Tieyun Qian
Controlling Multimodal Conversational Agents with Coverage-Enhanced Latent Actions
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models are increasingly employed as multimodal conversational agents (MCAs) for diverse conversational tasks. Recently, reinforcement learning (RL) has been widely explored for adapting MCAs to various human-AI interaction scenarios. Despite showing great enhancement in generalization performance, fine-tuning MCAs via RL still faces challenges in handling the extremely large text token space. To address this, we learn a compact latent action space for RL fine-tuning instead. Specifically, we adopt the learning from observation mechanism to construct the codebook for the latent action space, where future observations are leveraged to estimate current latent actions that could further be used to reconstruct future observations. However, the scarcity of paired image-text data hinders learning a codebook with sufficient coverage. Thus, we leverage both paired image-text data and text-only data to construct the latent action space, using a cross-modal projector for transforming text embeddings into image-text embeddings. We initialize the cross-modal projector on paired image-text data, and further train it on massive text-only data with a novel cycle consistency loss to enhance its robustness. We show that our latent action based method outperforms competitive baselines on two conversation tasks across various RL algorithms.
Understanding Generalization in Role-Playing Models via Information Theory
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Role-playing models (RPMs) are widely used in real-world applications but underperform when deployed in the wild. This degradation can be attributed to distribution shifts, including user, character, and dialogue compositional shifts. Existing methods like LLM-as-a-judge fall short in providing a fine-grained diagnosis of how these shifts affect RPM generalization, and thus there lack formal frameworks to characterize RPM generalization behaviors. To bridge these gaps, we introduce an information-theoretic metric, named reasoning-based effective mutual information difference (R-EMID), to measure RPM performance degradation in an interpretable way. We also derive an upper bound on R-EMID to predict the worst-case generalization performance of RPMs and theoretically reveal how various shifts contribute to the RPM performance degradation. Moreover, we propose a co-evolving reinforcement learning framework to adaptively model the connection among user, character, and dialogue context and thus enhance the estimation of dialogue response generation probability, which is critical for calculating R-EMID. Finally, we evaluate the generalization performance of various RPMs using R-EMID, finding that user shift poses the highest risk among all shifts and reinforcement learning is the most effective approach for enhancing RPM generalization.
Can a Small Model Learn to Look Before It Leaps? Dynamic Learning and Proactive Correction for Hallucination Detection
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Hallucination in large language models (LLMs) remains a critical barrier to their safe deployment. Existing tool-augmented hallucination detection methods require pre-defined fixed verification strategies, which are crucial to the quality and effectiveness of tool calls. Some methods directly employ powerful closed-source LLMs such as GPT-4 as detectors, which are effective but too costly. To mitigate the cost issue, some methods adopt the teacher-student architecture and finetune open-source small models as detectors via agent tuning. However, these methods are limited by fixed strategies. When faced with a dynamically changing execution environment, they may lack adaptability and inappropriately call tools, ultimately leading to detection failure. To address the problem of insufficient strategy adaptability, we propose the innovative ``Learning to Evaluate and Adaptively Plan''(LEAP) framework, which endows an efficient student model with the dynamic learning and proactive correction capabilities of the teacher model. Specifically, our method formulates the hallucination detection problem as a dynamic strategy learning problem. We first employ a teacher model to generate trajectories within the dynamic learning loop and dynamically adjust the strategy based on execution failures. We then distill this dynamic planning capability into an efficient student model via agent tuning. Finally, during strategy execution, the student model adopts a proactive correction mechanism, enabling it to propose, review, and optimize its own verification strategies before execution. We demonstrate through experiments on three challenging benchmarks that our LEAP-tuned model outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
Privacy-protected Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge Graph Question Answering
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:LLMs often suffer from hallucinations and outdated or incomplete knowledge. RAG is proposed to address these issues by integrating external knowledge like that in KGs into LLMs. However, leveraging private KGs in RAG systems poses significant privacy risks due to the black-box nature of LLMs and potential insecure data transmission, especially when using third-party LLM APIs lacking transparency and control. In this paper, we investigate the privacy-protected RAG scenario for the first time, where entities in KGs are anonymous for LLMs, thus preventing them from accessing entity semantics. Due to the loss of semantics of entities, previous RAG systems cannot retrieve question-relevant knowledge from KGs by matching questions with the meaningless identifiers of anonymous entities. To realize an effective RAG system in this scenario, two key challenges must be addressed: (1) How can anonymous entities be converted into retrievable information. (2) How to retrieve question-relevant anonymous entities. Hence, we propose a novel ARoG framework including relation-centric abstraction and structure-oriented abstraction strategies. For challenge (1), the first strategy abstracts entities into high-level concepts by dynamically capturing the semantics of their adjacent relations. It supplements meaningful semantics which can further support the retrieval process. For challenge (2), the second strategy transforms unstructured natural language questions into structured abstract concept paths. These paths can be more effectively aligned with the abstracted concepts in KGs, thereby improving retrieval performance. To guide LLMs to effectively retrieve knowledge from KGs, the two strategies strictly protect privacy from being exposed to LLMs. Experiments on three datasets demonstrate that ARoG achieves strong performance and privacy-robustness.
A Survey on Training-free Alignment of Large Language Models
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:The alignment of large language models (LLMs) aims to ensure their outputs adhere to human values, ethical standards, and legal norms. Traditional alignment methods often rely on resource-intensive fine-tuning (FT), which may suffer from knowledge degradation and face challenges in scenarios where the model accessibility or computational resources are constrained. In contrast, training-free (TF) alignment techniques--leveraging in-context learning, decoding-time adjustments, and post-generation corrections--offer a promising alternative by enabling alignment without heavily retraining LLMs, making them adaptable to both open-source and closed-source environments. This paper presents the first systematic review of TF alignment methods, categorizing them by stages of pre-decoding, in-decoding, and post-decoding. For each stage, we provide a detailed examination from the viewpoint of LLMs and multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), highlighting their mechanisms and limitations. Furthermore, we identify key challenges and future directions, paving the way for more inclusive and effective TF alignment techniques. By synthesizing and organizing the rapidly growing body of research, this survey offers a guidance for practitioners and advances the development of safer and more reliable LLMs.
CAVGAN: Unifying Jailbreak and Defense of LLMs via Generative Adversarial Attacks on their Internal Representations
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Security alignment enables the Large Language Model (LLM) to gain the protection against malicious queries, but various jailbreak attack methods reveal the vulnerability of this security mechanism. Previous studies have isolated LLM jailbreak attacks and defenses. We analyze the security protection mechanism of the LLM, and propose a framework that combines attack and defense. Our method is based on the linearly separable property of LLM intermediate layer embedding, as well as the essence of jailbreak attack, which aims to embed harmful problems and transfer them to the safe area. We utilize generative adversarial network (GAN) to learn the security judgment boundary inside the LLM to achieve efficient jailbreak attack and defense. The experimental results indicate that our method achieves an average jailbreak success rate of 88.85\% across three popular LLMs, while the defense success rate on the state-of-the-art jailbreak dataset reaches an average of 84.17\%. This not only validates the effectiveness of our approach but also sheds light on the internal security mechanisms of LLMs, offering new insights for enhancing model security The code and data are available at https://github.com/NLPGM/CAVGAN.
Reasoning based on symbolic and parametric knowledge bases: a survey
Jan 02, 2025Abstract:Reasoning is fundamental to human intelligence, and critical for problem-solving, decision-making, and critical thinking. Reasoning refers to drawing new conclusions based on existing knowledge, which can support various applications like clinical diagnosis, basic education, and financial analysis. Though a good number of surveys have been proposed for reviewing reasoning-related methods, none of them has systematically investigated these methods from the viewpoint of their dependent knowledge base. Both the scenarios to which the knowledge bases are applied and their storage formats are significantly different. Hence, investigating reasoning methods from the knowledge base perspective helps us better understand the challenges and future directions. To fill this gap, this paper first classifies the knowledge base into symbolic and parametric ones. The former explicitly stores information in human-readable symbols, and the latter implicitly encodes knowledge within parameters. Then, we provide a comprehensive overview of reasoning methods using symbolic knowledge bases, parametric knowledge bases, and both of them. Finally, we identify the future direction toward enhancing reasoning capabilities to bridge the gap between human and machine intelligence.
Toxicity Detection towards Adaptability to Changing Perturbations
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Toxicity detection is crucial for maintaining the peace of the society. While existing methods perform well on normal toxic contents or those generated by specific perturbation methods, they are vulnerable to evolving perturbation patterns. However, in real-world scenarios, malicious users tend to create new perturbation patterns for fooling the detectors. For example, some users may circumvent the detector of large language models (LLMs) by adding `I am a scientist' at the beginning of the prompt. In this paper, we introduce a novel problem, i.e., continual learning jailbreak perturbation patterns, into the toxicity detection field. To tackle this problem, we first construct a new dataset generated by 9 types of perturbation patterns, 7 of them are summarized from prior work and 2 of them are developed by us. We then systematically validate the vulnerability of current methods on this new perturbation pattern-aware dataset via both the zero-shot and fine tuned cross-pattern detection. Upon this, we present the domain incremental learning paradigm and the corresponding benchmark to ensure the detector's robustness to dynamically emerging types of perturbed toxic text. Our code and dataset are provided in the appendix and will be publicly available at GitHub, by which we wish to offer new research opportunities for the security-relevant communities.
Enhancing Relation Extraction via Supervised Rationale Verification and Feedback
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Despite the rapid progress that existing automated feedback methods have made in correcting the output of large language models (LLMs), these methods cannot be well applied to the relation extraction (RE) task due to their designated feedback objectives and correction manner. To address this problem, we propose a novel automated feedback framework for RE, which presents a rationale supervisor to verify the rationale and provide re-selected demonstrations as feedback to correct the initial prediction. Specifically, we first design a causal intervention and observation method for to collect biased/unbiased rationales for contrastive training the rationale supervisor. Then, we present a verification-feedback-correction procedure to iteratively enhance LLMs' capability of handling the RE task. Extensive experiments prove that our proposed framework significantly outperforms existing methods.
Origin-Destination Demand Prediction: An Urban Radiation and Attraction Perspective
Nov 29, 2024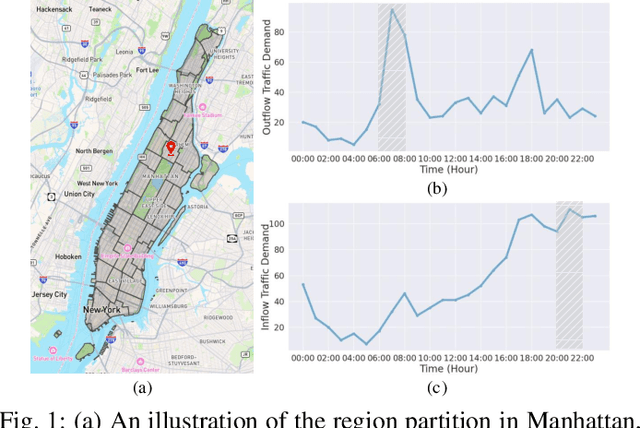
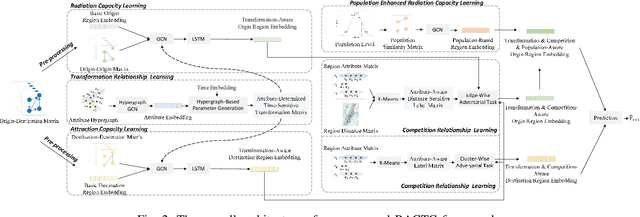
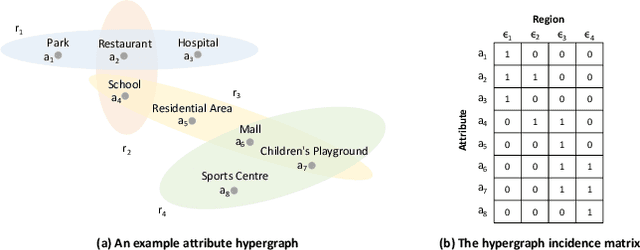
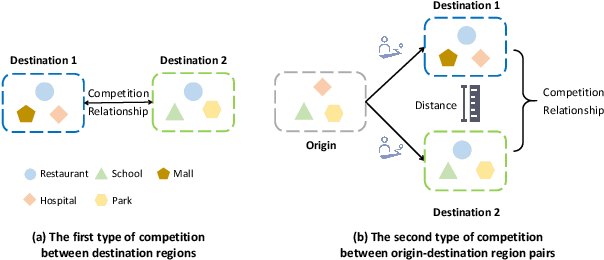
Abstract:In recent years, origin-destination (OD) demand prediction has gained significant attention for its profound implications in urban development. Existing data-driven deep learning methods primarily focus on the spatial or temporal dependency between regions yet neglecting regions' fundamental functional difference. Though knowledge-driven physical methods have characterised regions' functions by their radiation and attraction capacities, these functions are defined on numerical factors like population without considering regions' intrinsic nominal attributes, e.g., a region is a residential or industrial district. Moreover, the complicated relationships between two types of capacities, e.g., the radiation capacity of a residential district in the morning will be transformed into the attraction capacity in the evening, are totally missing from physical methods. In this paper, we not only generalize the physical radiation and attraction capacities into the deep learning framework with the extended capability to fulfil regions' functions, but also present a new model that captures the relationships between two types of capacities. Specifically, we first model regions' radiation and attraction capacities using a bilateral branch network, each equipped with regions' attribute representations. We then describe the transformation relationship of different capacities of the same region using a hypergraph-based parameter generation method. We finally unveil the competition relationship of different regions with the same attraction capacity through cluster-based adversarial learning. Extensive experiments on two datasets demonstrate the consistent improvements of our method over the state-of-the-art baselines, as well as the good explainability of regions' functions using their nominal attributes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge