Weiping Shi
Fellow, IEEE
STAR-RIS-UAV Aided Coordinated Multipoint Cellular System for Multi-user Networks
May 22, 2023Abstract:Different with conventional reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), simultaneous transmitting and reflecting RIS (STAR-RIS) can reflect and transmit the signals to the receiver. In this paper, to serve more ground users and increase the deployment flexibility, we investigate an unmanned aerial vehicle equipped with a STAR-RIS (STAR-RIS-UAV) aided wireless communications for multi-user networks. Energy splitting (ES) and mode switching (MS) protocols are considered to control the reflection and transmission coefficients of STAR-RIS elements. To maximize the sum rate of the STAR-RIS-UAV aided coordinated multipoint cellular system for multi-user networks, the corresponding beamforming vectors as well as transmitted and reflected coefficients matrices are optimized. Specifically, instead of adopting the alternating optimization, we design an iteration method to optimize all variables for both ES and MS protocols at the same time. Simulation results reveal that STAR-RIS-UAV aided wireless communication system has a much higher sum rate than the system with conventional RIS or without RIS. Furthermore, the proposed structure is more flexible than a fixed STAR-RIS and could greatly promote the sum rate.
Precoding and Beamforming Design for Intelligent Reconfigurable Surface-Aided Hybrid Secure Spatial Modulation
Feb 15, 2023Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is an emerging technology for wireless communication composed of a large number of low-cost passive devices with reconfigurable parameters, which can reflect signals with a certain phase shift and is capable of building programmable communication environment. In this paper, to avoid the high hardware cost and energy consumption in spatial modulation (SM), an IRS-aided hybrid secure SM (SSM) system with a hybrid precoder is proposed. To improve the security performance, we formulate an optimization problem to maximize the secrecy rate (SR) by jointly optimizing the beamforming at IRS and hybrid precoding at the transmitter. Considering that the SR has no closed form expression, an approximate SR (ASR) expression is derived as the objective function. To improve the SR performance, three IRS beamforming methods, called IRS alternating direction method of multipliers (IRS-ADMM), IRS block coordinate ascend (IRS-BCA) and IRS semi-definite relaxation (IRS-SDR), are proposed. As for the hybrid precoding design, approximated secrecy rate-successive convex approximation (ASR-SCA) method and cut-off rate-gradient ascend (COR-GA) method are proposed. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed IRS-SDR and IRS-ADMM beamformers harvest substantial SR performance gains over IRS-BCA. Particularly, the proposed IRS-ADMM and IRS-BCA are of low-complexity at the expense of a little performance loss compared with IRS-SDR. For hybrid precoding, the proposed ASR-SCA performs better than COR-GA in the high transmit power region.
Enhanced-rate Iterative Beamformers for Active IRS-assisted Wireless Communications
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:Compared to passive intelligent reflecting surface (IRS), active IRS is viewed as a more efficient promising technique to combat the double-fading impact in IRS-aided wireless network. In this paper, in order to boost the achievable rate of user in such a wireless network, three enhanced-rate iterative beamforming methods are proposed by designing the amplifying factors and the corresponding phases at active IRS. The first method, called generalized maximum ratio reflection (GMRR), is presented with a closed-form expression, which is motivated by the maximum ratio combing. To further improve rate, maximize the simplified signal-to-noise ratio (Max-SSNR) is designed by omitting the cross-term in the definition of rate. Using the Rayleigh-Ritz (RR) theorem and the fractional programming (FP), two enhanced methods, Max-SSNR-RR and Max-SSNR-FP are proposed to iteratively optimize the norm of beamforming vector and its associated normalized vector. Simulation results indicate that the proposed three methods make an obvious rate enhancement over Max-reflecting signal-to-noise ratio (RSNR) and passive IRS, and are in increasing order of rate performance as follows: GMRR, Max-SSNR-RR, and Max-SSNR-FP.
Power Allocation for IRS-aided Two-way Decode-and-Forward Relay Wireless Network
Mar 26, 2022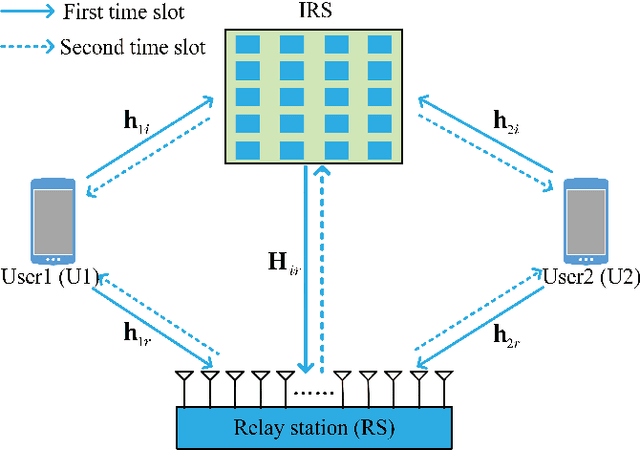

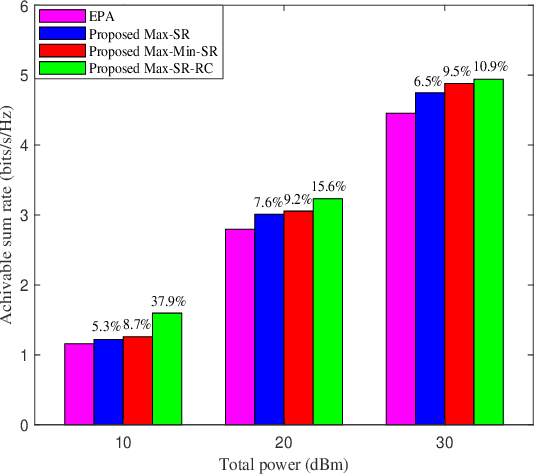
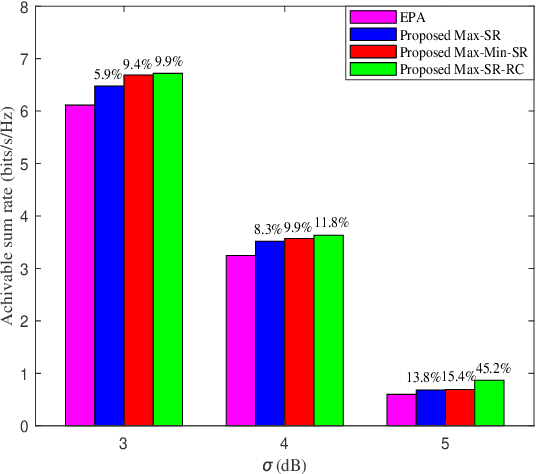
Abstract:In this paper, an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-aided two-way decode-and-forward (DF) relay wireless network is considered, where two users exchange information via IRS and DF relay. To enhance the sum rate performance, three power allocation (PA) strategies are proposed. Firstly, a method of maximizing sum rate (Max-SR) is proposed to jointly optimize the PA factors of user U1, user U2 and relay station (RS). To further improve the sum rate performance, two high-performance schemes, namely maximizing minimum sum rate (Max-Min-SR) and maximizing sum rate with rate constraint (Max-SR-RC), are presented. Simulation results show that the proposed three methods outperform the equal power allocation (EPA) method in terms of sum rate performance. In particular, the highest performance gain achieved by Max-SR-RC method is up to 45.2% over EPA. Furthermore, it is verified that the total power and random shadow variable X{\sigma} have a substantial impact on the sum rate performance.
High-performance Estimation of Jamming Covariance Matrix for IRS-aided Directional Modulation Network with a Malicious Attacker
Oct 22, 2021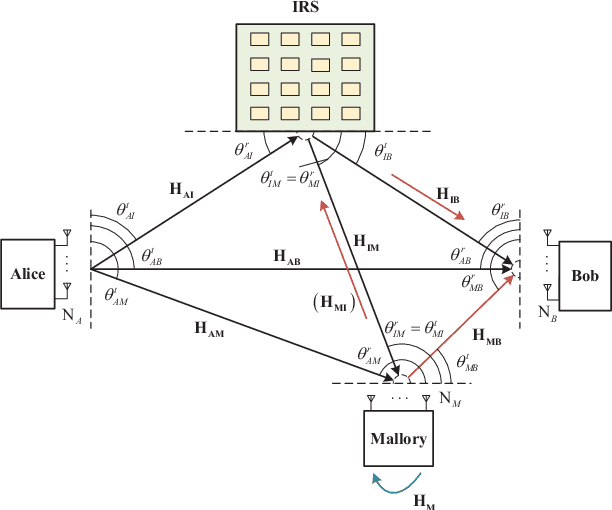
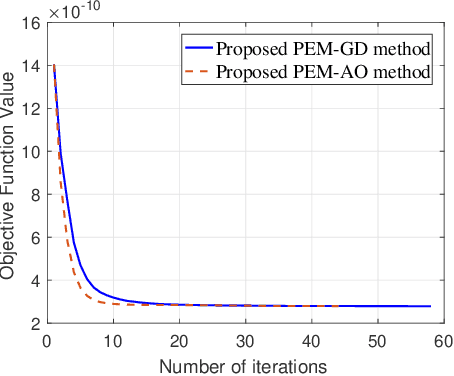
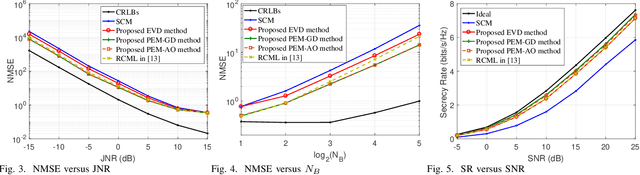
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the anti-jamming problem of a directional modulation (DM) system with the aid of intelligent reflecting surface (IRS). As an efficient tool to combat malicious jamming, receive beamforming (RBF) is usually designed to be on null-space of jamming channel or covariance matrix from Mallory to Bob. Thus, it is very necessary to estimate the receive jamming covariance matrix (JCM) at Bob. To achieve a precise JCM estimate, three JCM estimation methods, including eigenvalue decomposition (EVD), parametric estimation method by gradient descend (PEM-GD) and parametric estimation method by alternating optimization (PEM-AO), are proposed. Here, the proposed EVD is under rank-2 constraint of JCM. The PEM-GD method fully explores the structure features of JCM and the PEM-AO is to decrease the computational complexity of the former via dimensionality reduction. The simulation results show that in low and medium jamming-noise ratio (JNR) regions, the proposed three methods perform better than the existing sample covariance matrix method. The proposed PEM-GD and PEM-AO outperform EVD method and existing clutter and disturbance covariance estimator RCML.
Beamforming and Transmit Power Design for Intelligent Reconfigurable Surface-aided Secure Spatial Modulation
Jun 07, 2021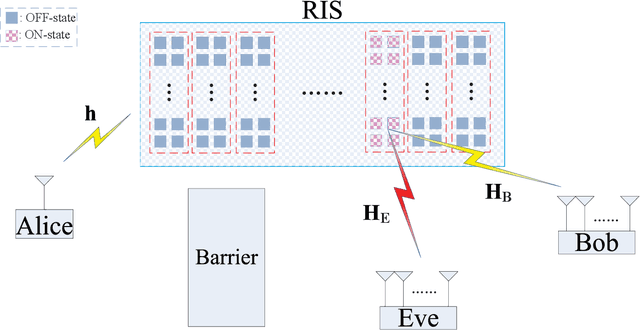
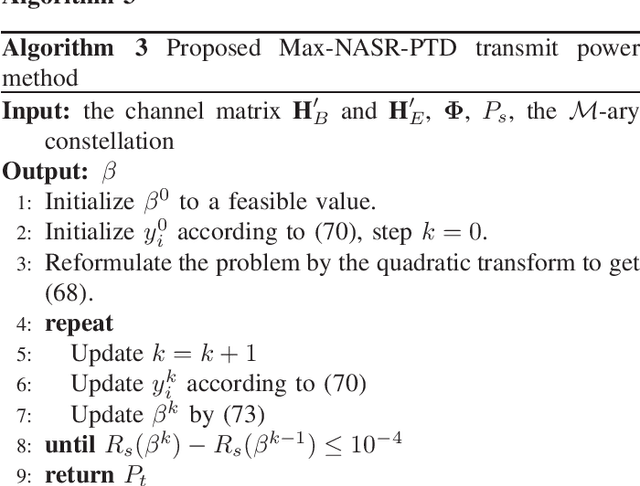
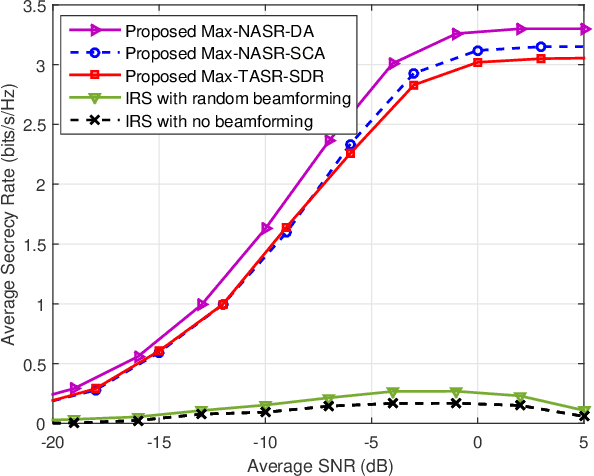
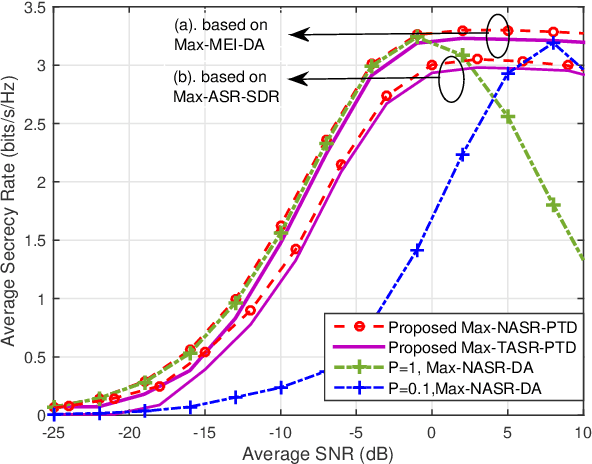
Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is a promising solution to build a programmable wireless environment for future communication systems, in which the reflector elements steer the incident signal in fully customizable ways by passive beamforming. In this paper, an IRS-aided secure spatial modulation (SM) is proposed, where the IRS perform passive beamforming and information transfer simultaneously by adjusting the on-off states of the reflecting elements. We formulate an optimization problem to maximize the average secrecy rate (SR) by jointly optimizing the passive beamforming at IRS and the transmit power at transmitter under the consideration that the direct pathes channels from transmitter to receivers are obstructed by obstacles. As the expression of SR is complex, we derive a newly fitting expression (NASR) for the expression of traditional approximate SR (TASR), which has simpler closed-form and more convenient for subsequent optimization. Based on the above two fitting expressions, three beamforming methods, called maximizing NASR via successive convex approximation (Max-NASR-SCA), maximizing NASR via dual ascent (Max-NASR-DA) and maximizing TASR via semi-definite relaxation (Max-TASR-SDR) are proposed to improve the SR performance. Additionally, two transmit power design (TPD) methods are proposed based on the above two approximate SR expressions, called Max-NASR-TPD and Max-TASR-TPD. Simulation results show that the proposed Max-NASR-DA and Max-NASR-SCA IRS beamformers harvest substantial SR performance gains over Max-TASR-SDR. For TPD, the proposed Max-NASR-TPD performs better than Max-TASR-TPD. Particularly, the Max-NASR-TPD has a closed-form solution.
Global Optimization for IRS-Assisted Wireless Communications: from Physics and Electromagnetic Perspectives
May 13, 2021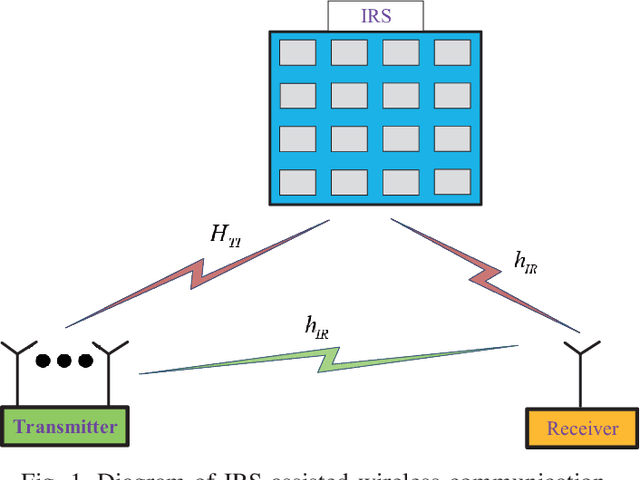

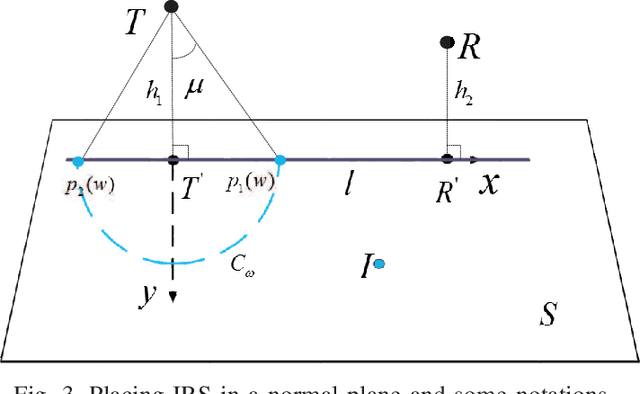
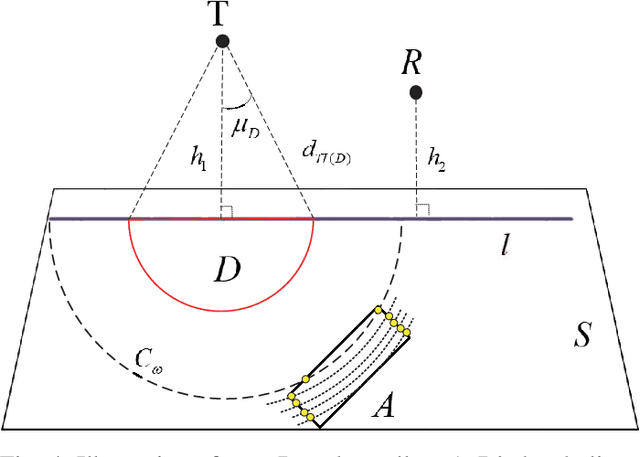
Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) are envisioned to be a disruptive wireless communication technique that is capable of reconfiguring the wireless propagation environment. In this paper, we study a far-field IRS-assisted multiple-input single-output (MISO) communication system operating in free space. To maximize the received power of the receiver from the physics and electromagnetic nature point of view, an optimization, including beamforming of the transmitter, phase shifts of the IRS, orientation and position of the IRS is formulated and solved. After exploiting the property of line-of-sight (LoS), we derive closed-form solutions of beamforming and phase shifts. For the non-trivial IRS position optimization problem in arbitrary three-dimensional space, a dimensional-reducing theory is proved, which is useful to reduce the complexity of search method. The simulation results show that the proposed closed-form beamforming and phase shifts are near-optimal solutions. Besides, the IRS significantly enhances the performance of the communication system when it is deployed at the optimal position.
Communication-efficient Coordinated RSS-based Distributed Passive Localization via Drone Cluster
Apr 01, 2021


Abstract:Recently, passive unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) localization has become popular due to mobility and convenience. In this paper, we consider a scenario of using distributed drone cluster to estimate the position of a passive emitter via received signal strength (RSS). First, a distributed majorizeminimization (DMM) RSS-based localization method is proposed. To accelerate its convergence, a tight upper bound of the objective function from the primary one is derived. Furthermore, to reduce communication overhead, a distributed estimation scheme using the Fisher information matrix (DEF) is presented, with only requiring one-round communication between edge UAVs and center UAV. Additionally, a local search solution is used as the initial value of DEF. Simulation results show that the proposed DMM performs better than the existing distributed Gauss-Newton method (DGN) in terms of root of mean square error (RMSE) under a limited low communication overhead constraint. Moreover, the proposed DEF performs much better than MM in terms of RMSE, but has a higher computational complexity than the latter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge