Tian Huey Teh
Papercup Technologies Ltd
Human-AI Complementarity: A Goal for Amplified Oversight
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Human feedback is critical for aligning AI systems to human values. As AI capabilities improve and AI is used to tackle more challenging tasks, verifying quality and safety becomes increasingly challenging. This paper explores how we can leverage AI to improve the quality of human oversight. We focus on an important safety problem that is already challenging for humans: fact-verification of AI outputs. We find that combining AI ratings and human ratings based on AI rater confidence is better than relying on either alone. Giving humans an AI fact-verification assistant further improves their accuracy, but the type of assistance matters. Displaying AI explanation, confidence, and labels leads to over-reliance, but just showing search results and evidence fosters more appropriate trust. These results have implications for Amplified Oversight -- the challenge of combining humans and AI to supervise AI systems even as they surpass human expert performance.
Insights on Disagreement Patterns in Multimodal Safety Perception across Diverse Rater Groups
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:AI systems crucially rely on human ratings, but these ratings are often aggregated, obscuring the inherent diversity of perspectives in real-world phenomenon. This is particularly concerning when evaluating the safety of generative AI, where perceptions and associated harms can vary significantly across socio-cultural contexts. While recent research has studied the impact of demographic differences on annotating text, there is limited understanding of how these subjective variations affect multimodal safety in generative AI. To address this, we conduct a large-scale study employing highly-parallel safety ratings of about 1000 text-to-image (T2I) generations from a demographically diverse rater pool of 630 raters balanced across 30 intersectional groups across age, gender, and ethnicity. Our study shows that (1) there are significant differences across demographic groups (including intersectional groups) on how severe they assess the harm to be, and that these differences vary across different types of safety violations, (2) the diverse rater pool captures annotation patterns that are substantially different from expert raters trained on specific set of safety policies, and (3) the differences we observe in T2I safety are distinct from previously documented group level differences in text-based safety tasks. To further understand these varying perspectives, we conduct a qualitative analysis of the open-ended explanations provided by raters. This analysis reveals core differences into the reasons why different groups perceive harms in T2I generations. Our findings underscore the critical need for incorporating diverse perspectives into safety evaluation of generative AI ensuring these systems are truly inclusive and reflect the values of all users.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Ensemble prosody prediction for expressive speech synthesis
Apr 03, 2023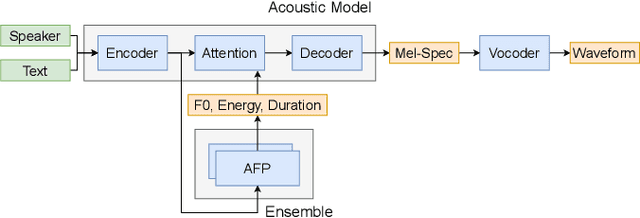
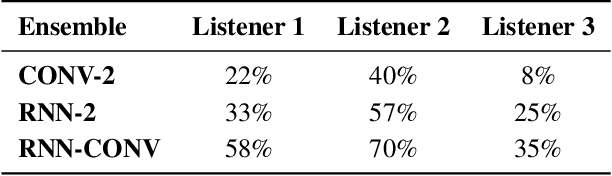
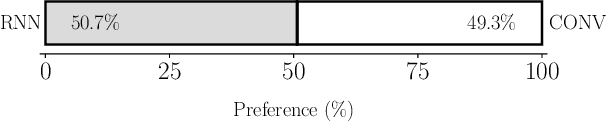
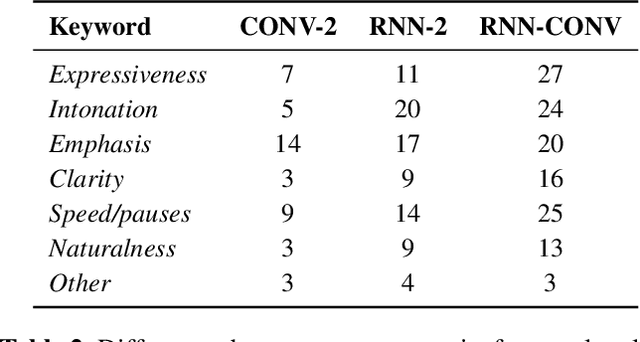
Abstract:Generating expressive speech with rich and varied prosody continues to be a challenge for Text-to-Speech. Most efforts have focused on sophisticated neural architectures intended to better model the data distribution. Yet, in evaluations it is generally found that no single model is preferred for all input texts. This suggests an approach that has rarely been used before for Text-to-Speech: an ensemble of models. We apply ensemble learning to prosody prediction. We construct simple ensembles of prosody predictors by varying either model architecture or model parameter values. To automatically select amongst the models in the ensemble when performing Text-to-Speech, we propose a novel, and computationally trivial, variance-based criterion. We demonstrate that even a small ensemble of prosody predictors yields useful diversity, which, combined with the proposed selection criterion, outperforms any individual model from the ensemble.
Controlling High-Dimensional Data With Sparse Input
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:We address the problem of human-in-the-loop control for generating highly-structured data. This task is challenging because existing generative models lack an efficient interface through which users can modify the output. Users have the option to either manually explore a non-interpretable latent space, or to laboriously annotate the data with conditioning labels. To solve this, we introduce a novel framework whereby an encoder maps a sparse, human interpretable control space onto the latent space of a generative model. We apply this framework to the task of controlling prosody in text-to-speech synthesis. We propose a model, called Multiple-Instance CVAE (MICVAE), that is specifically designed to encode sparse prosodic features and output complete waveforms. We show empirically that MICVAE displays desirable qualities of a sparse human-in-the-loop control mechanism: efficiency, robustness, and faithfulness. With even a very small number of input values (~4), MICVAE enables users to improve the quality of the output significantly, in terms of listener preference (4:1).
Ctrl-P: Temporal Control of Prosodic Variation for Speech Synthesis
Jun 15, 2021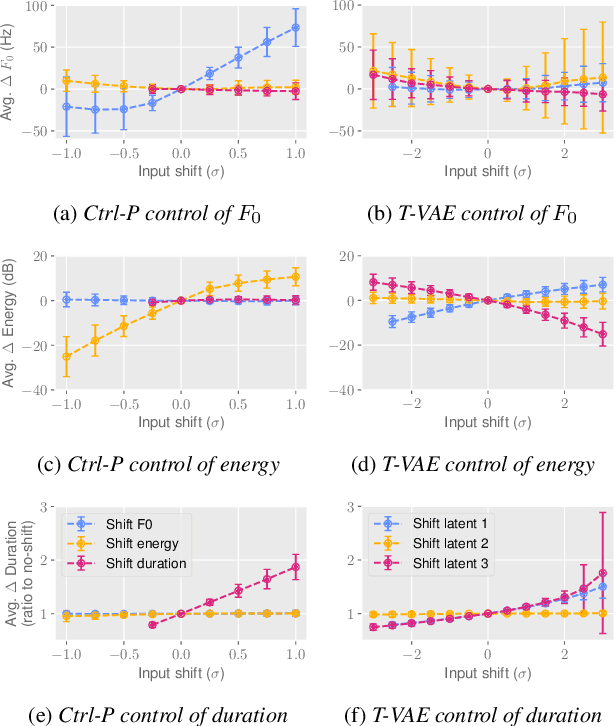
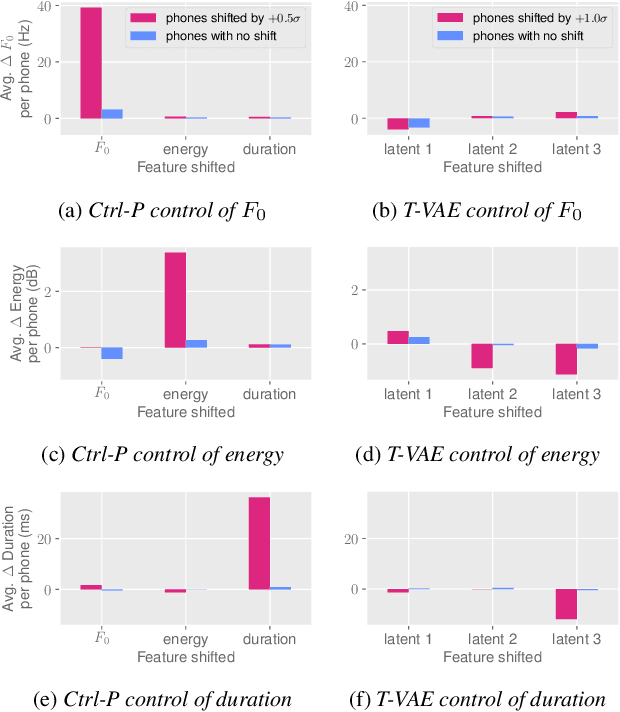
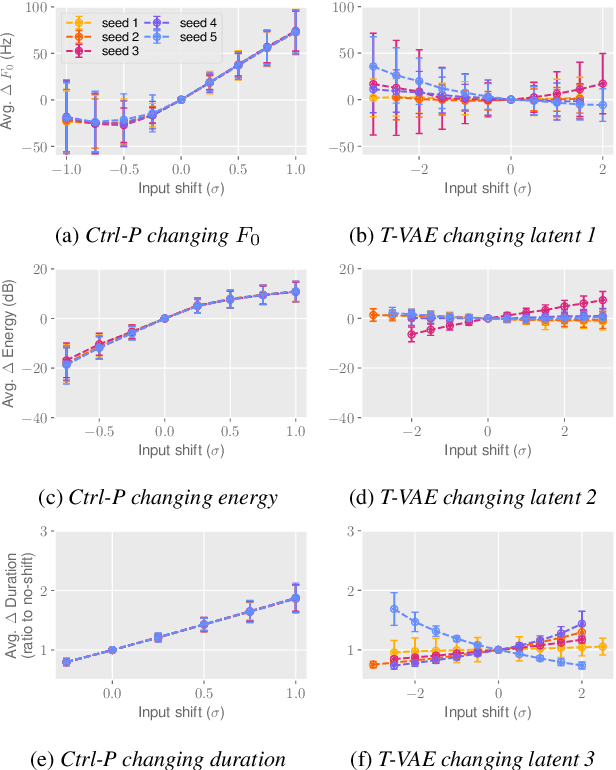
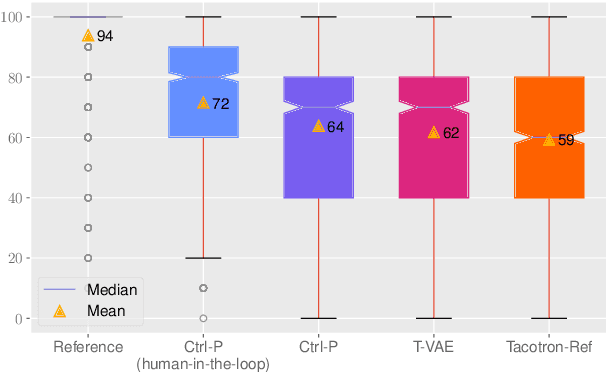
Abstract:Text does not fully specify the spoken form, so text-to-speech models must be able to learn from speech data that vary in ways not explained by the corresponding text. One way to reduce the amount of unexplained variation in training data is to provide acoustic information as an additional learning signal. When generating speech, modifying this acoustic information enables multiple distinct renditions of a text to be produced. Since much of the unexplained variation is in the prosody, we propose a model that generates speech explicitly conditioned on the three primary acoustic correlates of prosody: $F_{0}$, energy and duration. The model is flexible about how the values of these features are specified: they can be externally provided, or predicted from text, or predicted then subsequently modified. Compared to a model that employs a variational auto-encoder to learn unsupervised latent features, our model provides more interpretable, temporally-precise, and disentangled control. When automatically predicting the acoustic features from text, it generates speech that is more natural than that from a Tacotron 2 model with reference encoder. Subsequent human-in-the-loop modification of the predicted acoustic features can significantly further increase naturalness.
ADEPT: A Dataset for Evaluating Prosody Transfer
Jun 15, 2021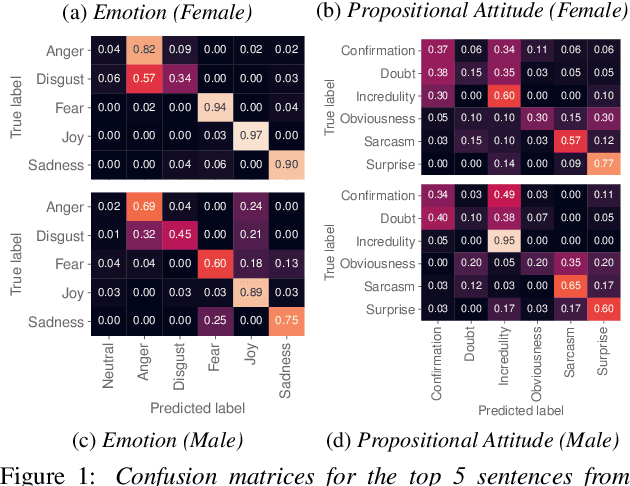
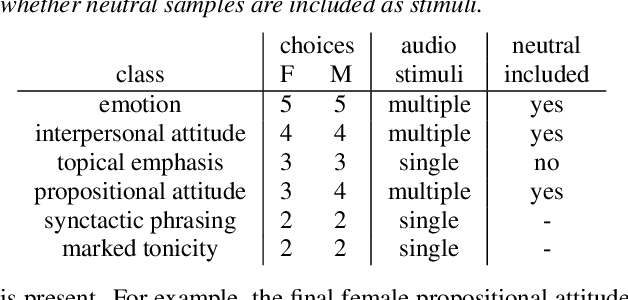
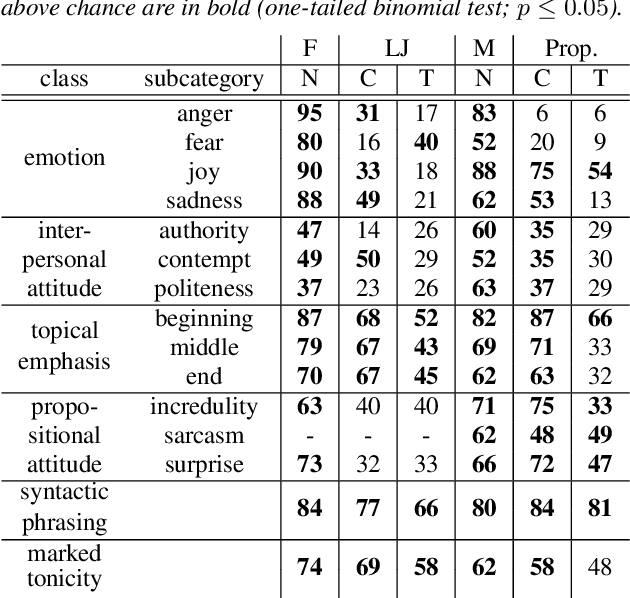
Abstract:Text-to-speech is now able to achieve near-human naturalness and research focus has shifted to increasing expressivity. One popular method is to transfer the prosody from a reference speech sample. There have been considerable advances in using prosody transfer to generate more expressive speech, but the field lacks a clear definition of what successful prosody transfer means and a method for measuring it. We introduce a dataset of prosodically-varied reference natural speech samples for evaluating prosody transfer. The samples include global variations reflecting emotion and interpersonal attitude, and local variations reflecting topical emphasis, propositional attitude, syntactic phrasing and marked tonicity. The corpus only includes prosodic variations that listeners are able to distinguish with reasonable accuracy, and we report these figures as a benchmark against which text-to-speech prosody transfer can be compared. We conclude the paper with a demonstration of our proposed evaluation methodology, using the corpus to evaluate two text-to-speech models that perform prosody transfer.
Incremental Text to Speech for Neural Sequence-to-Sequence Models using Reinforcement Learning
Aug 07, 2020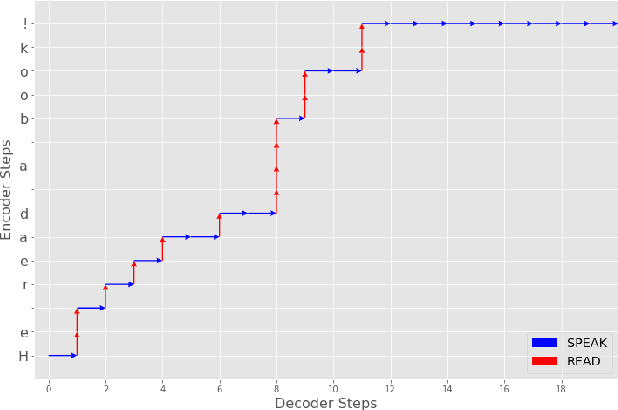
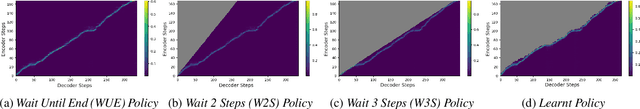
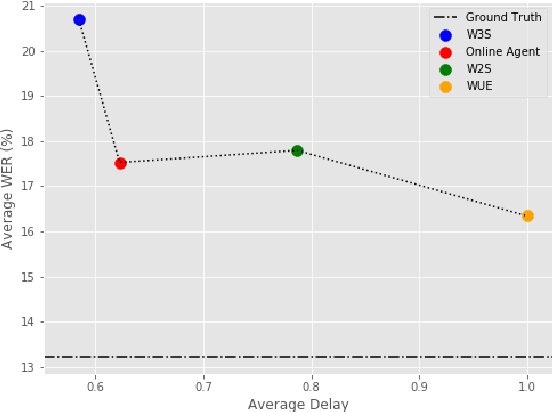
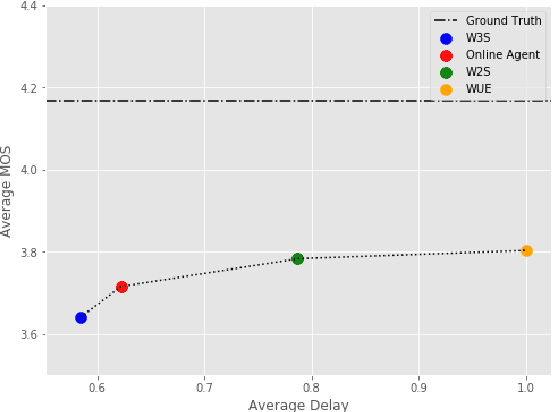
Abstract:Modern approaches to text to speech require the entire input character sequence to be processed before any audio is synthesised. This latency limits the suitability of such models for time-sensitive tasks like simultaneous interpretation. Interleaving the action of reading a character with that of synthesising audio reduces this latency. However, the order of this sequence of interleaved actions varies across sentences, which raises the question of how the actions should be chosen. We propose a reinforcement learning based framework to train an agent to make this decision. We compare our performance against that of deterministic, rule-based systems. Our results demonstrate that our agent successfully balances the trade-off between the latency of audio generation and the quality of synthesised audio. More broadly, we show that neural sequence-to-sequence models can be adapted to run in an incremental manner.
Phonological Features for 0-shot Multilingual Speech Synthesis
Aug 06, 2020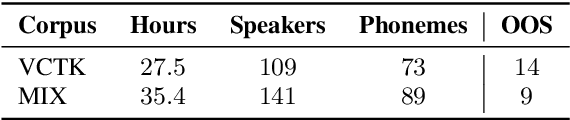
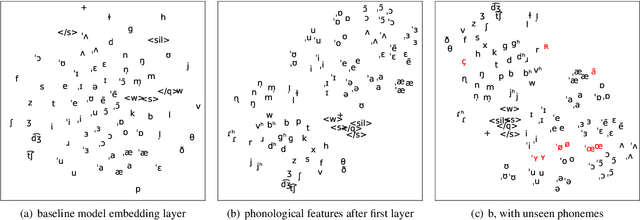

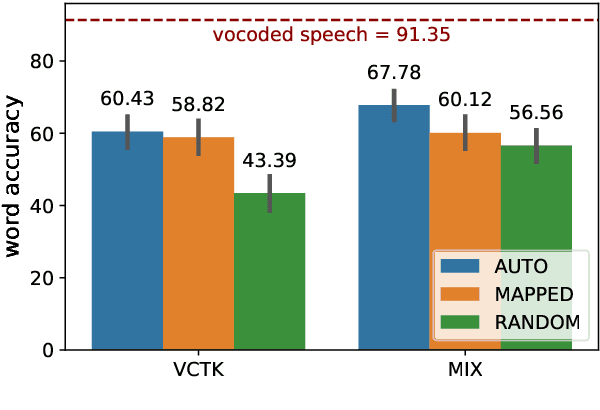
Abstract:Code-switching---the intra-utterance use of multiple languages---is prevalent across the world. Within text-to-speech (TTS), multilingual models have been found to enable code-switching. By modifying the linguistic input to sequence-to-sequence TTS, we show that code-switching is possible for languages unseen during training, even within monolingual models. We use a small set of phonological features derived from the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), such as vowel height and frontness, consonant place and manner. This allows the model topology to stay unchanged for different languages, and enables new, previously unseen feature combinations to be interpreted by the model. We show that this allows us to generate intelligible, code-switched speech in a new language at test time, including the approximation of sounds never seen in training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge