Mohamed Chafik Bakkay
Precipitaion Nowcasting using Deep Neural Network
Mar 24, 2022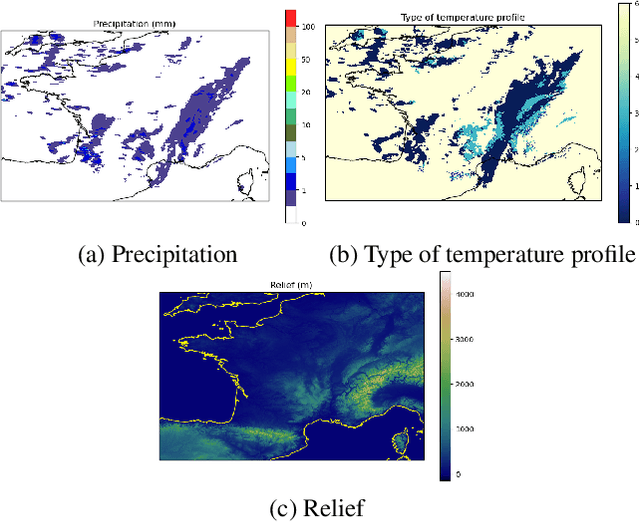
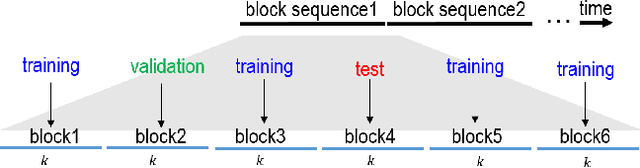
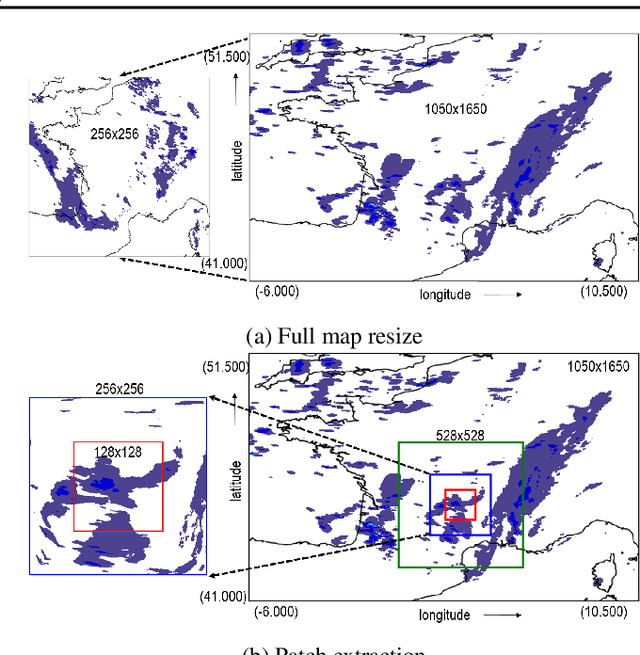
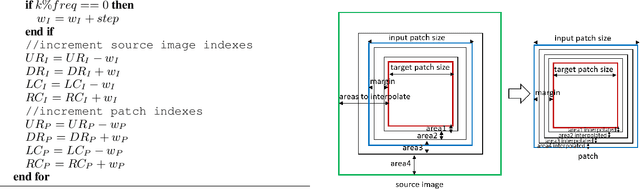
Abstract:Precipitation nowcasting is of great importance for weather forecast users, for activities ranging from outdoor activities and sports competitions to airport traffic management. In contrast to long-term precipitation forecasts which are traditionally obtained from numerical models, precipitation nowcasting needs to be very fast. It is therefore more challenging to obtain because of this time constraint. Recently, many machine learning based methods had been proposed. We propose the use three popular deep learning models (U-net, ConvLSTM and SVG-LP) trained on two-dimensional precipitation maps for precipitation nowcasting. We proposed an algorithm for patch extraction to obtain high resolution precipitation maps. We proposed a loss function to solve the blurry image issue and to reduce the influence of zero value pixels in precipitation maps.
Support Vector Machine (SVM) Recognition Approach adapted to Individual and Touching Moths Counting in Trap Images
Sep 18, 2018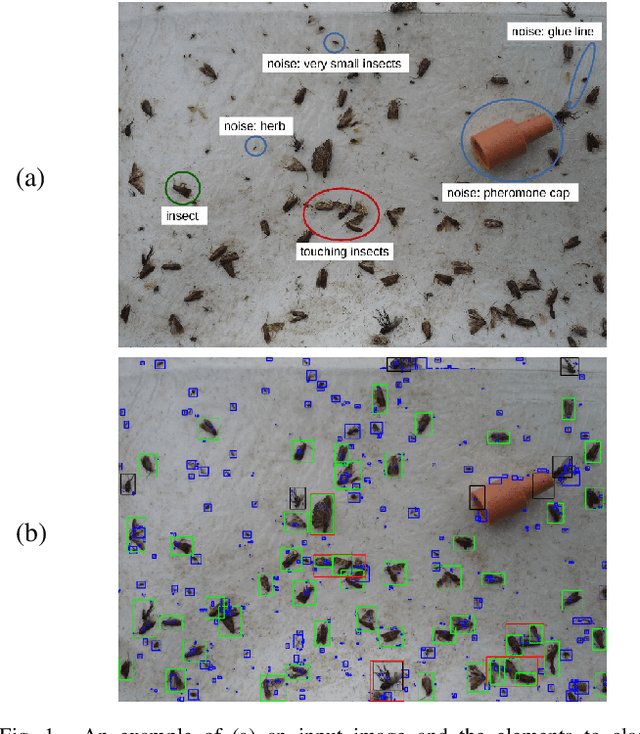
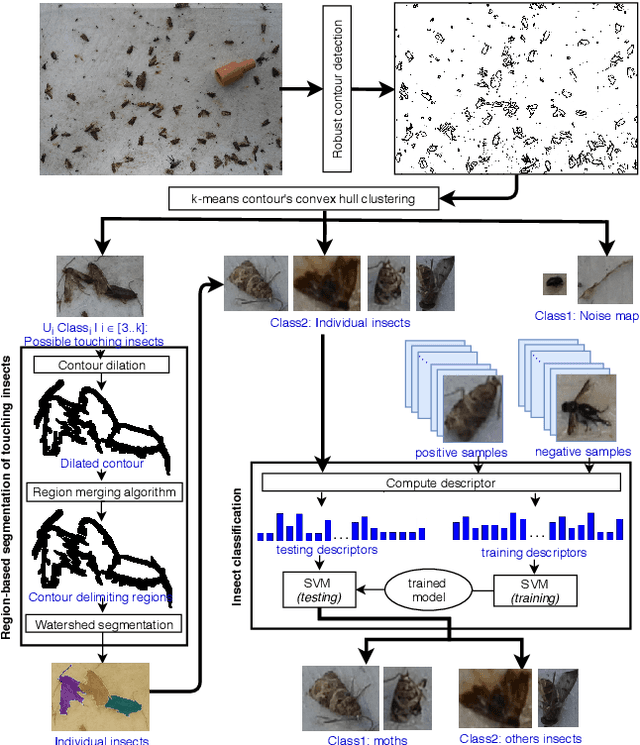

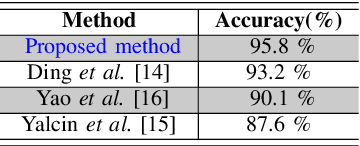
Abstract:This paper aims at developing an automatic algorithm for moth recognition from trap images in real-world conditions. This method uses our previous work for detection [1] and introduces an adapted classification step. More precisely, SVM classifier is trained with a multi-scale descriptor, Histogram Of Curviness Saliency (HCS). This descriptor is robust to illumination changes and is able to detect and to describe the external and the internal contours of the target insect in multi-scale. The proposed classification method can be trained with a small set of images. Quantitative evaluations show that the proposed method is able to classify insects with higher accuracy (rate of 95.8%) than the state-of-the art approaches.
Seuillage par hystérésis pour le test de photo-consistance des voxels dans le cadre de la reconstruction 3D
Sep 17, 2018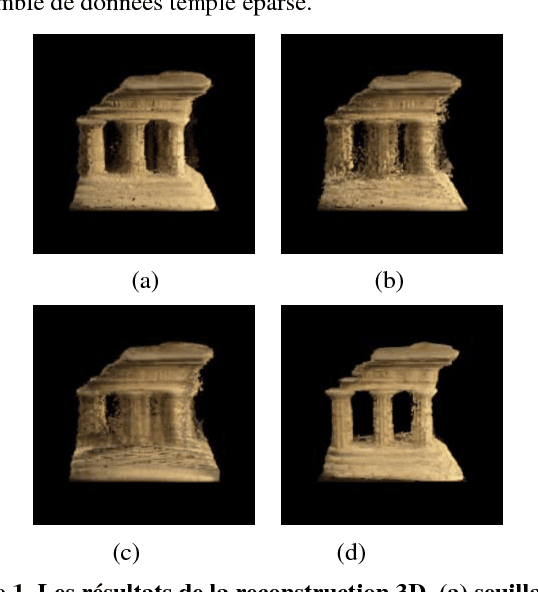
Abstract:Voxel coloring is a popular method of reconstructing a three-dimensional surface model from a set of calibrated 2D images. However, the reconstruction quality is largely dependent on a thresholding procedure allowing the authors to decide, for each voxel, whether it is photo-consistent or not. Even so, this method is widely used because of its simplicity and low computational cost. We have returned to this method in order to propose an improvement in the thresholding step which will be fully automated. Indeed, the geometrical information is implicitly integrated using an hysteresis thresholding which takes into account the spatial coherence of color voxels. Moreover, the ambiguity of choosing the thresholds is extremely minimized by defining a fuzzy degree of membership of each voxel into the class of consistent voxels. Also, there is no need for preset thresholds since the hysteresis ones are defined automatically and adaptively depending on the number of images that the voxel isprojected onto. Preliminary results are very promising and demonstrate that the proposed method performs automatically precise and smooth volumetric scene reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge