Tamaz Amiranashvili
Energy Matching: Unifying Flow Matching and Energy-Based Models for Generative Modeling
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Generative models often map noise to data by matching flows or scores, but these approaches become cumbersome for incorporating partial observations or additional priors. Inspired by recent advances in Wasserstein gradient flows, we propose Energy Matching, a framework that unifies flow-based approaches with the flexibility of energy-based models (EBMs). Far from the data manifold, samples move along curl-free, optimal transport paths from noise to data. As they approach the data manifold, an entropic energy term guides the system into a Boltzmann equilibrium distribution, explicitly capturing the underlying likelihood structure of the data. We parameterize this dynamic with a single time-independent scalar field, which serves as both a powerful generator and a flexible prior for effective regularization of inverse problems. Our method substantially outperforms existing EBMs on CIFAR-10 generation (FID 3.97 compared to 8.61), while retaining the simulation-free training of transport-based approaches away from the data manifold. Additionally, we exploit the flexibility of our method and introduce an interaction energy for diverse mode exploration. Our approach focuses on learning a static scalar potential energy -- without time conditioning, auxiliary generators, or additional networks -- marking a significant departure from recent EBM methods. We believe this simplified framework significantly advances EBM capabilities and paves the way for their broader adoption in generative modeling across diverse domains.
vesselFM: A Foundation Model for Universal 3D Blood Vessel Segmentation
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Segmenting 3D blood vessels is a critical yet challenging task in medical image analysis. This is due to significant imaging modality-specific variations in artifacts, vascular patterns and scales, signal-to-noise ratios, and background tissues. These variations, along with domain gaps arising from varying imaging protocols, limit the generalization of existing supervised learning-based methods, requiring tedious voxel-level annotations for each dataset separately. While foundation models promise to alleviate this limitation, they typically fail to generalize to the task of blood vessel segmentation, posing a unique, complex problem. In this work, we present vesselFM, a foundation model designed specifically for the broad task of 3D blood vessel segmentation. Unlike previous models, vesselFM can effortlessly generalize to unseen domains. To achieve zero-shot generalization, we train vesselFM on three heterogeneous data sources: a large, curated annotated dataset, data generated by a domain randomization scheme, and data sampled from a flow matching-based generative model. Extensive evaluations show that vesselFM outperforms state-of-the-art medical image segmentation foundation models across four (pre-)clinically relevant imaging modalities in zero-, one-, and few-shot scenarios, therefore providing a universal solution for 3D blood vessel segmentation.
Physics-Regularized Multi-Modal Image Assimilation for Brain Tumor Localization
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Physical models in the form of partial differential equations represent an important prior for many under-constrained problems. One example is tumor treatment planning, which heavily depends on accurate estimates of the spatial distribution of tumor cells in a patient's anatomy. Medical imaging scans can identify the bulk of the tumor, but they cannot reveal its full spatial distribution. Tumor cells at low concentrations remain undetectable, for example, in the most frequent type of primary brain tumors, glioblastoma. Deep-learning-based approaches fail to estimate the complete tumor cell distribution due to a lack of reliable training data. Most existing works therefore rely on physics-based simulations to match observed tumors, providing anatomically and physiologically plausible estimations. However, these approaches struggle with complex and unknown initial conditions and are limited by overly rigid physical models. In this work, we present a novel method that balances data-driven and physics-based cost functions. In particular, we propose a unique discretization scheme that quantifies the adherence of our learned spatiotemporal tumor and brain tissue distributions to their corresponding growth and elasticity equations. This quantification, serving as a regularization term rather than a hard constraint, enables greater flexibility and proficiency in assimilating patient data than existing models. We demonstrate improved coverage of tumor recurrence areas compared to existing techniques on real-world data from a cohort of patients. The method holds the potential to enhance clinical adoption of model-driven treatment planning for glioblastoma.
3D Vessel Graph Generation Using Denoising Diffusion
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Blood vessel networks, represented as 3D graphs, help predict disease biomarkers, simulate blood flow, and aid in synthetic image generation, relevant in both clinical and pre-clinical settings. However, generating realistic vessel graphs that correspond to an anatomy of interest is challenging. Previous methods aimed at generating vessel trees mostly in an autoregressive style and could not be applied to vessel graphs with cycles such as capillaries or specific anatomical structures such as the Circle of Willis. Addressing this gap, we introduce the first application of \textit{denoising diffusion models} in 3D vessel graph generation. Our contributions include a novel, two-stage generation method that sequentially denoises node coordinates and edges. We experiment with two real-world vessel datasets, consisting of microscopic capillaries and major cerebral vessels, and demonstrate the generalizability of our method for producing diverse, novel, and anatomically plausible vessel graphs.
Probabilistic Contrastive Learning with Explicit Concentration on the Hypersphere
May 26, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised contrastive learning has predominantly adopted deterministic methods, which are not suited for environments characterized by uncertainty and noise. This paper introduces a new perspective on incorporating uncertainty into contrastive learning by embedding representations within a spherical space, inspired by the von Mises-Fisher distribution (vMF). We introduce an unnormalized form of vMF and leverage the concentration parameter, kappa, as a direct, interpretable measure to quantify uncertainty explicitly. This approach not only provides a probabilistic interpretation of the embedding space but also offers a method to calibrate model confidence against varying levels of data corruption and characteristics. Our empirical results demonstrate that the estimated concentration parameter correlates strongly with the degree of unforeseen data corruption encountered at test time, enables failure analysis, and enhances existing out-of-distribution detection methods.
Simulation-Based Segmentation of Blood Vessels in Cerebral 3D OCTA Images
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:Segmentation of blood vessels in murine cerebral 3D OCTA images is foundational for in vivo quantitative analysis of the effects of neurovascular disorders, such as stroke or Alzheimer's, on the vascular network. However, to accurately segment blood vessels with state-of-the-art deep learning methods, a vast amount of voxel-level annotations is required. Since cerebral 3D OCTA images are typically plagued by artifacts and generally have a low signal-to-noise ratio, acquiring manual annotations poses an especially cumbersome and time-consuming task. To alleviate the need for manual annotations, we propose utilizing synthetic data to supervise segmentation algorithms. To this end, we extract patches from vessel graphs and transform them into synthetic cerebral 3D OCTA images paired with their matching ground truth labels by simulating the most dominant 3D OCTA artifacts. In extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our approach achieves competitive results, enabling annotation-free blood vessel segmentation in cerebral 3D OCTA images.
A Domain-specific Perceptual Metric via Contrastive Self-supervised Representation: Applications on Natural and Medical Images
Dec 03, 2022



Abstract:Quantifying the perceptual similarity of two images is a long-standing problem in low-level computer vision. The natural image domain commonly relies on supervised learning, e.g., a pre-trained VGG, to obtain a latent representation. However, due to domain shift, pre-trained models from the natural image domain might not apply to other image domains, such as medical imaging. Notably, in medical imaging, evaluating the perceptual similarity is exclusively performed by specialists trained extensively in diverse medical fields. Thus, medical imaging remains devoid of task-specific, objective perceptual measures. This work answers the question: Is it necessary to rely on supervised learning to obtain an effective representation that could measure perceptual similarity, or is self-supervision sufficient? To understand whether recent contrastive self-supervised representation (CSR) may come to the rescue, we start with natural images and systematically evaluate CSR as a metric across numerous contemporary architectures and tasks and compare them with existing methods. We find that in the natural image domain, CSR behaves on par with the supervised one on several perceptual tests as a metric, and in the medical domain, CSR better quantifies perceptual similarity concerning the experts' ratings. We also demonstrate that CSR can significantly improve image quality in two image synthesis tasks. Finally, our extensive results suggest that perceptuality is an emergent property of CSR, which can be adapted to many image domains without requiring annotations.
Landmark-free Statistical Shape Modeling via Neural Flow Deformations
Sep 14, 2022

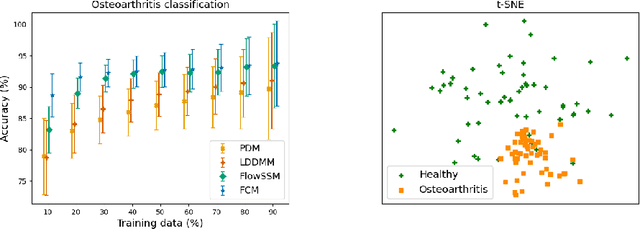
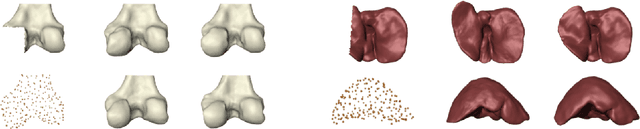
Abstract:Statistical shape modeling aims at capturing shape variations of an anatomical structure that occur within a given population. Shape models are employed in many tasks, such as shape reconstruction and image segmentation, but also shape generation and classification. Existing shape priors either require dense correspondence between training examples or lack robustness and topological guarantees. We present FlowSSM, a novel shape modeling approach that learns shape variability without requiring dense correspondence between training instances. It relies on a hierarchy of continuous deformation flows, which are parametrized by a neural network. Our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods in providing an expressive and robust shape prior for distal femur and liver. We show that the emerging latent representation is discriminative by separating healthy from pathological shapes. Ultimately, we demonstrate its effectiveness on two shape reconstruction tasks from partial data. Our source code is publicly available (https://github.com/davecasp/flowssm).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge