Vivek Kumar Singh
Colored Jones Polynomials and the Volume Conjecture
Feb 25, 2025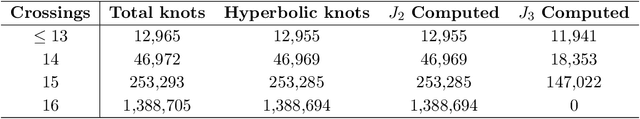
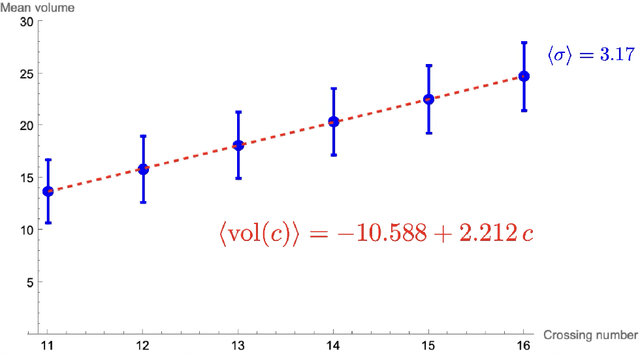
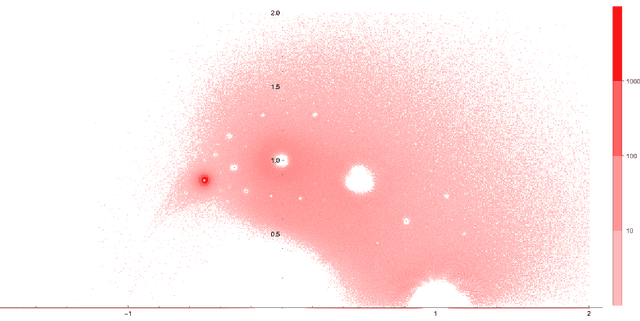
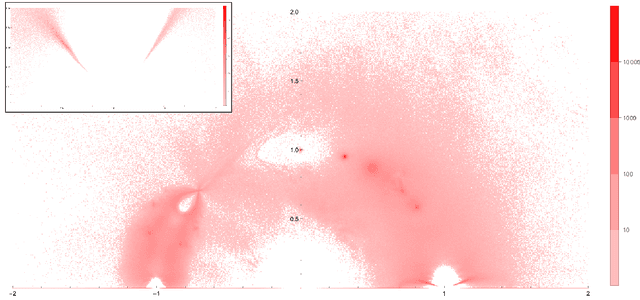
Abstract:Using the vertex model approach for braid representations, we compute polynomials for spin-1 placed on hyperbolic knots up to 15 crossings. These polynomials are referred to as 3-colored Jones polynomials or adjoint Jones polynomials. Training a subset of the data using a fully connected feedforward neural network, we predict the volume of the knot complement of hyperbolic knots from the adjoint Jones polynomial or its evaluations with 99.34% accuracy. A function of the adjoint Jones polynomial evaluated at the phase $q=e^{ 8 \pi i / 15 }$ predicts the volume with nearly the same accuracy as the neural network. From an analysis of 2-colored and 3-colored Jones polynomials, we conjecture the best phase for $n$-colored Jones polynomials, and use this hypothesis to motivate an improved statement of the volume conjecture. This is tested for knots for which closed form expressions for the $n$-colored Jones polynomial are known, and we show improved convergence to the volume.
A Hybrid Transformer-Sequencer approach for Age and Gender classification from in-wild facial images
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:The advancements in computer vision and image processing techniques have led to emergence of new application in the domain of visual surveillance, targeted advertisement, content-based searching, and human-computer interaction etc. Out of the various techniques in computer vision, face analysis, in particular, has gained much attention. Several previous studies have tried to explore different applications of facial feature processing for a variety of tasks, including age and gender classification. However, despite several previous studies having explored the problem, the age and gender classification of in-wild human faces is still far from the achieving the desired levels of accuracy required for real-world applications. This paper, therefore, attempts to bridge this gap by proposing a hybrid model that combines self-attention and BiLSTM approaches for age and gender classification problems. The proposed models performance is compared with several state-of-the-art model proposed so far. An improvement of approximately 10percent and 6percent over the state-of-the-art implementations for age and gender classification, respectively, are noted for the proposed model. The proposed model is thus found to achieve superior performance and is found to provide a more generalized learning. The model can, therefore, be applied as a core classification component in various image processing and computer vision problems.
* 22 pages
Breast Cancer Immunohistochemical Image Generation: a Benchmark Dataset and Challenge Review
May 05, 2023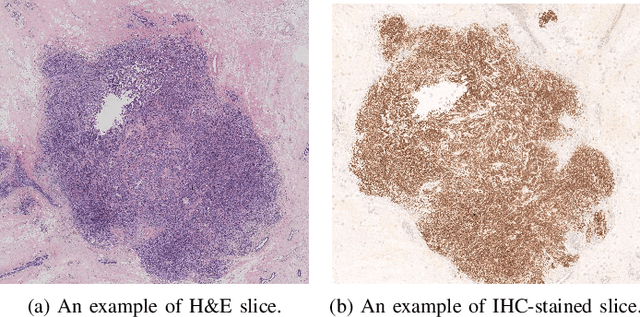
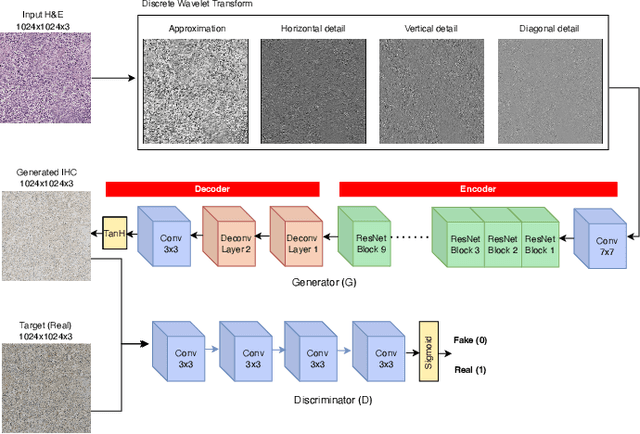
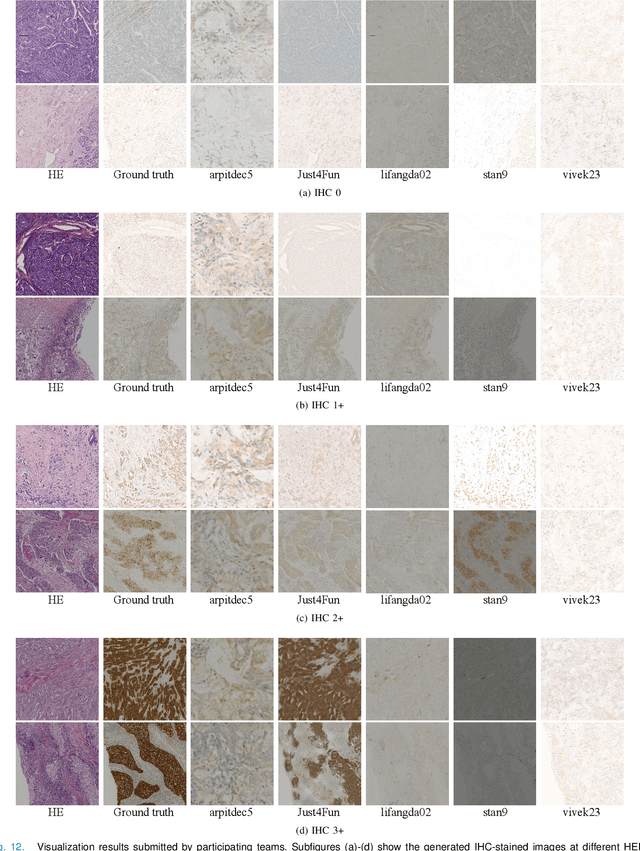
Abstract:For invasive breast cancer, immunohistochemical (IHC) techniques are often used to detect the expression level of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) in breast tissue to formulate a precise treatment plan. From the perspective of saving manpower, material and time costs, directly generating IHC-stained images from hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained images is a valuable research direction. Therefore, we held the breast cancer immunohistochemical image generation challenge, aiming to explore novel ideas of deep learning technology in pathological image generation and promote research in this field. The challenge provided registered H&E and IHC-stained image pairs, and participants were required to use these images to train a model that can directly generate IHC-stained images from corresponding H&E-stained images. We selected and reviewed the five highest-ranking methods based on their PSNR and SSIM metrics, while also providing overviews of the corresponding pipelines and implementations. In this paper, we further analyze the current limitations in the field of breast cancer immunohistochemical image generation and forecast the future development of this field. We hope that the released dataset and the challenge will inspire more scholars to jointly study higher-quality IHC-stained image generation.
Detection of Homophobia & Transphobia in Dravidian Languages: Exploring Deep Learning Methods
Apr 03, 2023Abstract:The increase in abusive content on online social media platforms is impacting the social life of online users. Use of offensive and hate speech has been making so-cial media toxic. Homophobia and transphobia constitute offensive comments against LGBT+ community. It becomes imperative to detect and handle these comments, to timely flag or issue a warning to users indulging in such behaviour. However, automated detection of such content is a challenging task, more so in Dravidian languages which are identified as low resource languages. Motivated by this, the paper attempts to explore applicability of different deep learning mod-els for classification of the social media comments in Malayalam and Tamil lan-guages as homophobic, transphobic and non-anti-LGBT+content. The popularly used deep learning models- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) using GloVe embedding and transformer-based learning models (Multilingual BERT and IndicBERT) are applied to the classification problem. Results obtained show that IndicBERT outperforms the other imple-mented models, with obtained weighted average F1-score of 0.86 and 0.77 for Malayalam and Tamil, respectively. Therefore, the present work confirms higher performance of IndicBERT on the given task in selected Dravidian languages.
Exploring Deep Learning Methods for Classification of SAR Images: Towards NextGen Convolutions via Transformers
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:Images generated by high-resolution SAR have vast areas of application as they can work better in adverse light and weather conditions. One such area of application is in the military systems. This study is an attempt to explore the suitability of current state-of-the-art models introduced in the domain of computer vision for SAR target classification (MSTAR). Since the application of any solution produced for military systems would be strategic and real-time, accuracy is often not the only criterion to measure its performance. Other important parameters like prediction time and input resiliency are equally important. The paper deals with these issues in the context of SAR images. Experimental results show that deep learning models can be suitably applied in the domain of SAR image classification with the desired performance levels.
* 6 pages, 9 figures
ICOS Protein Expression Segmentation: Can Transformer Networks Give Better Results?
Jun 23, 2022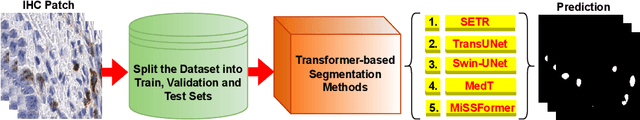
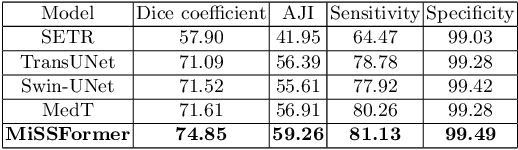
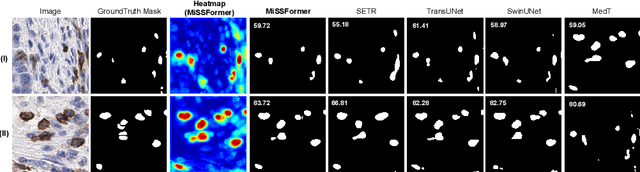
Abstract:Biomarkers identify a patients response to treatment. With the recent advances in artificial intelligence based on the Transformer networks, there is only limited research has been done to measure the performance on challenging histopathology images. In this paper, we investigate the efficacy of the numerous state-of-the-art Transformer networks for immune-checkpoint biomarker, Inducible Tcell COStimulator (ICOS) protein cell segmentation in colon cancer from immunohistochemistry (IHC) slides. Extensive and comprehensive experimental results confirm that MiSSFormer achieved the highest Dice score of 74.85% than the rest evaluated Transformer and Efficient U-Net methods.
Network-Agnostic Knowledge Transfer for Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 23, 2021
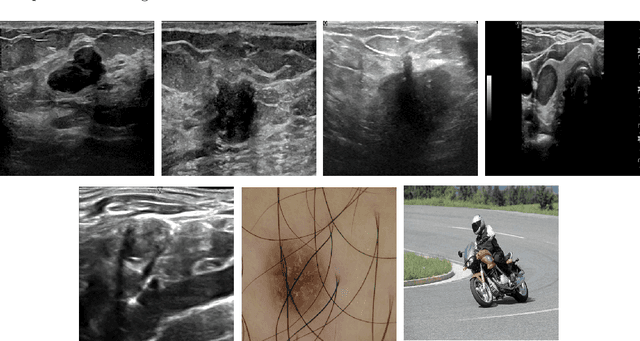
Abstract:Conventional transfer learning leverages weights of pre-trained networks, but mandates the need for similar neural architectures. Alternatively, knowledge distillation can transfer knowledge between heterogeneous networks but often requires access to the original training data or additional generative networks. Knowledge transfer between networks can be improved by being agnostic to the choice of network architecture and reducing the dependence on original training data. We propose a knowledge transfer approach from a teacher to a student network wherein we train the student on an independent transferal dataset, whose annotations are generated by the teacher. Experiments were conducted on five state-of-the-art networks for semantic segmentation and seven datasets across three imaging modalities. We studied knowledge transfer from a single teacher, combination of knowledge transfer and fine-tuning, and knowledge transfer from multiple teachers. The student model with a single teacher achieved similar performance as the teacher; and the student model with multiple teachers achieved better performance than the teachers. The salient features of our algorithm include: 1)no need for original training data or generative networks, 2) knowledge transfer between different architectures, 3) ease of implementation for downstream tasks by using the downstream task dataset as the transferal dataset, 4) knowledge transfer of an ensemble of models, trained independently, into one student model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is effective for knowledge transfer and easily tunable.
Adversarial Learning with Multiscale Features and Kernel Factorization for Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation
Jul 05, 2019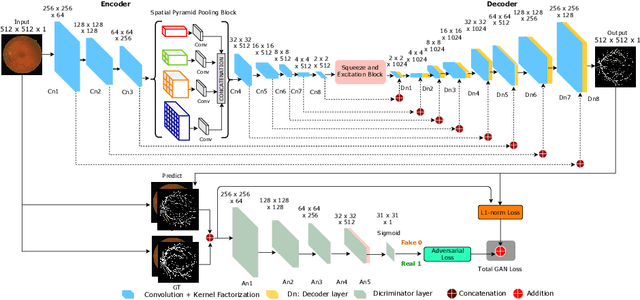
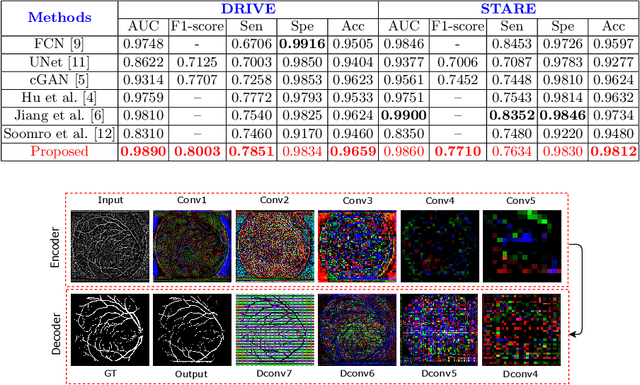
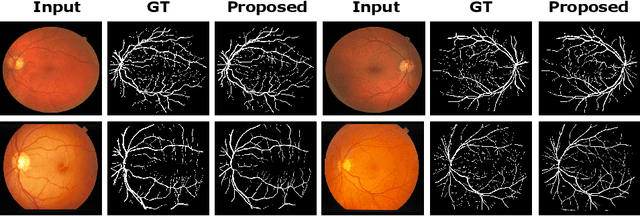
Abstract:In this paper, we propose an efficient blood vessel segmentation method for the eye fundus images using adversarial learning with multiscale features and kernel factorization. In the generator network of the adversarial framework, spatial pyramid pooling, kernel factorization and squeeze excitation block are employed to enhance the feature representation in spatial domain on different scales with reduced computational complexity. In turn, the discriminator network of the adversarial framework is formulated by combining convolutional layers with an additional squeeze excitation block to differentiate the generated segmentation mask from its respective ground truth. Before feeding the images to the network, we pre-processed them by using edge sharpening and Gaussian regularization to reach an optimized solution for vessel segmentation. The output of the trained model is post-processed using morphological operations to remove the small speckles of noise. The proposed method qualitatively and quantitatively outperforms state-of-the-art vessel segmentation methods using DRIVE and STARE datasets.
An Efficient Solution for Breast Tumor Segmentation and Classification in Ultrasound Images Using Deep Adversarial Learning
Jul 01, 2019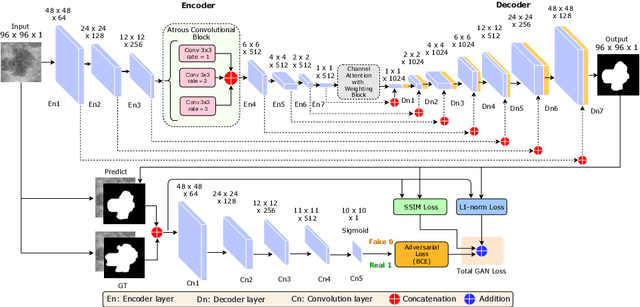
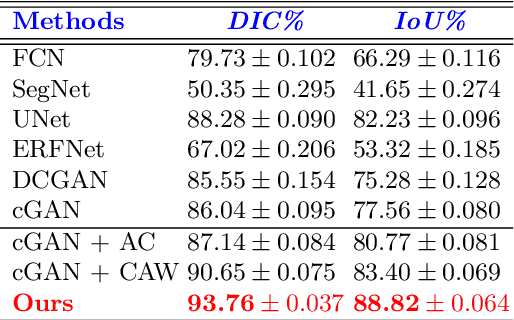
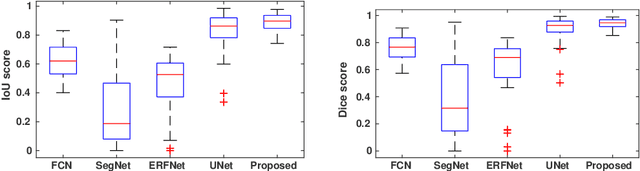
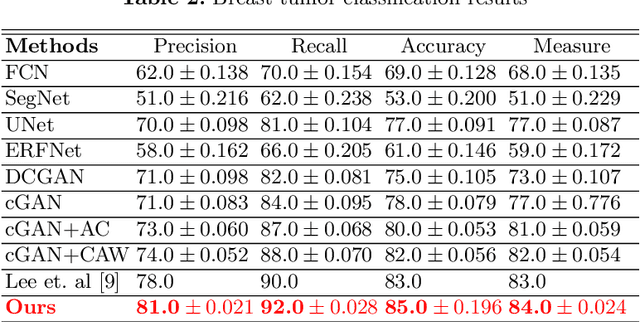
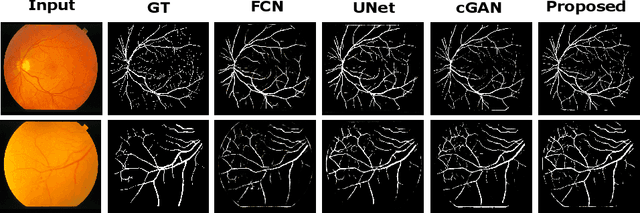
Abstract:This paper proposes an efficient solution for tumor segmentation and classification in breast ultrasound (BUS) images. We propose to add an atrous convolution layer to the conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) segmentation model to learn tumor features at different resolutions of BUS images. To automatically re-balance the relative impact of each of the highest level encoded features, we also propose to add a channel-wise weighting block in the network. In addition, the SSIM and L1-norm loss with the typical adversarial loss are used as a loss function to train the model. Our model outperforms the state-of-the-art segmentation models in terms of the Dice and IoU metrics, achieving top scores of 93.76% and 88.82%, respectively. In the classification stage, we show that few statistics features extracted from the shape of the boundaries of the predicted masks can properly discriminate between benign and malignant tumors with an accuracy of 85%$
MobileGAN: Skin Lesion Segmentation Using a Lightweight Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 01, 2019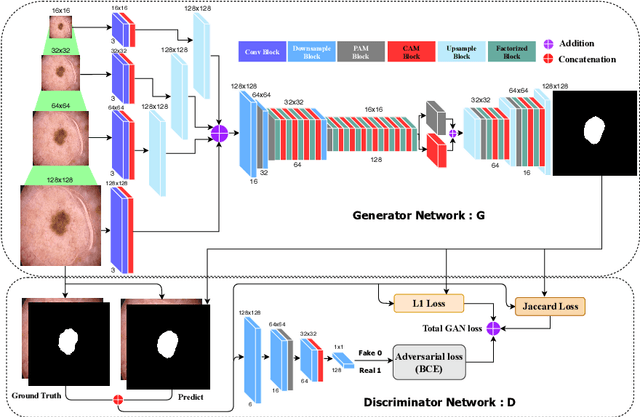
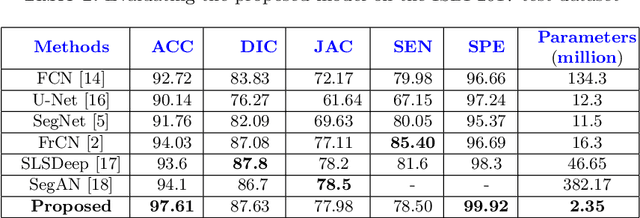
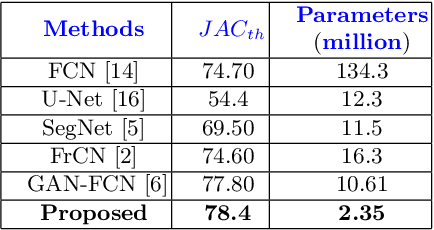
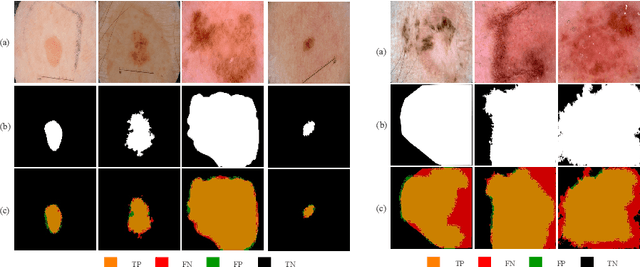
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic images is a challenge due to their blurry and irregular boundaries. Most of the segmentation approaches based on deep learning are time and memory consuming due to the hundreds of millions of parameters. Consequently, it is difficult to apply them to real dermatoscope devices with limited GPU and memory resources. In this paper, we propose a lightweight and efficient Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) model, called MobileGAN for skin lesion segmentation. More precisely, the MobileGAN combines 1D non-bottleneck factorization networks with position and channel attention modules in a GAN model. The proposed model is evaluated on the test dataset of the ISBI 2017 challenges and the validation dataset of ISIC 2018 challenges. Although the proposed network has only 2.35 millions of parameters, it is still comparable with the state-of-the-art. The experimental results show that our MobileGAN obtains comparable performance with an accuracy of 97.61%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge