Qirui Chen
Weaver: End-to-End Agentic System Training for Video Interleaved Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Video reasoning constitutes a comprehensive assessment of a model's capabilities, as it demands robust perceptual and interpretive skills, thereby serving as a means to explore the boundaries of model performance. While recent research has leveraged text-centric Chain-of-Thought reasoning to augment these capabilities, such approaches frequently suffer from representational mismatch and restricted by limited perceptual acuity. To address these limitations, we propose Weaver, a novel, end-to-end trainable multimodal reasoning agentic system. Weaver empowers its policy model to dynamically invoke diverse tools throughout the reasoning process, enabling progressive acquisition of crucial visual cues and construction of authentic multimodal reasoning trajectories. Furthermore, we integrate a reinforcement learning algorithm to allow the system to freely explore strategies for employing and combining these tools with trajectory-free data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our system, Weaver, enhances performance on several complex video reasoning benchmarks, particularly those involving long videos.
HardSecBench: Benchmarking the Security Awareness of LLMs for Hardware Code Generation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are being increasingly integrated into practical hardware and firmware development pipelines for code generation. Existing studies have primarily focused on evaluating the functional correctness of LLM-generated code, yet paid limited attention to its security issues. However, LLM-generated code that appears functionally sound may embed security flaws which could induce catastrophic damages after deployment. This critical research gap motivates us to design a benchmark for assessing security awareness under realistic specifications. In this work, we introduce HardSecBench, a benchmark with 924 tasks spanning Verilog Register Transfer Level (RTL) and firmware-level C, covering 76 hardware-relevant Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) entries. Each task includes a structured specification, a secure reference implementation, and executable tests. To automate artifact synthesis, we propose a multi-agent pipeline that decouples synthesis from verification and grounds evaluation in execution evidence, enabling reliable evaluation. Using HardSecBench, we evaluate a range of LLMs on hardware and firmware code generation and find that models often satisfy functional requirements while still leaving security risks. We also find that security results vary with prompting. These findings highlight pressing challenges and offer actionable insights for future advancements in LLM-assisted hardware design. Our data and code will be released soon.
Learning Streaming Video Representation via Multitask Training
Apr 28, 2025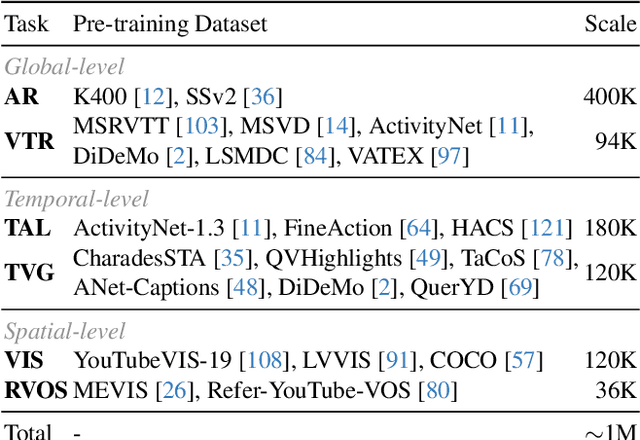
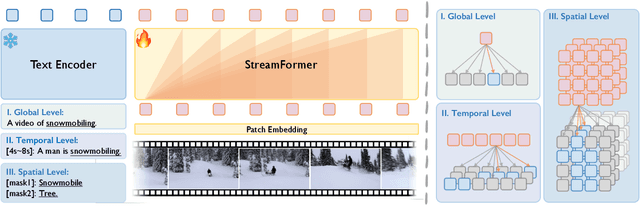
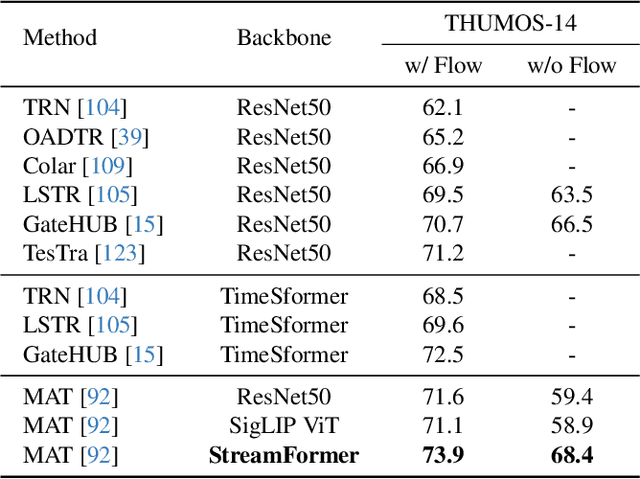
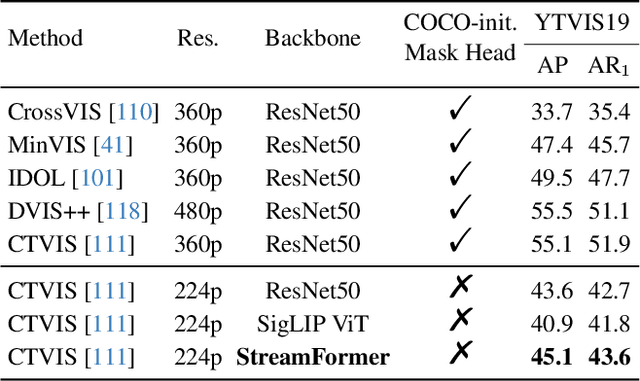
Abstract:Understanding continuous video streams plays a fundamental role in real-time applications including embodied AI and autonomous driving. Unlike offline video understanding, streaming video understanding requires the ability to process video streams frame by frame, preserve historical information, and make low-latency decisions.To address these challenges, our main contributions are three-fold. (i) We develop a novel streaming video backbone, termed as StreamFormer, by incorporating causal temporal attention into a pre-trained vision transformer. This enables efficient streaming video processing while maintaining image representation capability.(ii) To train StreamFormer, we propose to unify diverse spatial-temporal video understanding tasks within a multitask visual-language alignment framework. Hence, StreamFormer learns global semantics, temporal dynamics, and fine-grained spatial relationships simultaneously. (iii) We conduct extensive experiments on online action detection, online video instance segmentation, and video question answering. StreamFormer achieves competitive results while maintaining efficiency, demonstrating its potential for real-time applications.
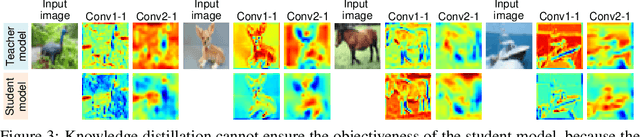
Unlocking Video-LLM via Agent-of-Thoughts Distillation
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:This paper tackles the problem of video question answering (VideoQA), a task that often requires multi-step reasoning and a profound understanding of spatial-temporal dynamics. While large video-language models perform well on benchmarks, they often lack explainability and spatial-temporal grounding. In this paper, we propose Agent-of-Thoughts Distillation (AoTD), a method that enhances models by incorporating automatically generated Chain-of-Thoughts (CoTs) into the instruction-tuning process. Specifically, we leverage an agent-based system to decompose complex questions into sub-tasks, and address them with specialized vision models, the intermediate results are then treated as reasoning chains. We also introduce a verification mechanism using a large language model (LLM) to ensure the reliability of generated CoTs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AoTD improves the performance on multiple-choice and open-ended benchmarks.
Grounded Multi-Hop VideoQA in Long-Form Egocentric Videos
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:This paper considers the problem of Multi-Hop Video Question Answering (MH-VidQA) in long-form egocentric videos. This task not only requires to answer visual questions, but also to localize multiple relevant time intervals within the video as visual evidences. We develop an automated pipeline to create multi-hop question-answering pairs with associated temporal evidence, enabling to construct a large-scale dataset for instruction-tuning. To monitor the progress of this new task, we further curate a high-quality benchmark, MultiHop-EgoQA, with careful manual verification and refinement. Experimental results reveal that existing multi-modal systems exhibit inadequate multi-hop grounding and reasoning abilities, resulting in unsatisfactory performance. We then propose a novel architecture, termed as Grounding Scattered Evidence with Large Language Model (GeLM), that enhances multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) by incorporating a grounding module to retrieve temporal evidence from videos using flexible grounding tokens. Trained on our visual instruction data, GeLM demonstrates improved multi-hop grounding and reasoning capabilities, setting a new baseline for this challenging task. Furthermore, when trained on third-person view videos, the same architecture also achieves state-of-the-art performance on the single-hop VidQA benchmark, ActivityNet-RTL, demonstrating its effectiveness.
A Strong Baseline for Temporal Video-Text Alignment
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we consider the problem of temporally aligning the video and texts from instructional videos, specifically, given a long-term video, and associated text sentences, our goal is to determine their corresponding timestamps in the video. To this end, we establish a simple, yet strong model that adopts a Transformer-based architecture with all texts as queries, iteratively attending to the visual features, to infer the optimal timestamp. We conduct thorough experiments to investigate: (i) the effect of upgrading ASR systems to reduce errors from speech recognition, (ii) the effect of various visual-textual backbones, ranging from CLIP to S3D, to the more recent InternVideo, (iii) the effect of transforming noisy ASR transcripts into descriptive steps by prompting a large language model (LLM), to summarize the core activities within the ASR transcript as a new training dataset. As a result, our proposed simple model demonstrates superior performance on both narration alignment and procedural step grounding tasks, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods by a significant margin on three public benchmarks, namely, 9.3% on HT-Step, 3.4% on HTM-Align and 4.7% on CrossTask. We believe the proposed model and dataset with descriptive steps can be treated as a strong baseline for future research in temporal video-text alignment. All codes, models, and the resulting dataset will be publicly released to the research community.
Towards Axiomatic, Hierarchical, and Symbolic Explanation for Deep Models
Nov 30, 2021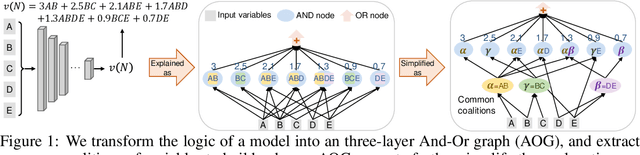
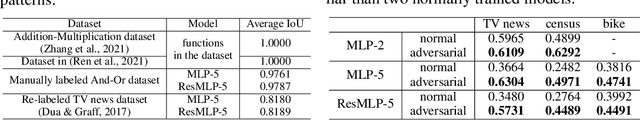
Abstract:This paper proposes a hierarchical and symbolic And-Or graph (AOG) to objectively explain the internal logic encoded by a well-trained deep model for inference. We first define the objectiveness of an explainer model in game theory, and we develop a rigorous representation of the And-Or logic encoded by the deep model. The objectiveness and trustworthiness of the AOG explainer are both theoretically guaranteed and experimentally verified. Furthermore, we propose several techniques to boost the conciseness of the explanation.
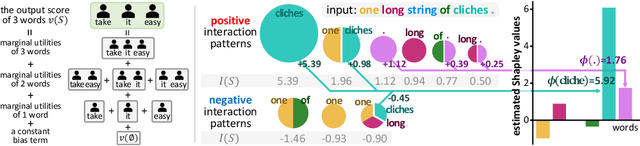
Learning Baseline Values for Shapley Values
May 22, 2021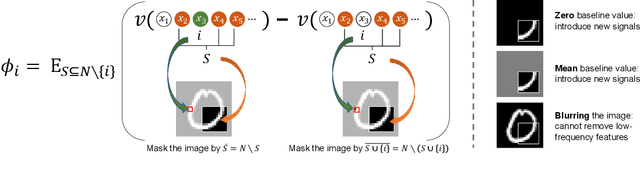



Abstract:This paper aims to formulate the problem of estimating the optimal baseline values for the Shapley value in game theory. The Shapley value measures the attribution of each input variable of a complex model, which is computed as the marginal benefit from the presence of this variable w.r.t.its absence under different contexts. To this end, people usually set the input variable to its baseline value to represent the absence of this variable (i.e.the no-signal state of this variable). Previous studies usually determine the baseline values in an empirical manner, which hurts the trustworthiness of the Shapley value. In this paper, we revisit the feature representation of a deep model from the perspective of game theory, and define the multi-variate interaction patterns of input variables to define the no-signal state of an input variable. Based on the multi-variate interaction, we learn the optimal baseline value of each input variable. Experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge