Vincent Charvillat
Improving Vehicle Re-Identification using CNN Latent Spaces: Metrics Comparison and Track-to-track Extension
Oct 21, 2019
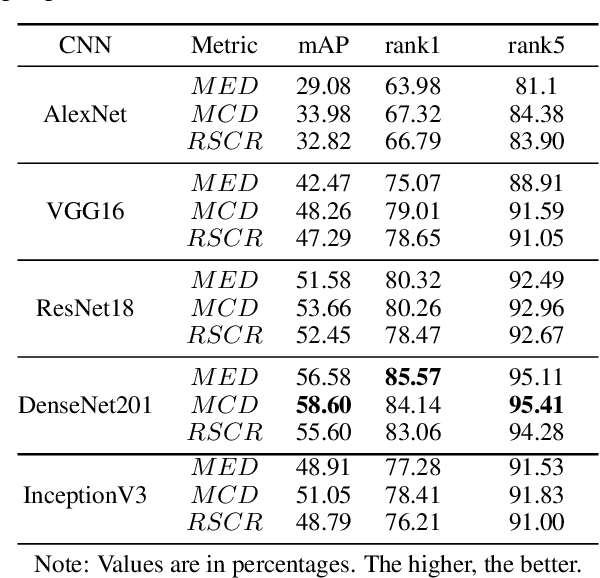
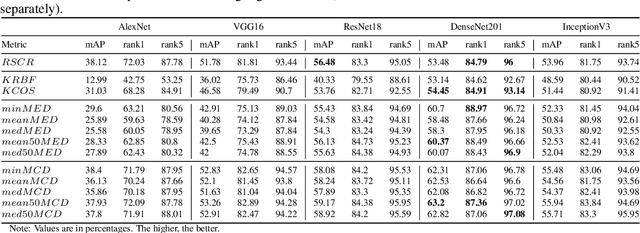
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of vehicle re-identification using distance comparison of images in CNN latent spaces. First, we study the impact of the distance metrics, comparing performances obtained with different metrics: the minimal Euclidean distance (MED), the minimal cosine distance (MCD), and the residue of the sparse coding reconstruction (RSCR). These metrics are applied using features extracted through five different CNN architectures, namely ResNet18, AlexNet, VGG16, InceptionV3 and DenseNet201. We use the specific vehicle re-identification dataset VeRI to fine-tune these CNNs and evaluate results. In overall, independently from the CNN used, MCD outperforms MED, commonly used in the literature. Secondly, the state-of-the-art image-to-track process (I2TP) is extended to a track-to-track process (T2TP) without using complementary metadata. Metrics are extended to measure distance between tracks, enabling the evaluation of T2TP and comparison with I2TP using the same CNN models. Results show that T2TP outperforms I2TP for MCD and RSCR. T2TP combining DenseNet201 and MCD-based metrics exhibits the best performances, outperforming the state-of-the-art I2TP models that use complementary metadata. Finally, our experiments highlight two main results: i) the importance of the metric choice for vehicle re-identification, and ii) T2TP improves the performances compared to I2TP, especially when coupled with MCD-based metrics.
Using Curvilinear Features in Focus for Registering a Single Image to a 3D Object
Feb 26, 2018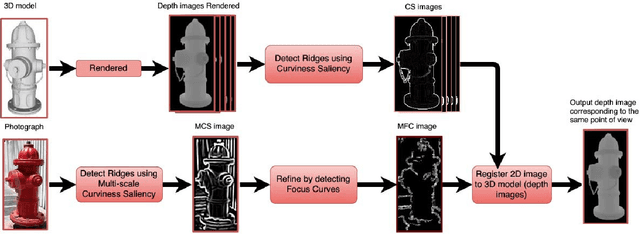

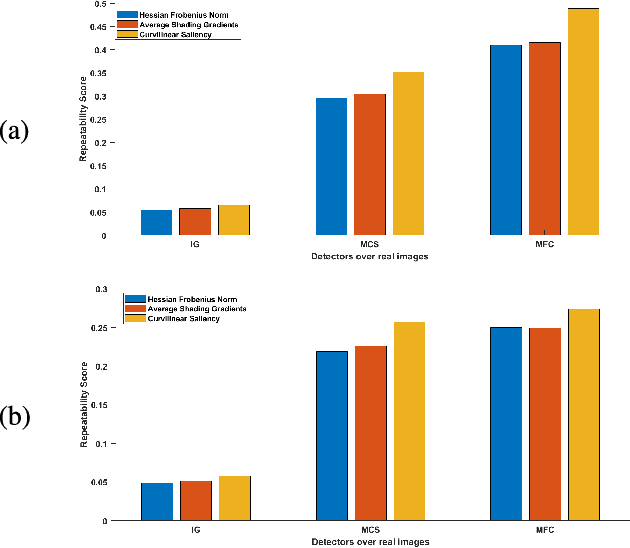
Abstract:In the context of 2D/3D registration, this paper introduces an approach that allows to match features detected in two different modalities: photographs and 3D models, by using a common 2D reprensentation. More precisely, 2D images are matched with a set of depth images, representing the 3D model. After introducing the concept of curvilinear saliency, related to curvature estimation, we propose a new ridge and valley detector for depth images rendered from 3D model. A variant of this detector is adapted to photographs, in particular by applying it in multi-scale and by combining this feature detector with the principle of focus curves. Finally, a registration algorithm for determining the correct viewpoint of the 3D model and thus the pose is proposed. It is based on using histogram of gradients features adapted to the features manipulated in 2D and in 3D, and the introduction of repeatability scores. The results presented highlight the quality of the features detected, in term of repeatability, and also the interest of the approach for registration and pose estimation.
Quality Control in Crowdsourced Object Segmentation
May 01, 2015

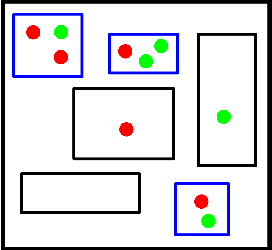
Abstract:This paper explores processing techniques to deal with noisy data in crowdsourced object segmentation tasks. We use the data collected with "Click'n'Cut", an online interactive segmentation tool, and we perform several experiments towards improving the segmentation results. First, we introduce different superpixel-based techniques to filter users' traces, and assess their impact on the segmentation result. Second, we present different criteria to detect and discard the traces from potential bad users, resulting in a remarkable increase in performance. Finally, we show a novel superpixel-based segmentation algorithm which does not require any prior filtering and is based on weighting each user's contribution according to his/her level of expertise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge