigation), a new approach that further investigates pretraining strategies for vision-based navigation models and contributes in two key areas. Model-wise, we identify two critical design choices that consistently improve the performance of pretrained navigation models: (1) integrating an early-fusion network structure to combine visual observations and goal images via appropriately pretrained Vision Transformer (ViT) image encoder, and (2) introducing suitable auxiliary tasks to enhance global navigation representation learning, thus further improving navigation performance. Dataset-wise, we propose a novel data preprocessing pipeline for efficiently labeling large-scale game video datasets for navigation model training. We demonstrate that augmenting existing open navigation datasets with diverse gameplay videos improves model performance. Our model achieves an average improvement of 22.6% in zero-shot settings and a 37.5% improvement in fine-tuning settings over existing visual navigation foundation models in two complex simulated environments and one real-world environment. These results advance the state-of-the-art in pretrained image-goal navigation models. Notably, our model maintains competitive performance while requiring significantly less fine-tuning data, highlighting its potential for real-world deployment with minimal labeled supervision.
Beyond Simple Sum of Delayed Rewards: Non-Markovian Reward Modeling for Reinforcement Learning
Oct 26, 2024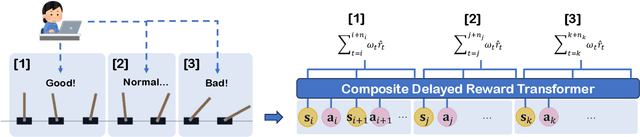
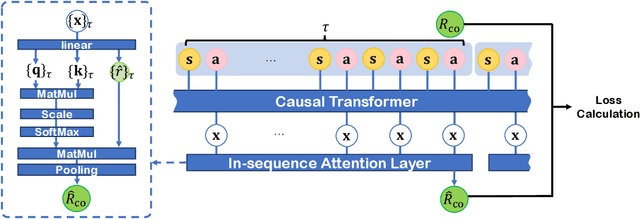
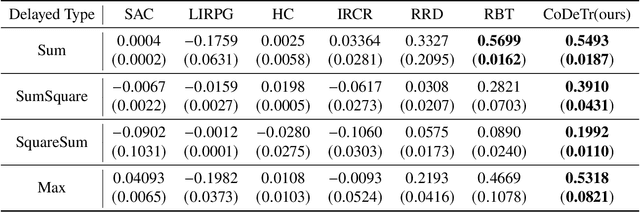
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) empowers agents to acquire various skills by learning from reward signals. Unfortunately, designing high-quality instance-level rewards often demands significant effort. An emerging alternative, RL with delayed reward, focuses on learning from rewards presented periodically, which can be obtained from human evaluators assessing the agent's performance over sequences of behaviors. However, traditional methods in this domain assume the existence of underlying Markovian rewards and that the observed delayed reward is simply the sum of instance-level rewards, both of which often do not align well with real-world scenarios. In this paper, we introduce the problem of RL from Composite Delayed Reward (RLCoDe), which generalizes traditional RL from delayed rewards by eliminating the strong assumption. We suggest that the delayed reward may arise from a more complex structure reflecting the overall contribution of the sequence. To address this problem, we present a framework for modeling composite delayed rewards, using a weighted sum of non-Markovian components to capture the different contributions of individual steps. Building on this framework, we propose Composite Delayed Reward Transformer (CoDeTr), which incorporates a specialized in-sequence attention mechanism to effectively model these contributions. We conduct experiments on challenging locomotion tasks where the agent receives delayed rewards computed from composite functions of observable step rewards. The experimental results indicate that CoDeTr consistently outperforms baseline methods across evaluated metrics. Additionally, we demonstrate that it effectively identifies the most significant time steps within the sequence and accurately predicts rewards that closely reflect the environment feedback.
Soft-Label Integration for Robust Toxicity Classification
Oct 18, 2024



Abstract:Toxicity classification in textual content remains a significant problem. Data with labels from a single annotator fall short of capturing the diversity of human perspectives. Therefore, there is a growing need to incorporate crowdsourced annotations for training an effective toxicity classifier. Additionally, the standard approach to training a classifier using empirical risk minimization (ERM) may fail to address the potential shifts between the training set and testing set due to exploiting spurious correlations. This work introduces a novel bi-level optimization framework that integrates crowdsourced annotations with the soft-labeling technique and optimizes the soft-label weights by Group Distributionally Robust Optimization (GroupDRO) to enhance the robustness against out-of-distribution (OOD) risk. We theoretically prove the convergence of our bi-level optimization algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing baseline methods in terms of both average and worst-group accuracy, confirming its effectiveness in leveraging crowdsourced annotations to achieve more effective and robust toxicity classification.
Leveraging Domain-Unlabeled Data in Offline Reinforcement Learning across Two Domains
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we investigate an offline reinforcement learning (RL) problem where datasets are collected from two domains. In this scenario, having datasets with domain labels facilitates efficient policy training. However, in practice, the task of assigning domain labels can be resource-intensive or infeasible at a large scale, leading to a prevalence of domain-unlabeled data. To formalize this challenge, we introduce a novel offline RL problem setting named Positive-Unlabeled Offline RL (PUORL), which incorporates domain-unlabeled data. To address PUORL, we develop an offline RL algorithm utilizing positive-unlabeled learning to predict the domain labels of domain-unlabeled data, enabling the integration of this data into policy training. Our experiments show the effectiveness of our method in accurately identifying domains and learning policies that outperform baselines in the PUORL setting, highlighting its capability to leverage domain-unlabeled data effectively.
An Animation-based Augmentation Approach for Action Recognition from Discontinuous Video
Apr 10, 2024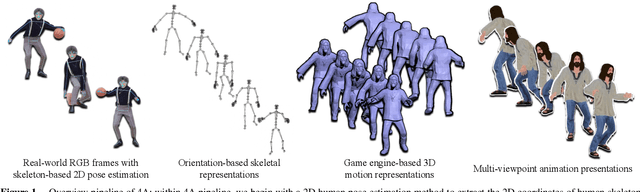
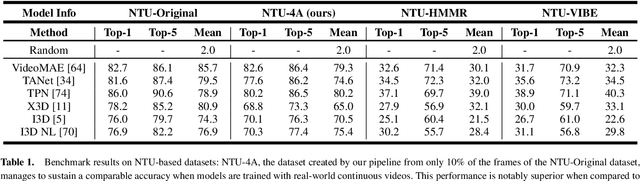
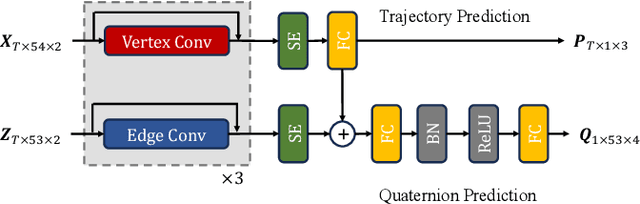
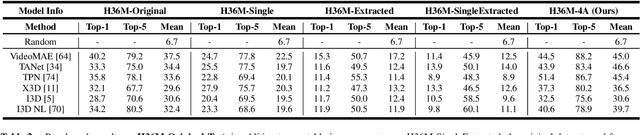
Abstract:The study of action recognition has attracted considerable attention recently due to its broad applications in multiple areas. However, with the issue of discontinuous training video, which not only decreases the performance of action recognition model, but complicates the data augmentation process as well, still remains under-exploration. In this study, we introduce the 4A (Action Animation-based Augmentation Approach), an innovative pipeline for data augmentation to address the problem. The main contributions remain in our work includes: (1) we investigate the problem of severe decrease on performance of action recognition task training by discontinuous video, and the limitation of existing augmentation methods on solving this problem. (2) we propose a novel augmentation pipeline, 4A, to address the problem of discontinuous video for training, while achieving a smoother and natural-looking action representation than the latest data augmentation methodology. (3) We achieve the same performance with only 10% of the original data for training as with all of the original data from the real-world dataset, and a better performance on In-the-wild videos, by employing our data augmentation techniques.
Reinforcement Learning from Bagged Reward: A Transformer-based Approach for Instance-Level Reward Redistribution
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:In reinforcement Learning (RL), an instant reward signal is generated for each action of the agent, such that the agent learns to maximize the cumulative reward to obtain the optimal policy. However, in many real-world applications, the instant reward signals are not obtainable by the agent. Instead, the learner only obtains rewards at the ends of bags, where a bag is defined as a partial sequence of a complete trajectory. In this situation, the learner has to face the significant difficulty of exploring the unknown instant rewards in the bags, which could not be addressed by existing approaches, including those trajectory-based approaches that consider only complete trajectories and ignore the inner reward distributions. To formally study this situation, we introduce a novel RL setting termed Reinforcement Learning from Bagged Rewards (RLBR), where only the bagged rewards of sequences can be obtained. We provide the theoretical study to establish the connection between RLBR and standard RL in Markov Decision Processes (MDPs). To effectively explore the reward distributions within the bagged rewards, we propose a Transformer-based reward model, the Reward Bag Transformer (RBT), which uses the self-attention mechanism for interpreting the contextual nuances and temporal dependencies within each bag. Extensive experimental analyses demonstrate the superiority of our method, particularly in its ability to mimic the original MDP's reward distribution, highlighting its proficiency in contextual understanding and adaptability to environmental dynamics.
Leveraging Multi-lingual Positive Instances in Contrastive Learning to Improve Sentence Embedding
Sep 16, 2023Abstract:Learning multi-lingual sentence embeddings is a fundamental and significant task in natural language processing. Recent trends of learning both mono-lingual and multi-lingual sentence embeddings are mainly based on contrastive learning (CL) with an anchor, one positive, and multiple negative instances. In this work, we argue that leveraging multiple positives should be considered for multi-lingual sentence embeddings because (1) positives in a diverse set of languages can benefit cross-lingual learning, and (2) transitive similarity across multiple positives can provide reliable structural information to learn. In order to investigate the impact of CL with multiple positives, we propose a novel approach MPCL to effectively utilize multiple positive instances to improve learning multi-lingual sentence embeddings. Our experimental results on various backbone models and downstream tasks support that compared with conventional CL, MPCL leads to better retrieval, semantic similarity, and classification performances. We also observe that on unseen languages, sentence embedding models trained on multiple positives have better cross-lingual transferring performance than models trained on a single positive instance.
Seeing Differently, Acting Similarly: Imitation Learning with Heterogeneous Observations
Jun 17, 2021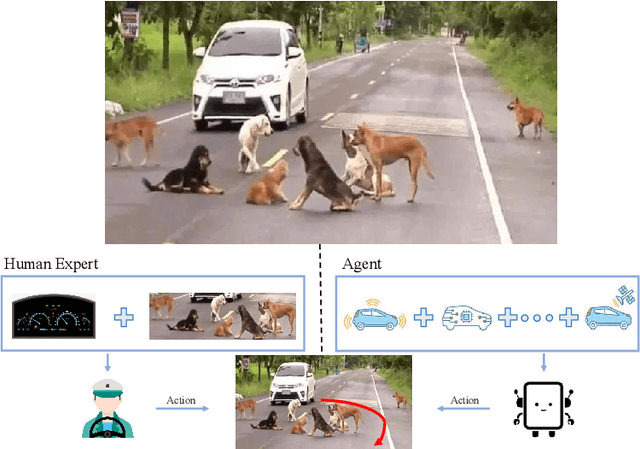
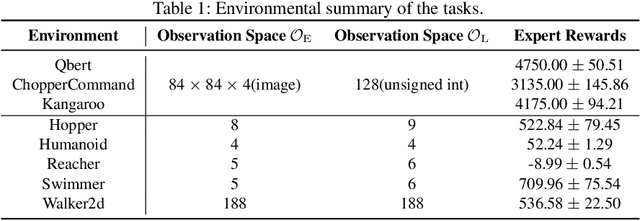
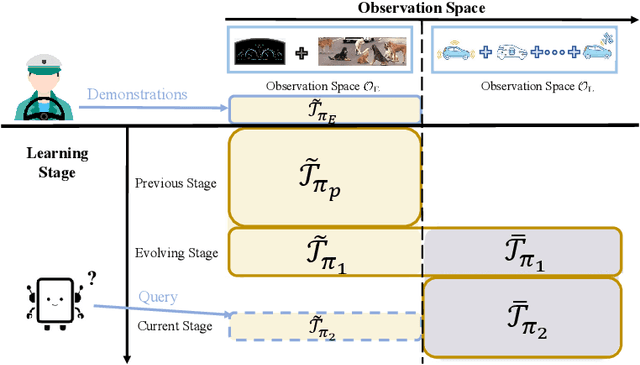
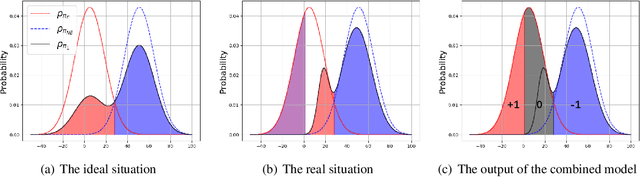
Abstract:In many real-world imitation learning tasks, the demonstrator and the learner have to act in different but full observation spaces. This situation generates significant obstacles for existing imitation learning approaches to work, even when they are combined with traditional space adaptation techniques. The main challenge lies in bridging expert's occupancy measures to learner's dynamically changing occupancy measures under the different observation spaces. In this work, we model the above learning problem as Heterogeneous Observations Imitation Learning (HOIL). We propose the Importance Weighting with REjection (IWRE) algorithm based on the techniques of importance-weighting, learning with rejection, and active querying to solve the key challenge of occupancy measure matching. Experimental results show that IWRE can successfully solve HOIL tasks, including the challenging task of transforming the vision-based demonstrations to random access memory (RAM)-based policies under the Atari domain.
Expert-Level Atari Imitation Learning from Demonstrations Only
Sep 09, 2019

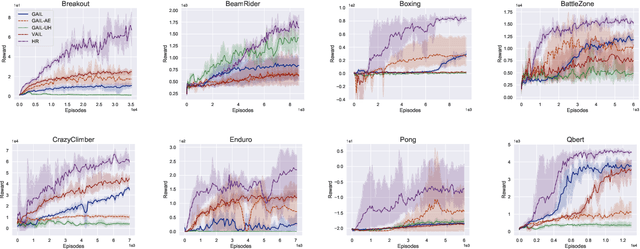
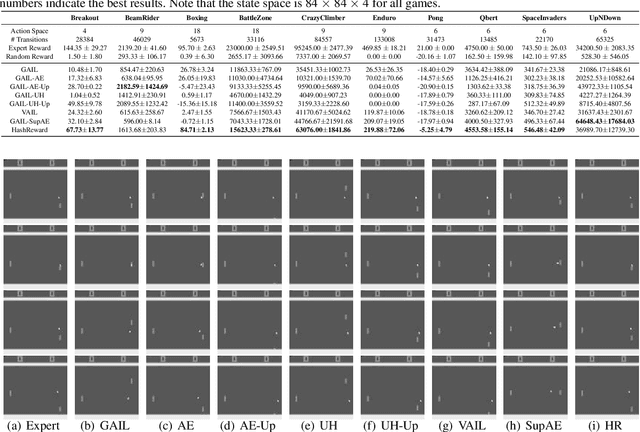
Abstract:One of the key issues for imitation learning lies in making policy learned from limited samples to generalize well in the whole state-action space. This problem is much more severe in high-dimensional state environments, such as game playing with raw pixel inputs. Under this situation, even state-of-the-art adversary based imitation learning algorithms fail. Through theoretical and empirical studies, we find that the main cause lies in the failure of training a powerful discriminator to generate meaningful rewards in high-dimensional environments. Theoretical results are provided to suggest the necessity of dimensionality reduction. However, since preserving important discriminative information via feature transformation is a non-trivial task, a straightforward application of off-the-shelf methods cannot achieve desirable performance. To address the above issues, we propose HashReward, which is a novel imitation learning algorithm utilizing the idea of supervised hashing to realize effective training of the discriminator. As far as we are aware, HashReward is the first pure imitation learning approach to achieve expert comparable performance in Atari game environments with raw pixel inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge