Wanglong Lu
Towards Biosignals-Free Autonomous Prosthetic Hand Control via Imitation Learning
Jun 10, 2025



Abstract:Limb loss affects millions globally, impairing physical function and reducing quality of life. Most traditional surface electromyographic (sEMG) and semi-autonomous methods require users to generate myoelectric signals for each control, imposing physically and mentally taxing demands. This study aims to develop a fully autonomous control system that enables a prosthetic hand to automatically grasp and release objects of various shapes using only a camera attached to the wrist. By placing the hand near an object, the system will automatically execute grasping actions with a proper grip force in response to the hand's movements and the environment. To release the object being grasped, just naturally place the object close to the table and the system will automatically open the hand. Such a system would provide individuals with limb loss with a very easy-to-use prosthetic control interface and greatly reduce mental effort while using. To achieve this goal, we developed a teleoperation system to collect human demonstration data for training the prosthetic hand control model using imitation learning, which mimics the prosthetic hand actions from human. Through training the model using only a few objects' data from one single participant, we have shown that the imitation learning algorithm can achieve high success rates, generalizing to more individuals and unseen objects with a variation of weights. The demonstrations are available at \href{https://sites.google.com/view/autonomous-prosthetic-hand}{https://sites.google.com/view/autonomous-prosthetic-hand}
TextDoctor: Unified Document Image Inpainting via Patch Pyramid Diffusion Models
Mar 06, 2025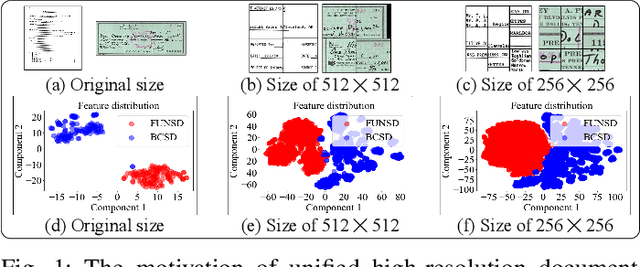

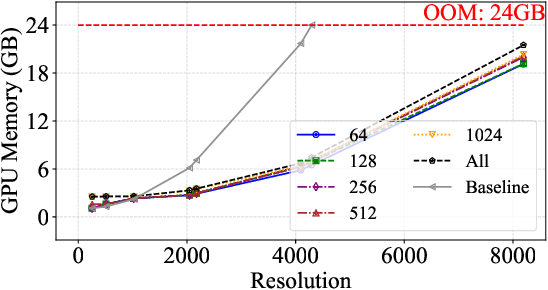
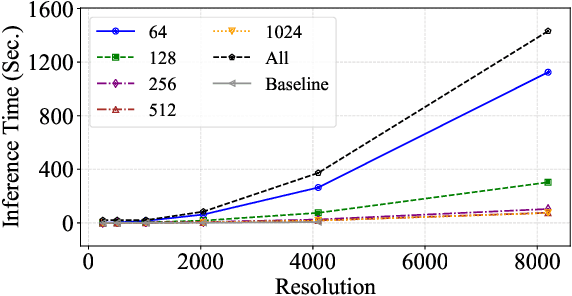
Abstract:Digital versions of real-world text documents often suffer from issues like environmental corrosion of the original document, low-quality scanning, or human interference. Existing document restoration and inpainting methods typically struggle with generalizing to unseen document styles and handling high-resolution images. To address these challenges, we introduce TextDoctor, a novel unified document image inpainting method. Inspired by human reading behavior, TextDoctor restores fundamental text elements from patches and then applies diffusion models to entire document images instead of training models on specific document types. To handle varying text sizes and avoid out-of-memory issues, common in high-resolution documents, we propose using structure pyramid prediction and patch pyramid diffusion models. These techniques leverage multiscale inputs and pyramid patches to enhance the quality of inpainting both globally and locally. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on seven public datasets validated that TextDoctor outperforms state-of-the-art methods in restoring various types of high-resolution document images.
Visual Style Prompt Learning Using Diffusion Models for Blind Face Restoration
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Blind face restoration aims to recover high-quality facial images from various unidentified sources of degradation, posing significant challenges due to the minimal information retrievable from the degraded images. Prior knowledge-based methods, leveraging geometric priors and facial features, have led to advancements in face restoration but often fall short of capturing fine details. To address this, we introduce a visual style prompt learning framework that utilizes diffusion probabilistic models to explicitly generate visual prompts within the latent space of pre-trained generative models. These prompts are designed to guide the restoration process. To fully utilize the visual prompts and enhance the extraction of informative and rich patterns, we introduce a style-modulated aggregation transformation layer. Extensive experiments and applications demonstrate the superiority of our method in achieving high-quality blind face restoration. The source code is available at \href{https://github.com/LonglongaaaGo/VSPBFR}{https://github.com/LonglongaaaGo/VSPBFR}.
* Published at Pattern Recognition; 13 pages, 11 figures
FACEMUG: A Multimodal Generative and Fusion Framework for Local Facial Editing
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Existing facial editing methods have achieved remarkable results, yet they often fall short in supporting multimodal conditional local facial editing. One of the significant evidences is that their output image quality degrades dramatically after several iterations of incremental editing, as they do not support local editing. In this paper, we present a novel multimodal generative and fusion framework for globally-consistent local facial editing (FACEMUG) that can handle a wide range of input modalities and enable fine-grained and semantic manipulation while remaining unedited parts unchanged. Different modalities, including sketches, semantic maps, color maps, exemplar images, text, and attribute labels, are adept at conveying diverse conditioning details, and their combined synergy can provide more explicit guidance for the editing process. We thus integrate all modalities into a unified generative latent space to enable multimodal local facial edits. Specifically, a novel multimodal feature fusion mechanism is proposed by utilizing multimodal aggregation and style fusion blocks to fuse facial priors and multimodalities in both latent and feature spaces. We further introduce a novel self-supervised latent warping algorithm to rectify misaligned facial features, efficiently transferring the pose of the edited image to the given latent codes. We evaluate our FACEMUG through extensive experiments and comparisons to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. The results demonstrate the superiority of FACEMUG in terms of editing quality, flexibility, and semantic control, making it a promising solution for a wide range of local facial editing tasks.
PromptRR: Diffusion Models as Prompt Generators for Single Image Reflection Removal
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Existing single image reflection removal (SIRR) methods using deep learning tend to miss key low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) differences in images, affecting their effectiveness in removing reflections. To address this problem, this paper proposes a novel prompt-guided reflection removal (PromptRR) framework that uses frequency information as new visual prompts for better reflection performance. Specifically, the proposed framework decouples the reflection removal process into the prompt generation and subsequent prompt-guided restoration. For the prompt generation, we first propose a prompt pre-training strategy to train a frequency prompt encoder that encodes the ground-truth image into LF and HF prompts. Then, we adopt diffusion models (DMs) as prompt generators to generate the LF and HF prompts estimated by the pre-trained frequency prompt encoder. For the prompt-guided restoration, we integrate specially generated prompts into the PromptFormer network, employing a novel Transformer-based prompt block to effectively steer the model toward enhanced reflection removal. The results on commonly used benchmarks show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches. The codes and models are available at https://github.com/TaoWangzj/PromptRR.
GRIG: Few-Shot Generative Residual Image Inpainting
Apr 24, 2023



Abstract:Image inpainting is the task of filling in missing or masked region of an image with semantically meaningful contents. Recent methods have shown significant improvement in dealing with large-scale missing regions. However, these methods usually require large training datasets to achieve satisfactory results and there has been limited research into training these models on a small number of samples. To address this, we present a novel few-shot generative residual image inpainting method that produces high-quality inpainting results. The core idea is to propose an iterative residual reasoning method that incorporates Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for feature extraction and Transformers for global reasoning within generative adversarial networks, along with image-level and patch-level discriminators. We also propose a novel forgery-patch adversarial training strategy to create faithful textures and detailed appearances. Extensive evaluations show that our method outperforms previous methods on the few-shot image inpainting task, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Restoring Vision in Hazy Weather with Hierarchical Contrastive Learning
Dec 22, 2022



Abstract:Image restoration under hazy weather condition, which is called single image dehazing, has been of significant interest for various computer vision applications. In recent years, deep learning-based methods have achieved success. However, existing image dehazing methods typically neglect the hierarchy of features in the neural network and fail to exploit their relationships fully. To this end, we propose an effective image dehazing method named Hierarchical Contrastive Dehazing (HCD), which is based on feature fusion and contrastive learning strategies. HCD consists of a hierarchical dehazing network (HDN) and a novel hierarchical contrastive loss (HCL). Specifically, the core design in the HDN is a Hierarchical Interaction Module, which utilizes multi-scale activation to revise the feature responses hierarchically. To cooperate with the training of HDN, we propose HCL which performs contrastive learning on hierarchically paired exemplars, facilitating haze removal. Extensive experiments on public datasets, RESIDE, HazeRD, and DENSE-HAZE, demonstrate that HCD quantitatively outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of PSNR, SSIM and achieves better visual quality.
Diverse facial inpainting guided by exemplars
Feb 15, 2022
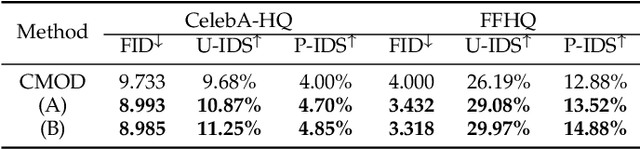
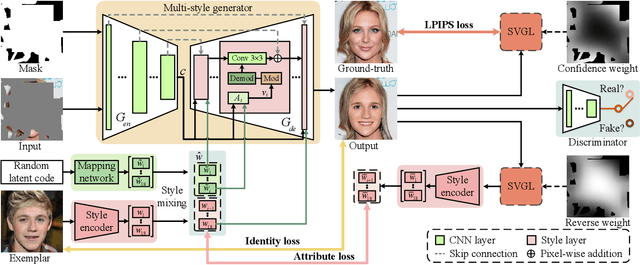
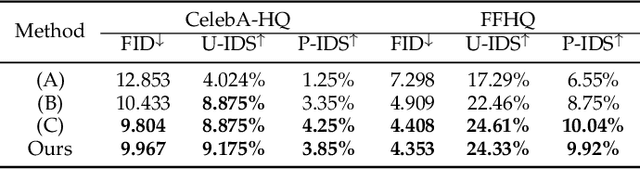
Abstract:Facial image inpainting is a task of filling visually realistic and semantically meaningful contents for missing or masked pixels in a face image. Although existing methods have made significant progress in achieving high visual quality, the controllable diversity of facial image inpainting remains an open problem in this field. This paper introduces EXE-GAN, a novel diverse and interactive facial inpainting framework, which can not only preserve the high-quality visual effect of the whole image but also complete the face image with exemplar-like facial attributes. The proposed facial inpainting is achieved based on generative adversarial networks by leveraging the global style of input image, the stochastic style, and the exemplar style of exemplar image. A novel attribute similarity metric is introduced to encourage networks to learn the style of facial attributes from the exemplar in a self-supervised way. To guarantee the natural transition across the boundary of inpainted regions, a novel spatial variant gradient backpropagation technique is designed to adjust the loss gradients based on the spatial location. A variety of experimental results and comparisons on public CelebA-HQ and FFHQ datasets are presented to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in terms of both the quality and diversity in facial inpainting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge