Xiaohu Li
CAVGAN: Unifying Jailbreak and Defense of LLMs via Generative Adversarial Attacks on their Internal Representations
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Security alignment enables the Large Language Model (LLM) to gain the protection against malicious queries, but various jailbreak attack methods reveal the vulnerability of this security mechanism. Previous studies have isolated LLM jailbreak attacks and defenses. We analyze the security protection mechanism of the LLM, and propose a framework that combines attack and defense. Our method is based on the linearly separable property of LLM intermediate layer embedding, as well as the essence of jailbreak attack, which aims to embed harmful problems and transfer them to the safe area. We utilize generative adversarial network (GAN) to learn the security judgment boundary inside the LLM to achieve efficient jailbreak attack and defense. The experimental results indicate that our method achieves an average jailbreak success rate of 88.85\% across three popular LLMs, while the defense success rate on the state-of-the-art jailbreak dataset reaches an average of 84.17\%. This not only validates the effectiveness of our approach but also sheds light on the internal security mechanisms of LLMs, offering new insights for enhancing model security The code and data are available at https://github.com/NLPGM/CAVGAN.
ClinicalGPT: Large Language Models Finetuned with Diverse Medical Data and Comprehensive Evaluation
Jun 16, 2023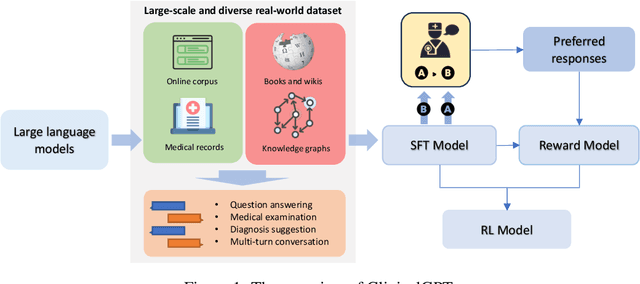
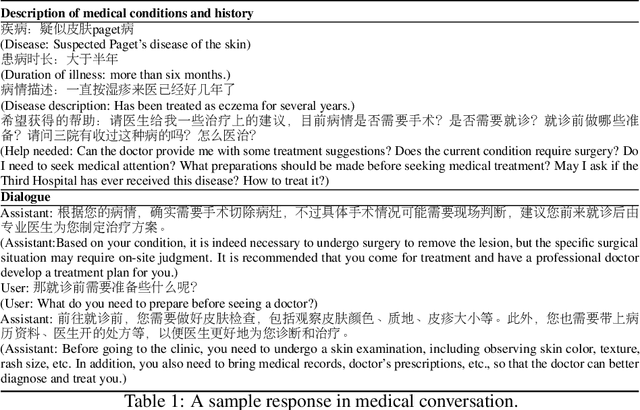
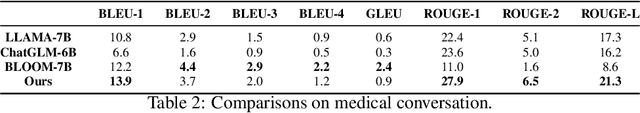

Abstract:Large language models have exhibited exceptional performance on various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, leveraging techniques such as the pre-training, and instruction fine-tuning. Despite these advances, their effectiveness in medical applications is limited, due to challenges such as factual inaccuracies, reasoning abilities, and lack grounding in real-world experience. In this study, we present ClinicalGPT, a language model explicitly designed and optimized for clinical scenarios. By incorporating extensive and diverse real-world data, such as medical records, domain-specific knowledge, and multi-round dialogue consultations in the training process, ClinicalGPT is better prepared to handle multiple clinical task. Furthermore, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework that includes medical knowledge question-answering, medical exams, patient consultations, and diagnostic analysis of medical records. Our results demonstrate that ClinicalGPT significantly outperforms other models in these tasks, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach in adapting large language models to the critical domain of healthcare.
Stochastically Dominant Distributional Reinforcement Learning
May 17, 2019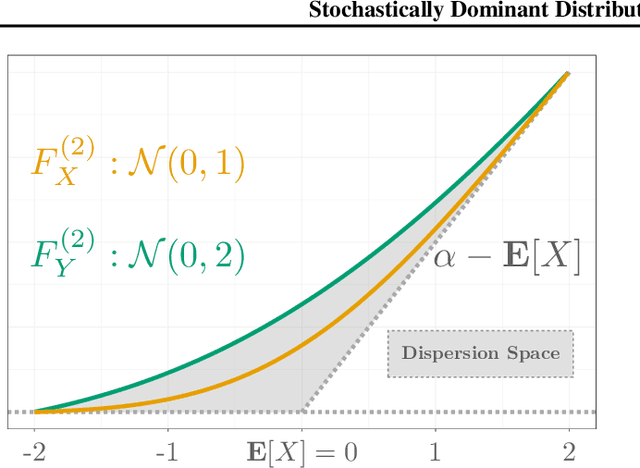
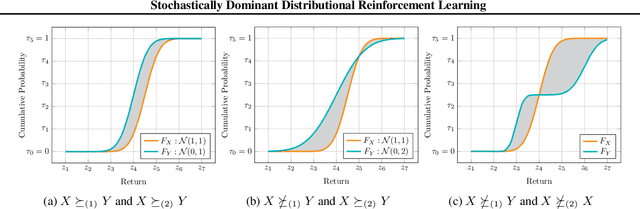
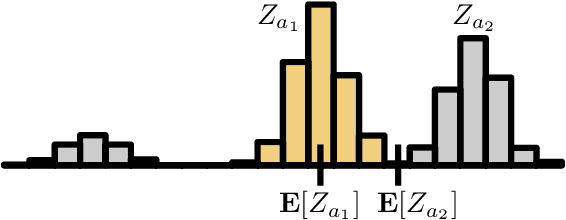
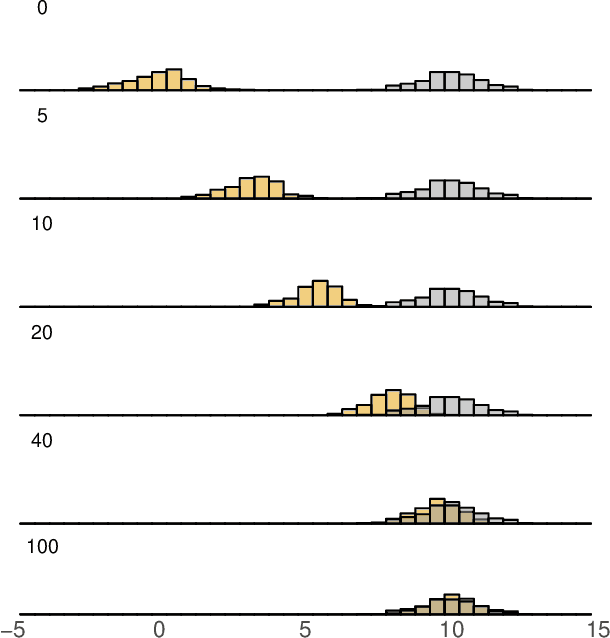
Abstract:We describe a new approach for mitigating risk in the Reinforcement Learning paradigm. Instead of reasoning about expected utility, we use second-order stochastic dominance (SSD) to directly compare the inherent risk of random returns induced by different actions. We frame the RL optimization within the space of probability measures to accommodate the SSD relation, treating Bellman's equation as a potential energy functional. This brings us to Wasserstein gradient flows, for which the optimality and convergence are well understood. We propose a discrete-measure approximation algorithm called the Dominant Particle Agent (DPA), and we demonstrate how safety and performance are better balanced with DPA than with existing baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge