Xiangui Kang
AdvAD: Exploring Non-Parametric Diffusion for Imperceptible Adversarial Attacks
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Imperceptible adversarial attacks aim to fool DNNs by adding imperceptible perturbation to the input data. Previous methods typically improve the imperceptibility of attacks by integrating common attack paradigms with specifically designed perception-based losses or the capabilities of generative models. In this paper, we propose Adversarial Attacks in Diffusion (AdvAD), a novel modeling framework distinct from existing attack paradigms. AdvAD innovatively conceptualizes attacking as a non-parametric diffusion process by theoretically exploring basic modeling approach rather than using the denoising or generation abilities of regular diffusion models requiring neural networks. At each step, much subtler yet effective adversarial guidance is crafted using only the attacked model without any additional network, which gradually leads the end of diffusion process from the original image to a desired imperceptible adversarial example. Grounded in a solid theoretical foundation of the proposed non-parametric diffusion process, AdvAD achieves high attack efficacy and imperceptibility with intrinsically lower overall perturbation strength. Additionally, an enhanced version AdvAD-X is proposed to evaluate the extreme of our novel framework under an ideal scenario. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed AdvAD and AdvAD-X. Compared with state-of-the-art imperceptible attacks, AdvAD achieves an average of 99.9$\%$ (+17.3$\%$) ASR with 1.34 (-0.97) $l_2$ distance, 49.74 (+4.76) PSNR and 0.9971 (+0.0043) SSIM against four prevalent DNNs with three different architectures on the ImageNet-compatible dataset. Code is available at https://github.com/XianguiKang/AdvAD.
* Accept by NeurIPS 2024. Please cite this paper using the following format: J. Li, Z. He, A. Luo, J. Hu, Z. Wang, X. Kang*, "AdvAD: Exploring Non-Parametric Diffusion for Imperceptible Adversarial Attacks", the 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, Canada, Dec 9-15, 2024. Code: https://github.com/XianguiKang/AdvAD
PGD-Imp: Rethinking and Unleashing Potential of Classic PGD with Dual Strategies for Imperceptible Adversarial Attacks
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Imperceptible adversarial attacks have recently attracted increasing research interests. Existing methods typically incorporate external modules or loss terms other than a simple $l_p$-norm into the attack process to achieve imperceptibility, while we argue that such additional designs may not be necessary. In this paper, we rethink the essence of imperceptible attacks and propose two simple yet effective strategies to unleash the potential of PGD, the common and classical attack, for imperceptibility from an optimization perspective. Specifically, the Dynamic Step Size is introduced to find the optimal solution with minimal attack cost towards the decision boundary of the attacked model, and the Adaptive Early Stop strategy is adopted to reduce the redundant strength of adversarial perturbations to the minimum level. The proposed PGD-Imperceptible (PGD-Imp) attack achieves state-of-the-art results in imperceptible adversarial attacks for both untargeted and targeted scenarios. When performing untargeted attacks against ResNet-50, PGD-Imp attains 100$\%$ (+0.3$\%$) ASR, 0.89 (-1.76) $l_2$ distance, and 52.93 (+9.2) PSNR with 57s (-371s) running time, significantly outperforming existing methods.
$L_p$-norm Distortion-Efficient Adversarial Attack
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Adversarial examples have shown a powerful ability to make a well-trained model misclassified. Current mainstream adversarial attack methods only consider one of the distortions among $L_0$-norm, $L_2$-norm, and $L_\infty$-norm. $L_0$-norm based methods cause large modification on a single pixel, resulting in naked-eye visible detection, while $L_2$-norm and $L_\infty$-norm based methods suffer from weak robustness against adversarial defense since they always diffuse tiny perturbations to all pixels. A more realistic adversarial perturbation should be sparse and imperceptible. In this paper, we propose a novel $L_p$-norm distortion-efficient adversarial attack, which not only owns the least $L_2$-norm loss but also significantly reduces the $L_0$-norm distortion. To this aim, we design a new optimization scheme, which first optimizes an initial adversarial perturbation under $L_2$-norm constraint, and then constructs a dimension unimportance matrix for the initial perturbation. Such a dimension unimportance matrix can indicate the adversarial unimportance of each dimension of the initial perturbation. Furthermore, we introduce a new concept of adversarial threshold for the dimension unimportance matrix. The dimensions of the initial perturbation whose unimportance is higher than the threshold will be all set to zero, greatly decreasing the $L_0$-norm distortion. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets show that under the same query budget, the adversarial examples generated by our method have lower $L_0$-norm and $L_2$-norm distortion than the state-of-the-art. Especially for the MNIST dataset, our attack reduces 8.1$\%$ $L_2$-norm distortion meanwhile remaining 47$\%$ pixels unattacked. This demonstrates the superiority of the proposed method over its competitors in terms of adversarial robustness and visual imperceptibility.
GM-DF: Generalized Multi-Scenario Deepfake Detection
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:Existing face forgery detection usually follows the paradigm of training models in a single domain, which leads to limited generalization capacity when unseen scenarios and unknown attacks occur. In this paper, we elaborately investigate the generalization capacity of deepfake detection models when jointly trained on multiple face forgery detection datasets. We first find a rapid degradation of detection accuracy when models are directly trained on combined datasets due to the discrepancy across collection scenarios and generation methods. To address the above issue, a Generalized Multi-Scenario Deepfake Detection framework (GM-DF) is proposed to serve multiple real-world scenarios by a unified model. First, we propose a hybrid expert modeling approach for domain-specific real/forgery feature extraction. Besides, as for the commonality representation, we use CLIP to extract the common features for better aligning visual and textual features across domains. Meanwhile, we introduce a masked image reconstruction mechanism to force models to capture rich forged details. Finally, we supervise the models via a domain-aware meta-learning strategy to further enhance their generalization capacities. Specifically, we design a novel domain alignment loss to strongly align the distributions of the meta-test domains and meta-train domains. Thus, the updated models are able to represent both specific and common real/forgery features across multiple datasets. In consideration of the lack of study of multi-dataset training, we establish a new benchmark leveraging multi-source data to fairly evaluate the models' generalization capacity on unseen scenarios. Both qualitative and quantitative experiments on five datasets conducted on traditional protocols as well as the proposed benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Forgery-aware Adaptive Vision Transformer for Face Forgery Detection
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:With the advancement in face manipulation technologies, the importance of face forgery detection in protecting authentication integrity becomes increasingly evident. Previous Vision Transformer (ViT)-based detectors have demonstrated subpar performance in cross-database evaluations, primarily because fully fine-tuning with limited Deepfake data often leads to forgetting pre-trained knowledge and over-fitting to data-specific ones. To circumvent these issues, we propose a novel Forgery-aware Adaptive Vision Transformer (FA-ViT). In FA-ViT, the vanilla ViT's parameters are frozen to preserve its pre-trained knowledge, while two specially designed components, the Local-aware Forgery Injector (LFI) and the Global-aware Forgery Adaptor (GFA), are employed to adapt forgery-related knowledge. our proposed FA-ViT effectively combines these two different types of knowledge to form the general forgery features for detecting Deepfakes. Specifically, LFI captures local discriminative information and incorporates these information into ViT via Neighborhood-Preserving Cross Attention (NPCA). Simultaneously, GFA learns adaptive knowledge in the self-attention layer, bridging the gap between the two different domain. Furthermore, we design a novel Single Domain Pairwise Learning (SDPL) to facilitate fine-grained information learning in FA-ViT. The extensive experiments demonstrate that our FA-ViT achieves state-of-the-art performance in cross-dataset evaluation and cross-manipulation scenarios, and improves the robustness against unseen perturbations.
Beyond the Prior Forgery Knowledge: Mining Critical Clues for General Face Forgery Detection
Apr 24, 2023Abstract:Face forgery detection is essential in combating malicious digital face attacks. Previous methods mainly rely on prior expert knowledge to capture specific forgery clues, such as noise patterns, blending boundaries, and frequency artifacts. However, these methods tend to get trapped in local optima, resulting in limited robustness and generalization capability. To address these issues, we propose a novel Critical Forgery Mining (CFM) framework, which can be flexibly assembled with various backbones to boost their generalization and robustness performance. Specifically, we first build a fine-grained triplet and suppress specific forgery traces through prior knowledge-agnostic data augmentation. Subsequently, we propose a fine-grained relation learning prototype to mine critical information in forgeries through instance and local similarity-aware losses. Moreover, we design a novel progressive learning controller to guide the model to focus on principal feature components, enabling it to learn critical forgery features in a coarse-to-fine manner. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art forgery detection performance under various challenging evaluation settings.
IStego100K: Large-scale Image Steganalysis Dataset
Nov 13, 2019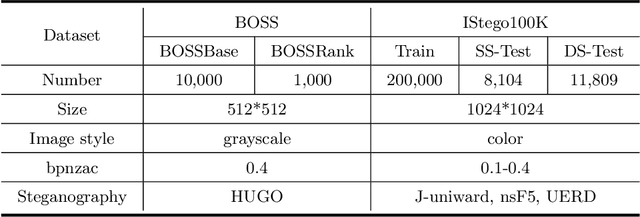
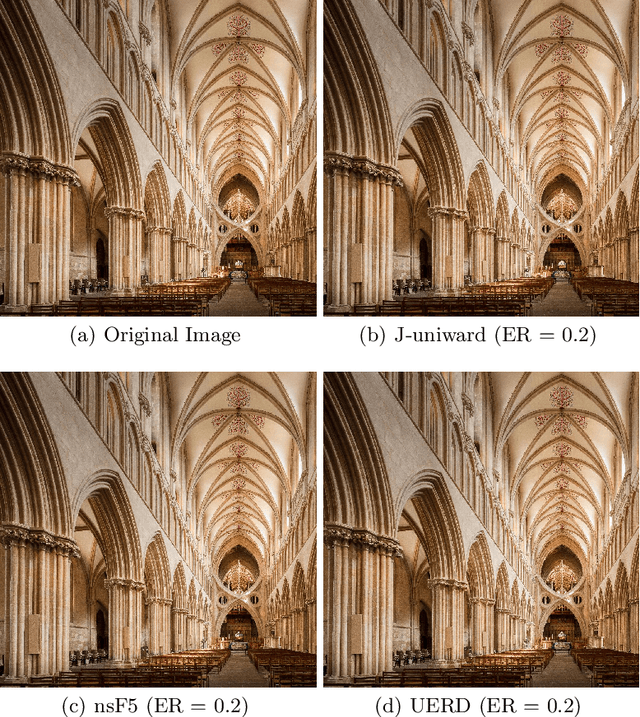

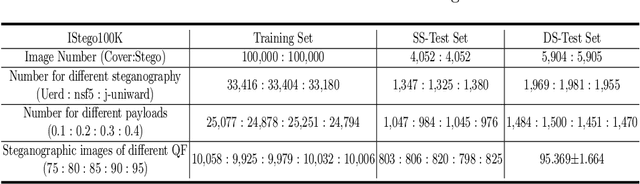
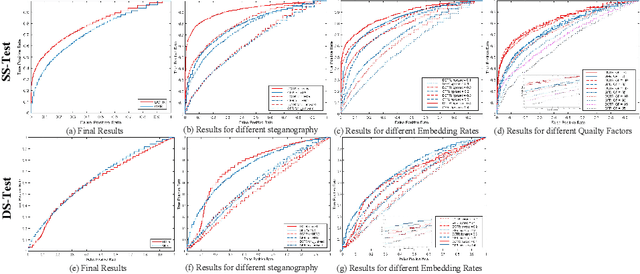
Abstract:In order to promote the rapid development of image steganalysis technology, in this paper, we construct and release a multivariable large-scale image steganalysis dataset called IStego100K. It contains 208,104 images with the same size of 1024*1024. Among them, 200,000 images (100,000 cover-stego image pairs) are divided as the training set and the remaining 8,104 as testing set. In addition, we hope that IStego100K can help researchers further explore the development of universal image steganalysis algorithms, so we try to reduce limits on the images in IStego100K. For each image in IStego100K, the quality factors is randomly set in the range of 75-95, the steganographic algorithm is randomly selected from three well-known steganographic algorithms, which are J-uniward, nsF5 and UERD, and the embedding rate is also randomly set to be a value of 0.1-0.4. In addition, considering the possible mismatch between training samples and test samples in real environment, we add a test set (DS-Test) whose source of samples are different from the training set. We hope that this test set can help to evaluate the robustness of steganalysis algorithms. We tested the performance of some latest steganalysis algorithms on IStego100K, with specific results and analysis details in the experimental part. We hope that the IStego100K dataset will further promote the development of universal image steganalysis technology. The description of IStego100K and instructions for use can be found at https://github.com/YangzlTHU/IStego100K
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge