Sylvie Chambon
CEASEFIRE: An AI-powered system for combatting illicit firearms trafficking
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Modern technologies have led illicit firearms trafficking to partially merge with cybercrime, while simultaneously permitting its off-line aspects to become more sophisticated. Law enforcement officers face difficult challenges that require hi-tech solutions. This article presents a real-world system, powered by advanced Artificial Intelligence, for facilitating them in their everyday work.
Improving Vehicle Re-Identification using CNN Latent Spaces: Metrics Comparison and Track-to-track Extension
Oct 21, 2019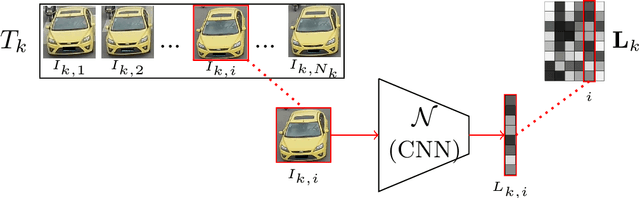
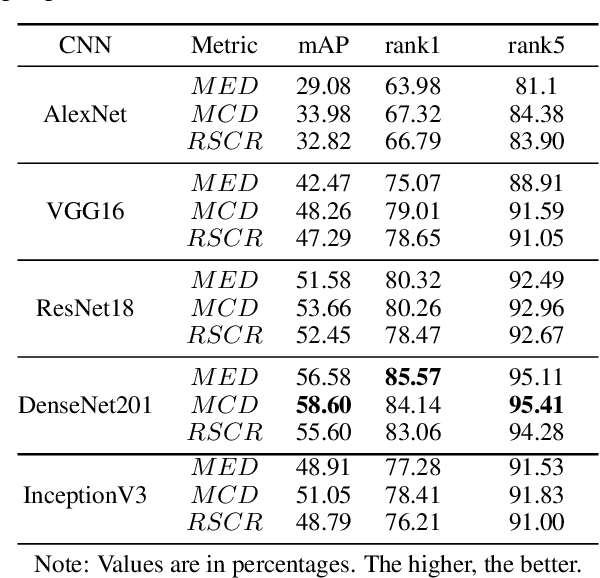
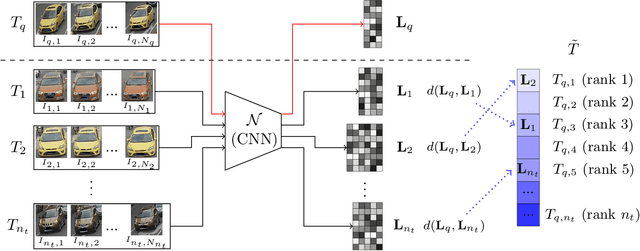
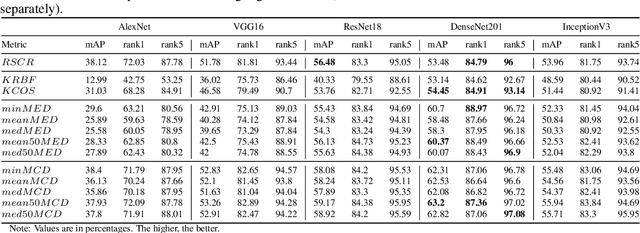
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of vehicle re-identification using distance comparison of images in CNN latent spaces. First, we study the impact of the distance metrics, comparing performances obtained with different metrics: the minimal Euclidean distance (MED), the minimal cosine distance (MCD), and the residue of the sparse coding reconstruction (RSCR). These metrics are applied using features extracted through five different CNN architectures, namely ResNet18, AlexNet, VGG16, InceptionV3 and DenseNet201. We use the specific vehicle re-identification dataset VeRI to fine-tune these CNNs and evaluate results. In overall, independently from the CNN used, MCD outperforms MED, commonly used in the literature. Secondly, the state-of-the-art image-to-track process (I2TP) is extended to a track-to-track process (T2TP) without using complementary metadata. Metrics are extended to measure distance between tracks, enabling the evaluation of T2TP and comparison with I2TP using the same CNN models. Results show that T2TP outperforms I2TP for MCD and RSCR. T2TP combining DenseNet201 and MCD-based metrics exhibits the best performances, outperforming the state-of-the-art I2TP models that use complementary metadata. Finally, our experiments highlight two main results: i) the importance of the metric choice for vehicle re-identification, and ii) T2TP improves the performances compared to I2TP, especially when coupled with MCD-based metrics.
MobileGAN: Skin Lesion Segmentation Using a Lightweight Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 01, 2019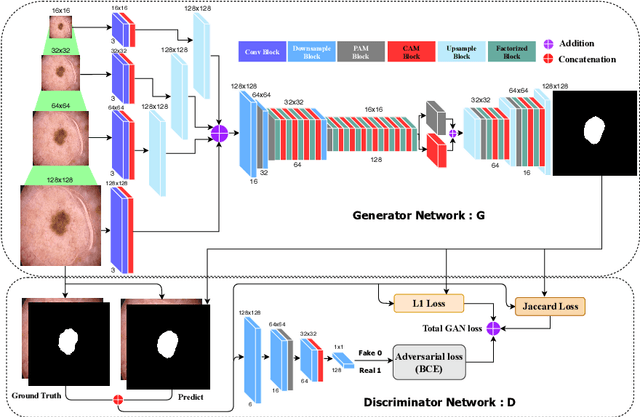
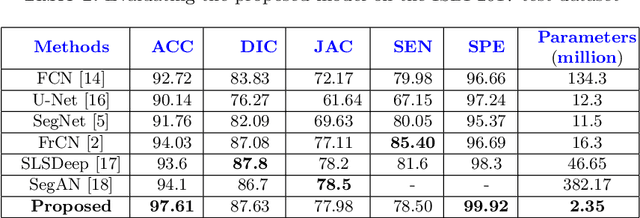
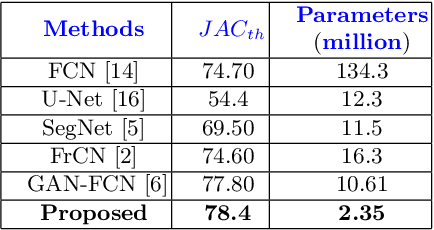
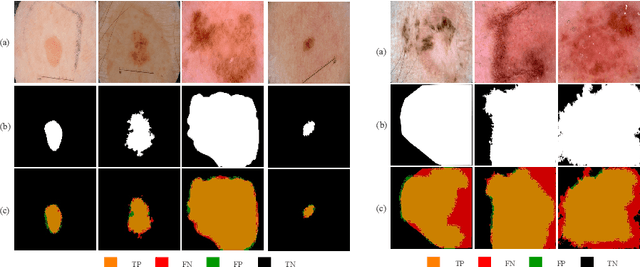
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic images is a challenge due to their blurry and irregular boundaries. Most of the segmentation approaches based on deep learning are time and memory consuming due to the hundreds of millions of parameters. Consequently, it is difficult to apply them to real dermatoscope devices with limited GPU and memory resources. In this paper, we propose a lightweight and efficient Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) model, called MobileGAN for skin lesion segmentation. More precisely, the MobileGAN combines 1D non-bottleneck factorization networks with position and channel attention modules in a GAN model. The proposed model is evaluated on the test dataset of the ISBI 2017 challenges and the validation dataset of ISIC 2018 challenges. Although the proposed network has only 2.35 millions of parameters, it is still comparable with the state-of-the-art. The experimental results show that our MobileGAN obtains comparable performance with an accuracy of 97.61%.
Support Vector Machine (SVM) Recognition Approach adapted to Individual and Touching Moths Counting in Trap Images
Sep 18, 2018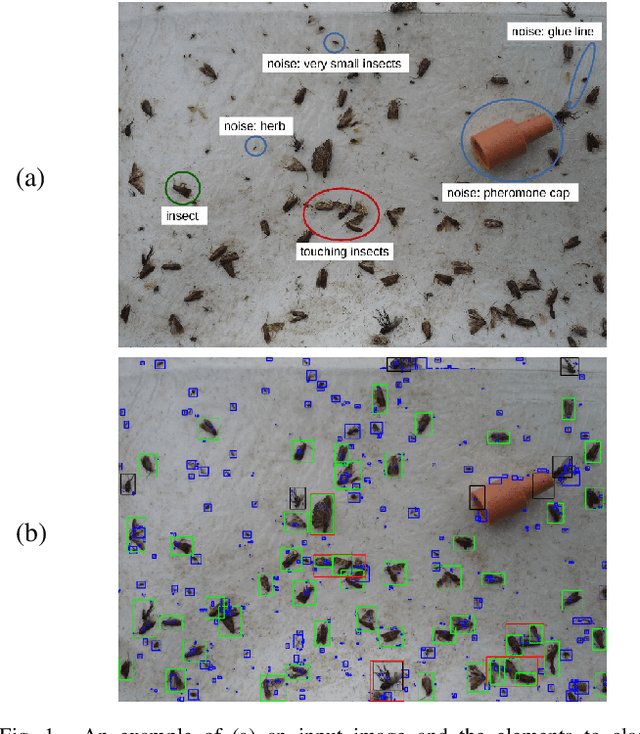
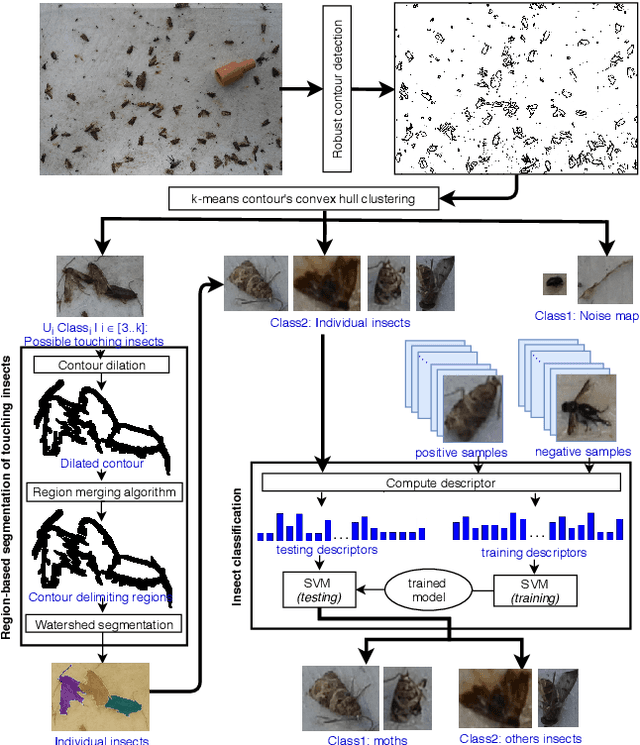

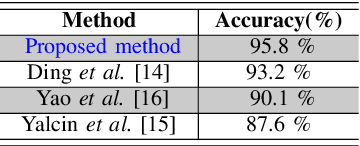
Abstract:This paper aims at developing an automatic algorithm for moth recognition from trap images in real-world conditions. This method uses our previous work for detection [1] and introduces an adapted classification step. More precisely, SVM classifier is trained with a multi-scale descriptor, Histogram Of Curviness Saliency (HCS). This descriptor is robust to illumination changes and is able to detect and to describe the external and the internal contours of the target insect in multi-scale. The proposed classification method can be trained with a small set of images. Quantitative evaluations show that the proposed method is able to classify insects with higher accuracy (rate of 95.8%) than the state-of-the art approaches.
Using Curvilinear Features in Focus for Registering a Single Image to a 3D Object
Feb 26, 2018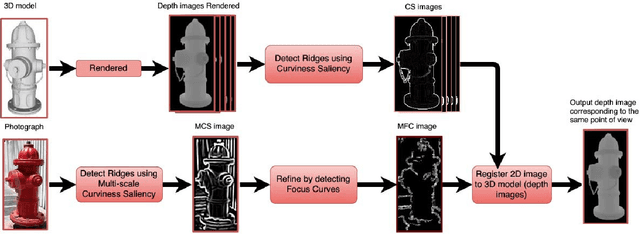

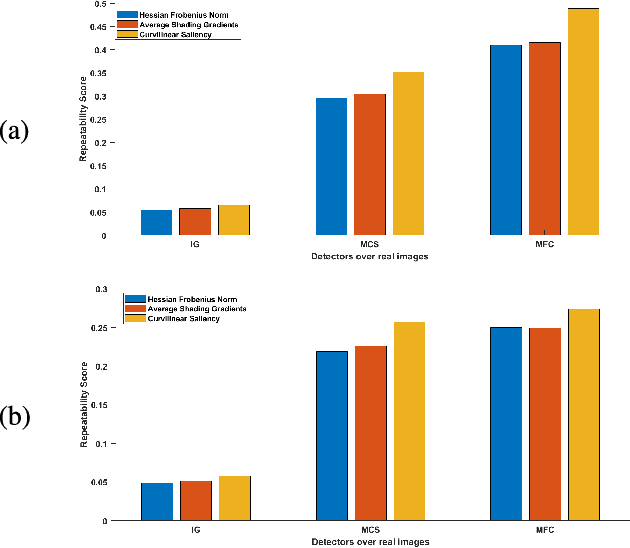
Abstract:In the context of 2D/3D registration, this paper introduces an approach that allows to match features detected in two different modalities: photographs and 3D models, by using a common 2D reprensentation. More precisely, 2D images are matched with a set of depth images, representing the 3D model. After introducing the concept of curvilinear saliency, related to curvature estimation, we propose a new ridge and valley detector for depth images rendered from 3D model. A variant of this detector is adapted to photographs, in particular by applying it in multi-scale and by combining this feature detector with the principle of focus curves. Finally, a registration algorithm for determining the correct viewpoint of the 3D model and thus the pose is proposed. It is based on using histogram of gradients features adapted to the features manipulated in 2D and in 3D, and the introduction of repeatability scores. The results presented highlight the quality of the features detected, in term of repeatability, and also the interest of the approach for registration and pose estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge