Tengda Han
Learning from Streaming Video with Orthogonal Gradients
Apr 02, 2025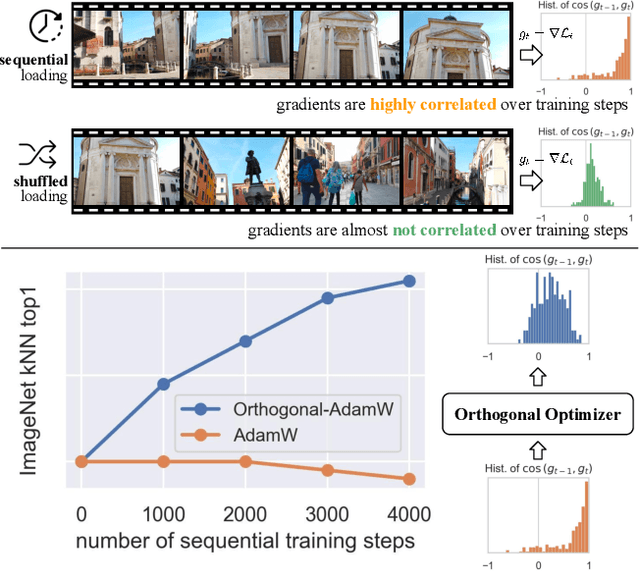
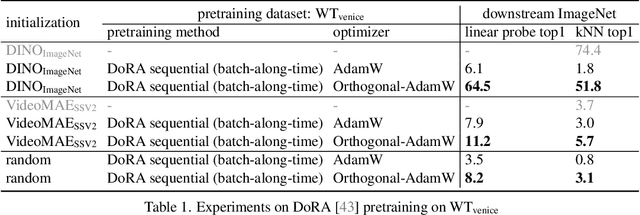
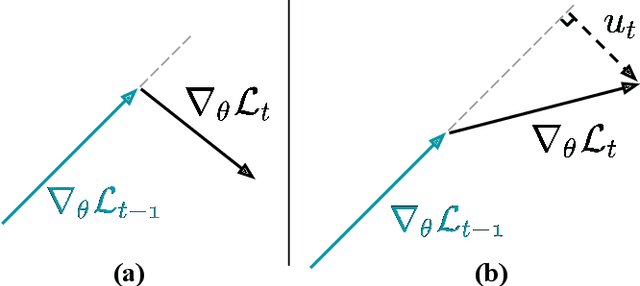
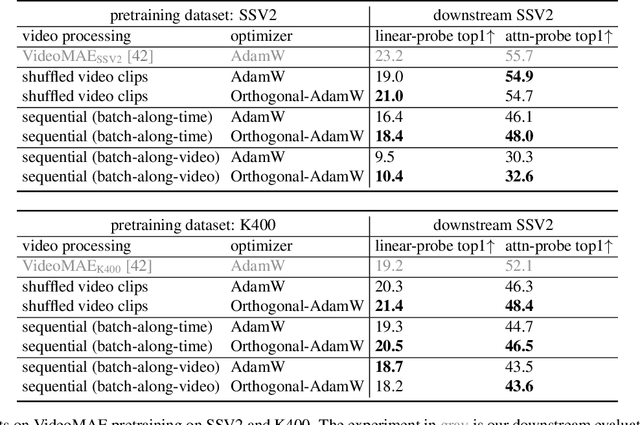
Abstract:We address the challenge of representation learning from a continuous stream of video as input, in a self-supervised manner. This differs from the standard approaches to video learning where videos are chopped and shuffled during training in order to create a non-redundant batch that satisfies the independently and identically distributed (IID) sample assumption expected by conventional training paradigms. When videos are only available as a continuous stream of input, the IID assumption is evidently broken, leading to poor performance. We demonstrate the drop in performance when moving from shuffled to sequential learning on three tasks: the one-video representation learning method DoRA, standard VideoMAE on multi-video datasets, and the task of future video prediction. To address this drop, we propose a geometric modification to standard optimizers, to decorrelate batches by utilising orthogonal gradients during training. The proposed modification can be applied to any optimizer -- we demonstrate it with Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) and AdamW. Our proposed orthogonal optimizer allows models trained from streaming videos to alleviate the drop in representation learning performance, as evaluated on downstream tasks. On three scenarios (DoRA, VideoMAE, future prediction), we show our orthogonal optimizer outperforms the strong AdamW in all three scenarios.
Shot-by-Shot: Film-Grammar-Aware Training-Free Audio Description Generation
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Our objective is the automatic generation of Audio Descriptions (ADs) for edited video material, such as movies and TV series. To achieve this, we propose a two-stage framework that leverages "shots" as the fundamental units of video understanding. This includes extending temporal context to neighbouring shots and incorporating film grammar devices, such as shot scales and thread structures, to guide AD generation. Our method is compatible with both open-source and proprietary Visual-Language Models (VLMs), integrating expert knowledge from add-on modules without requiring additional training of the VLMs. We achieve state-of-the-art performance among all prior training-free approaches and even surpass fine-tuned methods on several benchmarks. To evaluate the quality of predicted ADs, we introduce a new evaluation measure -- an action score -- specifically targeted to assessing this important aspect of AD. Additionally, we propose a novel evaluation protocol that treats automatic frameworks as AD generation assistants and asks them to generate multiple candidate ADs for selection.
It's Just Another Day: Unique Video Captioning by Discriminative Prompting
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Long videos contain many repeating actions, events and shots. These repetitions are frequently given identical captions, which makes it difficult to retrieve the exact desired clip using a text search. In this paper, we formulate the problem of unique captioning: Given multiple clips with the same caption, we generate a new caption for each clip that uniquely identifies it. We propose Captioning by Discriminative Prompting (CDP), which predicts a property that can separate identically captioned clips, and use it to generate unique captions. We introduce two benchmarks for unique captioning, based on egocentric footage and timeloop movies - where repeating actions are common. We demonstrate that captions generated by CDP improve text-to-video R@1 by 15% for egocentric videos and 10% in timeloop movies.
AutoAD-Zero: A Training-Free Framework for Zero-Shot Audio Description
Jul 22, 2024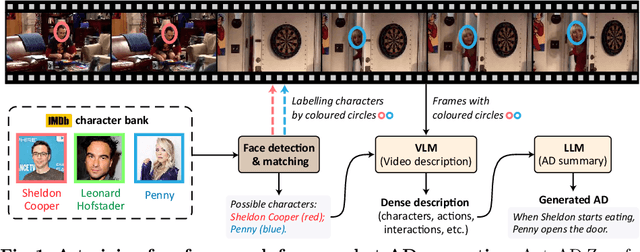

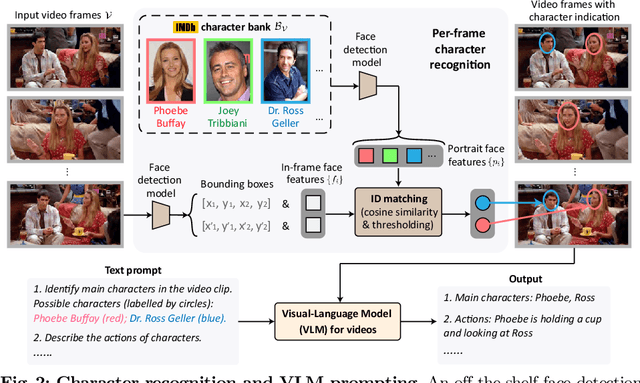

Abstract:Our objective is to generate Audio Descriptions (ADs) for both movies and TV series in a training-free manner. We use the power of off-the-shelf Visual-Language Models (VLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs), and develop visual and text prompting strategies for this task. Our contributions are three-fold: (i) We demonstrate that a VLM can successfully name and refer to characters if directly prompted with character information through visual indications without requiring any fine-tuning; (ii) A two-stage process is developed to generate ADs, with the first stage asking the VLM to comprehensively describe the video, followed by a second stage utilising a LLM to summarise dense textual information into one succinct AD sentence; (iii) A new dataset for TV audio description is formulated. Our approach, named AutoAD-Zero, demonstrates outstanding performance (even competitive with some models fine-tuned on ground truth ADs) in AD generation for both movies and TV series, achieving state-of-the-art CRITIC scores.
CountGD: Multi-Modal Open-World Counting
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:The goal of this paper is to improve the generality and accuracy of open-vocabulary object counting in images. To improve the generality, we repurpose an open-vocabulary detection foundation model (GroundingDINO) for the counting task, and also extend its capabilities by introducing modules to enable specifying the target object to count by visual exemplars. In turn, these new capabilities - being able to specify the target object by multi-modalites (text and exemplars) - lead to an improvement in counting accuracy. We make three contributions: First, we introduce the first open-world counting model, CountGD, where the prompt can be specified by a text description or visual exemplars or both; Second, we show that the performance of the model significantly improves the state of the art on multiple counting benchmarks - when using text only, CountGD is comparable to or outperforms all previous text-only works, and when using both text and visual exemplars, we outperform all previous models; Third, we carry out a preliminary study into different interactions between the text and visual exemplar prompts, including the cases where they reinforce each other and where one restricts the other. The code and an app to test the model are available at https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/countgd/.
AutoAD III: The Prequel -- Back to the Pixels
Apr 22, 2024Abstract:Generating Audio Description (AD) for movies is a challenging task that requires fine-grained visual understanding and an awareness of the characters and their names. Currently, visual language models for AD generation are limited by a lack of suitable training data, and also their evaluation is hampered by using performance measures not specialized to the AD domain. In this paper, we make three contributions: (i) We propose two approaches for constructing AD datasets with aligned video data, and build training and evaluation datasets using these. These datasets will be publicly released; (ii) We develop a Q-former-based architecture which ingests raw video and generates AD, using frozen pre-trained visual encoders and large language models; and (iii) We provide new evaluation metrics to benchmark AD quality that are well-matched to human performance. Taken together, we improve the state of the art on AD generation.
Stale Diffusion: Hyper-realistic 5D Movie Generation Using Old-school Methods
Apr 01, 2024
Abstract:Two years ago, Stable Diffusion achieved super-human performance at generating images with super-human numbers of fingers. Following the steady decline of its technical novelty, we propose Stale Diffusion, a method that solidifies and ossifies Stable Diffusion in a maximum-entropy state. Stable Diffusion works analogously to a barn (the Stable) from which an infinite set of horses have escaped (the Diffusion). As the horses have long left the barn, our proposal may be seen as antiquated and irrelevant. Nevertheless, we vigorously defend our claim of novelty by identifying as early adopters of the Slow Science Movement, which will produce extremely important pearls of wisdom in the future. Our speed of contributions can also be seen as a quasi-static implementation of the recent call to pause AI experiments, which we wholeheartedly support. As a result of a careful archaeological expedition to 18-months-old Git commit histories, we found that naturally-accumulating errors have produced a novel entropy-maximising Stale Diffusion method, that can produce sleep-inducing hyper-realistic 5D video that is as good as one's imagination.
A Strong Baseline for Temporal Video-Text Alignment
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we consider the problem of temporally aligning the video and texts from instructional videos, specifically, given a long-term video, and associated text sentences, our goal is to determine their corresponding timestamps in the video. To this end, we establish a simple, yet strong model that adopts a Transformer-based architecture with all texts as queries, iteratively attending to the visual features, to infer the optimal timestamp. We conduct thorough experiments to investigate: (i) the effect of upgrading ASR systems to reduce errors from speech recognition, (ii) the effect of various visual-textual backbones, ranging from CLIP to S3D, to the more recent InternVideo, (iii) the effect of transforming noisy ASR transcripts into descriptive steps by prompting a large language model (LLM), to summarize the core activities within the ASR transcript as a new training dataset. As a result, our proposed simple model demonstrates superior performance on both narration alignment and procedural step grounding tasks, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods by a significant margin on three public benchmarks, namely, 9.3% on HT-Step, 3.4% on HTM-Align and 4.7% on CrossTask. We believe the proposed model and dataset with descriptive steps can be treated as a strong baseline for future research in temporal video-text alignment. All codes, models, and the resulting dataset will be publicly released to the research community.
AutoAD II: The Sequel -- Who, When, and What in Movie Audio Description
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:Audio Description (AD) is the task of generating descriptions of visual content, at suitable time intervals, for the benefit of visually impaired audiences. For movies, this presents notable challenges -- AD must occur only during existing pauses in dialogue, should refer to characters by name, and ought to aid understanding of the storyline as a whole. To this end, we develop a new model for automatically generating movie AD, given CLIP visual features of the frames, the cast list, and the temporal locations of the speech; addressing all three of the 'who', 'when', and 'what' questions: (i) who -- we introduce a character bank consisting of the character's name, the actor that played the part, and a CLIP feature of their face, for the principal cast of each movie, and demonstrate how this can be used to improve naming in the generated AD; (ii) when -- we investigate several models for determining whether an AD should be generated for a time interval or not, based on the visual content of the interval and its neighbours; and (iii) what -- we implement a new vision-language model for this task, that can ingest the proposals from the character bank, whilst conditioning on the visual features using cross-attention, and demonstrate how this improves over previous architectures for AD text generation in an apples-to-apples comparison.
Semantic Counting from Self-Collages
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:While recent supervised methods for reference-based object counting continue to improve the performance on benchmark datasets, they have to rely on small datasets due to the cost associated with manually annotating dozens of objects in images. We propose Unsupervised Counter (UnCo), a model that can learn this task without requiring any manual annotations. To this end, we construct "SelfCollages", images with various pasted objects as training samples, that provide a rich learning signal covering arbitrary object types and counts. Our method builds on existing unsupervised representations and segmentation techniques to successfully demonstrate the ability to count objects without manual supervision. Our experiments show that our method not only outperforms simple baselines and generic models such as FasterRCNN, but also matches the performance of supervised counting models in some domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge