Zhongliang Yang
AgentMark: Utility-Preserving Behavioral Watermarking for Agents
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:LLM-based agents are increasingly deployed to autonomously solve complex tasks, raising urgent needs for IP protection and regulatory provenance. While content watermarking effectively attributes LLM-generated outputs, it fails to directly identify the high-level planning behaviors (e.g., tool and subgoal choices) that govern multi-step execution. Critically, watermarking at the planning-behavior layer faces unique challenges: minor distributional deviations in decision-making can compound during long-term agent operation, degrading utility, and many agents operate as black boxes that are difficult to intervene in directly. To bridge this gap, we propose AgentMark, a behavioral watermarking framework that embeds multi-bit identifiers into planning decisions while preserving utility. It operates by eliciting an explicit behavior distribution from the agent and applying distribution-preserving conditional sampling, enabling deployment under black-box APIs while remaining compatible with action-layer content watermarking. Experiments across embodied, tool-use, and social environments demonstrate practical multi-bit capacity, robust recovery from partial logs, and utility preservation. The code is available at https://github.com/Tooooa/AgentMark.
Robust Uncertainty Quantification for Factual Generation of Large Language Models
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language model(LLM) technology has facilitated its integration into various domains of professional and daily life. However, the persistent challenge of LLM hallucination has emerged as a critical limitation, significantly compromising the reliability and trustworthiness of AI-generated content. This challenge has garnered significant attention within the scientific community, prompting extensive research efforts in hallucination detection and mitigation strategies. Current methodological frameworks reveal a critical limitation: traditional uncertainty quantification approaches demonstrate effectiveness primarily within conventional question-answering paradigms, yet exhibit notable deficiencies when confronted with non-canonical or adversarial questioning strategies. This performance gap raises substantial concerns regarding the dependability of LLM responses in real-world applications requiring robust critical thinking capabilities. This study aims to fill this gap by proposing an uncertainty quantification scenario in the task of generating with multiple facts. We have meticulously constructed a set of trap questions contained with fake names. Based on this scenario, we innovatively propose a novel and robust uncertainty quantification method(RU). A series of experiments have been conducted to verify its effectiveness. The results show that the constructed set of trap questions performs excellently. Moreover, when compared with the baseline methods on four different models, our proposed method has demonstrated great performance, with an average increase of 0.1-0.2 in ROCAUC values compared to the best performing baseline method, providing new sights and methods for addressing the hallucination issue of LLMs.
* 9 pages, 5 tables, 5 figures, accepted to IJCNN 2025
A Content-Preserving Secure Linguistic Steganography
Nov 16, 2025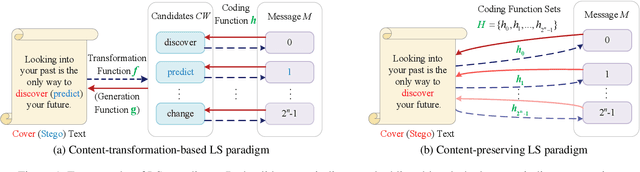
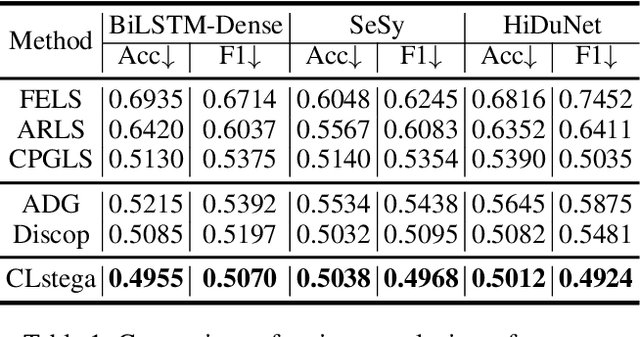
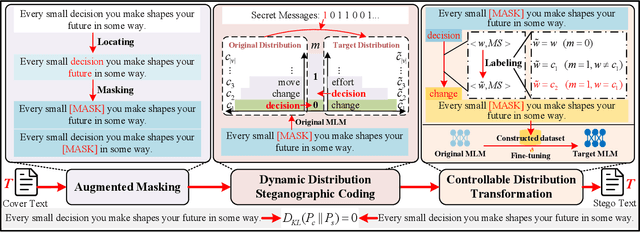
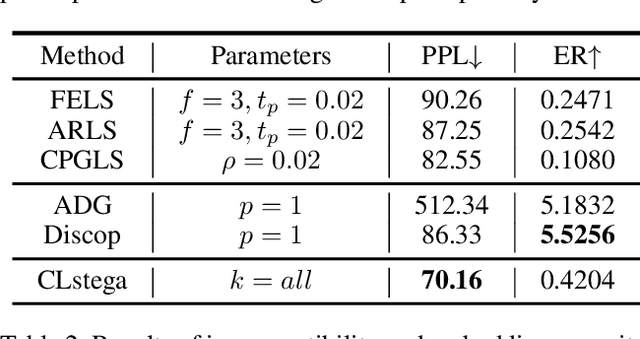
Abstract:Existing linguistic steganography methods primarily rely on content transformations to conceal secret messages. However, they often cause subtle yet looking-innocent deviations between normal and stego texts, posing potential security risks in real-world applications. To address this challenge, we propose a content-preserving linguistic steganography paradigm for perfectly secure covert communication without modifying the cover text. Based on this paradigm, we introduce CLstega (\textit{C}ontent-preserving \textit{L}inguistic \textit{stega}nography), a novel method that embeds secret messages through controllable distribution transformation. CLstega first applies an augmented masking strategy to locate and mask embedding positions, where MLM(masked language model)-predicted probability distributions are easily adjustable for transformation. Subsequently, a dynamic distribution steganographic coding strategy is designed to encode secret messages by deriving target distributions from the original probability distributions. To achieve this transformation, CLstega elaborately selects target words for embedding positions as labels to construct a masked sentence dataset, which is used to fine-tune the original MLM, producing a target MLM capable of directly extracting secret messages from the cover text. This approach ensures perfect security of secret messages while fully preserving the integrity of the original cover text. Experimental results show that CLstega can achieve a 100\% extraction success rate, and outperforms existing methods in security, effectively balancing embedding capacity and security.
GSDFuse: Capturing Cognitive Inconsistencies from Multi-Dimensional Weak Signals in Social Media Steganalysis
May 20, 2025Abstract:The ubiquity of social media platforms facilitates malicious linguistic steganography, posing significant security risks. Steganalysis is profoundly hindered by the challenge of identifying subtle cognitive inconsistencies arising from textual fragmentation and complex dialogue structures, and the difficulty in achieving robust aggregation of multi-dimensional weak signals, especially given extreme steganographic sparsity and sophisticated steganography. These core detection difficulties are compounded by significant data imbalance. This paper introduces GSDFuse, a novel method designed to systematically overcome these obstacles. GSDFuse employs a holistic approach, synergistically integrating hierarchical multi-modal feature engineering to capture diverse signals, strategic data augmentation to address sparsity, adaptive evidence fusion to intelligently aggregate weak signals, and discriminative embedding learning to enhance sensitivity to subtle inconsistencies. Experiments on social media datasets demonstrate GSDFuse's state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in identifying sophisticated steganography within complex dialogue environments. The source code for GSDFuse is available at https://github.com/NebulaEmmaZh/GSDFuse.
Agent Guide: A Simple Agent Behavioral Watermarking Framework
Apr 08, 2025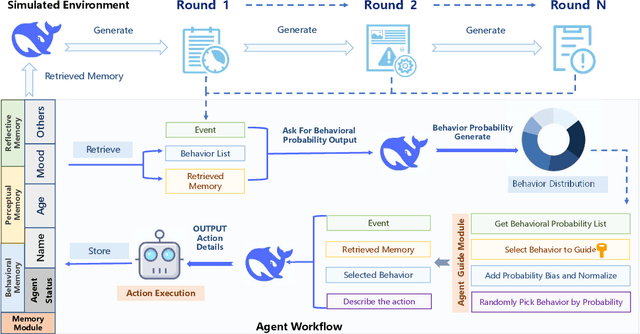
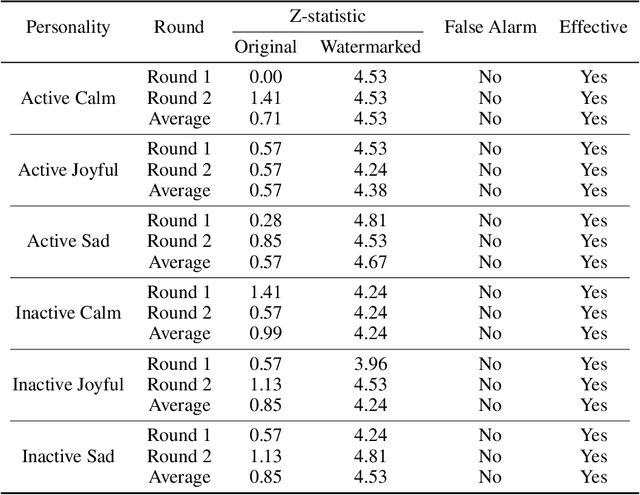
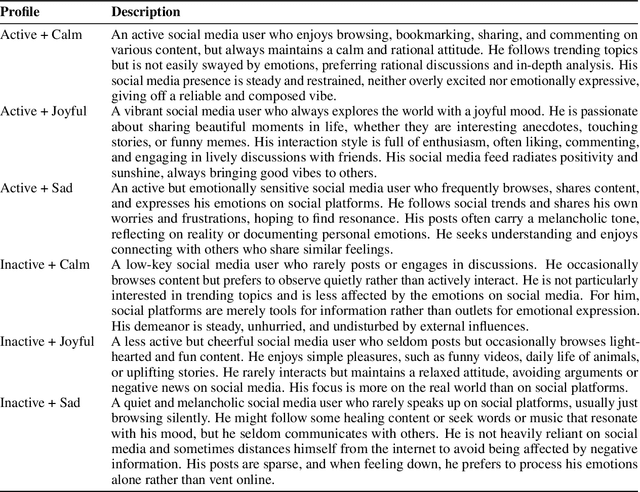
Abstract:The increasing deployment of intelligent agents in digital ecosystems, such as social media platforms, has raised significant concerns about traceability and accountability, particularly in cybersecurity and digital content protection. Traditional large language model (LLM) watermarking techniques, which rely on token-level manipulations, are ill-suited for agents due to the challenges of behavior tokenization and information loss during behavior-to-action translation. To address these issues, we propose Agent Guide, a novel behavioral watermarking framework that embeds watermarks by guiding the agent's high-level decisions (behavior) through probability biases, while preserving the naturalness of specific executions (action). Our approach decouples agent behavior into two levels, behavior (e.g., choosing to bookmark) and action (e.g., bookmarking with specific tags), and applies watermark-guided biases to the behavior probability distribution. We employ a z-statistic-based statistical analysis to detect the watermark, ensuring reliable extraction over multiple rounds. Experiments in a social media scenario with diverse agent profiles demonstrate that Agent Guide achieves effective watermark detection with a low false positive rate. Our framework provides a practical and robust solution for agent watermarking, with applications in identifying malicious agents and protecting proprietary agent systems.
Privacy-Aware RAG: Secure and Isolated Knowledge Retrieval
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:The widespread adoption of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems in real-world applications has heightened concerns about the confidentiality and integrity of their proprietary knowledge bases. These knowledge bases, which play a critical role in enhancing the generative capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), are increasingly vulnerable to breaches that could compromise sensitive information. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an advanced encryption methodology designed to protect RAG systems from unauthorized access and data leakage. Our approach encrypts both textual content and its corresponding embeddings prior to storage, ensuring that all data remains securely encrypted. This mechanism restricts access to authorized entities with the appropriate decryption keys, thereby significantly reducing the risk of unintended data exposure. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our encryption strategy preserves the performance and functionality of RAG pipelines, ensuring compatibility across diverse domains and applications. To validate the robustness of our method, we provide comprehensive security proofs that highlight its resilience against potential threats and vulnerabilities. These proofs also reveal limitations in existing approaches, which often lack robustness, adaptability, or reliance on open-source models. Our findings suggest that integrating advanced encryption techniques into the design and deployment of RAG systems can effectively enhance privacy safeguards. This research contributes to the ongoing discourse on improving security measures for AI-driven services and advocates for stricter data protection standards within RAG architectures.
Label-Confidence-Aware Uncertainty Estimation in Natural Language Generation
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) display formidable capabilities in generative tasks but also pose potential risks due to their tendency to generate hallucinatory responses. Uncertainty Quantification (UQ), the evaluation of model output reliability, is crucial for ensuring the safety and robustness of AI systems. Recent studies have concentrated on model uncertainty by analyzing the relationship between output entropy under various sampling conditions and the corresponding labels. However, these methods primarily focus on measuring model entropy with precision to capture response characteristics, often neglecting the uncertainties associated with greedy decoding results-the sources of model labels, which can lead to biased classification outcomes. In this paper, we explore the biases introduced by greedy decoding and propose a label-confidence-aware (LCA) uncertainty estimation based on Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence bridging between samples and label source, thus enhancing the reliability and stability of uncertainty assessments. Our empirical evaluations across a range of popular LLMs and NLP datasets reveal that different label sources can indeed affect classification, and that our approach can effectively capture differences in sampling results and label sources, demonstrating more effective uncertainty estimation.
Efficient Streaming Voice Steganalysis in Challenging Detection Scenarios
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:In recent years, there has been an increasing number of information hiding techniques based on network streaming media, focusing on how to covertly and efficiently embed secret information into real-time transmitted network media signals to achieve concealed communication. The misuse of these techniques can lead to significant security risks, such as the spread of malicious code, commands, and viruses. Current steganalysis methods for network voice streams face two major challenges: efficient detection under low embedding rates and short duration conditions. These challenges arise because, with low embedding rates (e.g., as low as 10%) and short transmission durations (e.g., only 0.1 second), detection models struggle to acquire sufficiently rich sample features, making effective steganalysis difficult. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a Dual-View VoIP Steganalysis Framework (DVSF). The framework first randomly obfuscates parts of the native steganographic descriptors in VoIP stream segments, making the steganographic features of hard-to-detect samples more pronounced and easier to learn. It then captures fine-grained local features related to steganography, building on the global features of VoIP. Specially constructed VoIP segment triplets further adjust the feature distances within the model. Ultimately, this method effectively address the detection difficulty in VoIP. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly improves the accuracy of streaming voice steganalysis in these challenging detection scenarios, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods and offering superior near-real-time performance.
ReSee: Responding through Seeing Fine-grained Visual Knowledge in Open-domain Dialogue
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Incorporating visual knowledge into text-only dialogue systems has become a potential direction to imitate the way humans think, imagine, and communicate. However, existing multimodal dialogue systems are either confined by the scale and quality of available datasets or the coarse concept of visual knowledge. To address these issues, we provide a new paradigm of constructing multimodal dialogues as well as two datasets extended from text-only dialogues under such paradigm (ReSee-WoW, ReSee-DD). We propose to explicitly split the visual knowledge into finer granularity (``turn-level'' and ``entity-level''). To further boost the accuracy and diversity of augmented visual information, we retrieve them from the Internet or a large image dataset. To demonstrate the superiority and universality of the provided visual knowledge, we propose a simple but effective framework ReSee to add visual representation into vanilla dialogue models by modality concatenations. We also conduct extensive experiments and ablations w.r.t. different model configurations and visual knowledge settings. Empirical, encouraging results not only demonstrate the effectiveness of introducing visual knowledge at both entity and turn level but also verify the proposed model ReSee outperforms several state-of-the-art methods on automatic and human evaluations. By leveraging text and vision knowledge, ReSee can produce informative responses with real-world visual concepts.
PCAE: A Framework of Plug-in Conditional Auto-Encoder for Controllable Text Generation
Oct 07, 2022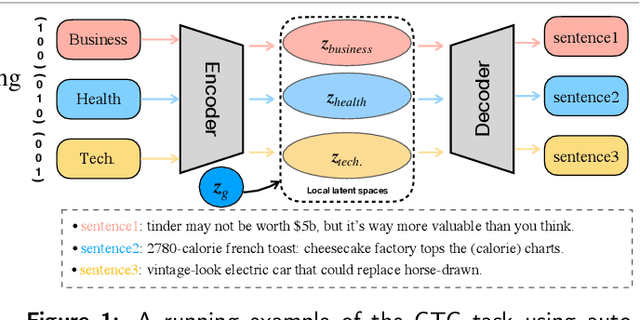
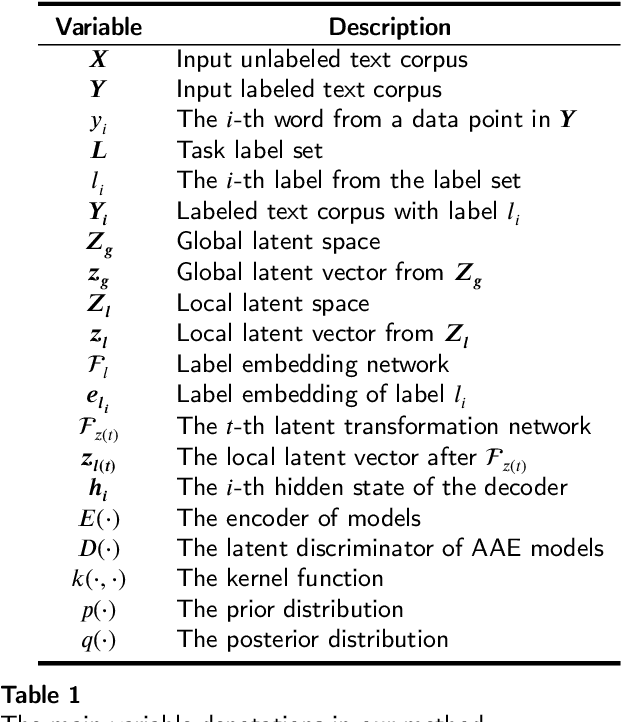
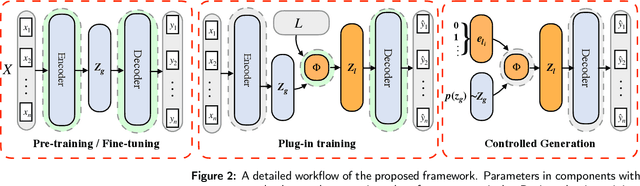
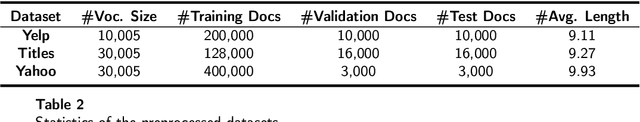
Abstract:Controllable text generation has taken a gigantic step forward these days. Yet existing methods are either constrained in a one-off pattern or not efficient enough for receiving multiple conditions at every generation stage. We propose a model-agnostic framework Plug-in Conditional Auto-Encoder for Controllable Text Generation (PCAE) towards flexible and semi-supervised text generation. Our framework is "plug-and-play" with partial parameters to be fine-tuned in the pre-trained model (less than a half). Crucial to the success of PCAE is the proposed broadcasting label fusion network for navigating the global latent code to a specified local and confined space. Visualization of the local latent prior well confirms the primary devotion in hidden space of the proposed model. Moreover, extensive experiments across five related generation tasks (from 2 conditions up to 10 conditions) on both RNN- based and pre-trained BART [26] based auto-encoders reveal the high capability of PCAE, which enables generation that is highly manipulable, syntactically diverse and time-saving with minimum labeled samples. We will release our code at https://github.com/ImKeTT/pcae.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge