Phonological Features for 0-shot Multilingual Speech Synthesis
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2020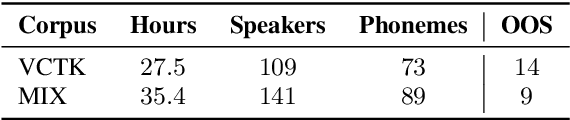
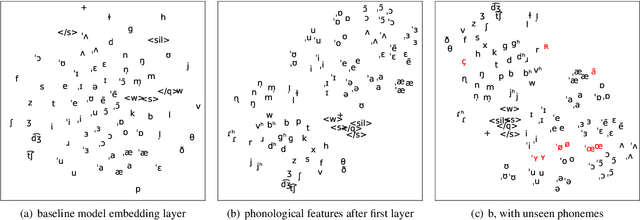

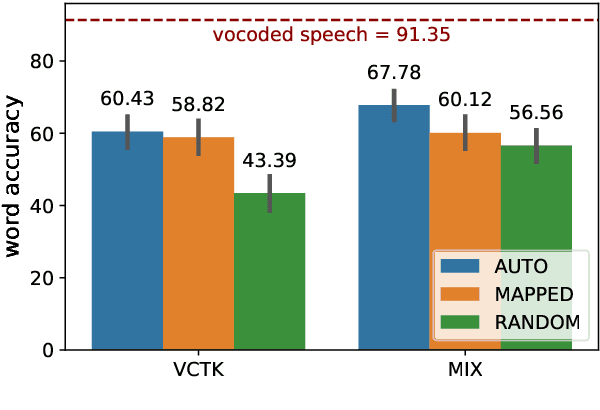
Code-switching---the intra-utterance use of multiple languages---is prevalent across the world. Within text-to-speech (TTS), multilingual models have been found to enable code-switching. By modifying the linguistic input to sequence-to-sequence TTS, we show that code-switching is possible for languages unseen during training, even within monolingual models. We use a small set of phonological features derived from the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), such as vowel height and frontness, consonant place and manner. This allows the model topology to stay unchanged for different languages, and enables new, previously unseen feature combinations to be interpreted by the model. We show that this allows us to generate intelligible, code-switched speech in a new language at test time, including the approximation of sounds never seen in training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge