Taehee Kim
Can Tool-augmented Large Language Models be Aware of Incomplete Conditions?
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in integrating large language models (LLMs) with tools have allowed the models to interact with real-world environments. However, these tool-augmented LLMs often encounter incomplete scenarios when users provide partial information or the necessary tools are unavailable. Recognizing and managing such scenarios is crucial for LLMs to ensure their reliability, but this exploration remains understudied. This study examines whether LLMs can identify incomplete conditions and appropriately determine when to refrain from using tools. To this end, we address a dataset by manipulating instances from two datasets by removing necessary tools or essential information for tool invocation. We confirm that most LLMs are challenged to identify the additional information required to utilize specific tools and the absence of appropriate tools. Our research can contribute to advancing reliable LLMs by addressing scenarios that commonly arise during interactions between humans and LLMs.
Pretraining Vision-Language Model for Difference Visual Question Answering in Longitudinal Chest X-rays
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Difference visual question answering (diff-VQA) is a challenging task that requires answering complex questions based on differences between a pair of images. This task is particularly important in reading chest X-ray images because radiologists often compare multiple images of the same patient taken at different times to track disease progression and changes in its severity in their clinical practice. However, previous works focused on designing specific network architectures for the diff-VQA task, missing opportunities to enhance the model's performance using a pretrained vision-language model (VLM). Here, we introduce a novel VLM called PLURAL, which is pretrained on natural and longitudinal chest X-ray data for the diff-VQA task. The model is developed using a step-by-step approach, starting with being pretrained on natural images and texts, followed by being trained using longitudinal chest X-ray data. The longitudinal data consist of pairs of X-ray images, along with question-answer sets and radiologist's reports that describe the changes in lung abnormalities and diseases over time. Our experimental results show that the PLURAL model outperforms state-of-the-art methods not only in diff-VQA for longitudinal X-rays but also in conventional VQA for a single X-ray image. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed VLM architecture and pretraining method in improving the model's performance.
Generalizing Visual Question Answering from Synthetic to Human-Written Questions via a Chain of QA with a Large Language Model
Jan 16, 2024



Abstract:Visual question answering (VQA) is a task where an image is given, and a series of questions are asked about the image. To build an efficient VQA algorithm, a large amount of QA data is required which is very expensive. Generating synthetic QA pairs based on templates is a practical way to obtain data. However, VQA models trained on those data do not perform well on complex, human-written questions. To address this issue, we propose a new method called {\it chain of QA for human-written questions} (CoQAH). CoQAH utilizes a sequence of QA interactions between a large language model and a VQA model trained on synthetic data to reason and derive logical answers for human-written questions. We tested the effectiveness of CoQAH on two types of human-written VQA datasets for 3D-rendered and chest X-ray images and found that it achieved state-of-the-art accuracy in both types of data. Notably, CoQAH outperformed general vision-language models, VQA models, and medical foundation models with no finetuning.
Fast and accurate sparse-view CBCT reconstruction using meta-learned neural attenuation field and hash-encoding regularization
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is an emerging medical imaging technique to visualize the internal anatomical structures of patients. During a CBCT scan, several projection images of different angles or views are collectively utilized to reconstruct a tomographic image. However, reducing the number of projections in a CBCT scan while preserving the quality of a reconstructed image is challenging due to the nature of an ill-posed inverse problem. Recently, a neural attenuation field (NAF) method was proposed by adopting a neural radiance field algorithm as a new way for CBCT reconstruction, demonstrating fast and promising results using only 50 views. However, decreasing the number of projections is still preferable to reduce potential radiation exposure, and a faster reconstruction time is required considering a typical scan time. In this work, we propose a fast and accurate sparse-view CBCT reconstruction (FACT) method to provide better reconstruction quality and faster optimization speed in the minimal number of view acquisitions ($<$ 50 views). In the FACT method, we meta-trained a neural network and a hash-encoder using a few scans (= 15), and a new regularization technique is utilized to reconstruct the details of an anatomical structure. In conclusion, we have shown that the FACT method produced better, and faster reconstruction results over the other conventional algorithms based on CBCT scans of different body parts (chest, head, and abdomen) and CT vendors (Siemens, Phillips, and GE).
Correlation-Driven Multi-Level Multimodal Learning for Anomaly Detection on Multiple Energy Sources
May 01, 2023Abstract:Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) has been widely used as an intelligent energy consumption measurement system. Electric power was the representative energy source that can be collected by AMI; most existing studies to detect abnormal energy consumption have focused on a single energy source, i.e., power. Recently, other energy sources such as water, gas, and heating have also been actively collected. As a result, it is necessary to develop a unified methodology for anomaly detection across multiple energy sources; however, research efforts have rarely been made to tackle this issue. The inherent difficulty with this issue stems from the fact that anomalies are not usually annotated. Moreover, existing works of anomaly definition depend on only individual energy sources. In this paper, we first propose a method for defining anomalies considering not only individual energy sources but also correlations between them. Then, we propose a new Correlation-driven Multi-Level Multimodal Learning model for anomaly detection on multiple energy sources. The distinguishing property of the model incorporates multiple energy sources in multi-levels based on the strengths of the correlations between them. Furthermore, we generalize the proposed model in order to integrate arbitrary new energy sources with further performance improvement, considering not only correlated but also non-correlated sources. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets consisting of three to five energy sources, we demonstrate that the proposed model clearly outperforms the existing multimodal learning and recent time-series anomaly detection models, and we observe that our model makes further the performance improvement as more correlated or non-correlated energy sources are integrated.
PePe: Personalized Post-editing Model utilizing User-generated Post-edits
Sep 21, 2022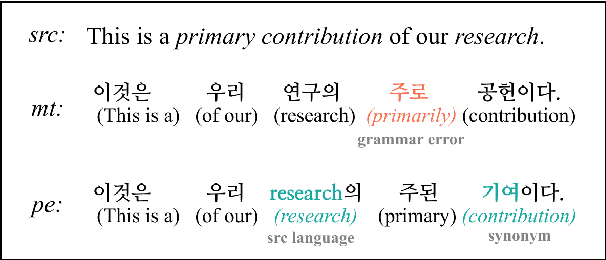
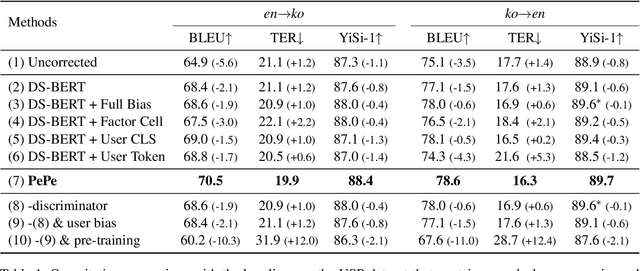
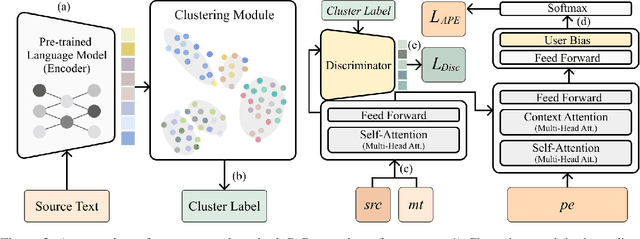
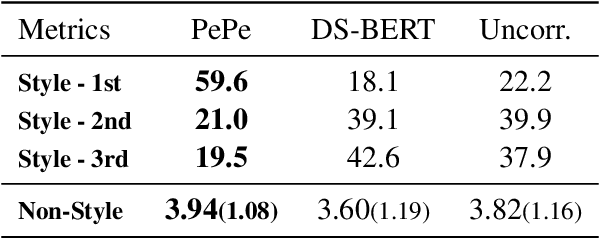
Abstract:Incorporating personal preference is crucial in advanced machine translation tasks. Despite the recent advancement of machine translation, it remains a demanding task to properly reflect personal style. In this paper, we introduce a personalized automatic post-editing framework to address this challenge, which effectively generates sentences considering distinct personal behaviors. To build this framework, we first collect post-editing data that connotes the user preference from a live machine translation system. Specifically, real-world users enter source sentences for translation and edit the machine-translated outputs according to the user's preferred style. We then propose a model that combines a discriminator module and user-specific parameters on the APE framework. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other baseline models on four different metrics (i.e., BLEU, TER, YiSi-1, and human evaluation).
Reweighting Strategy based on Synthetic Data Identification for Sentence Similarity
Aug 30, 2022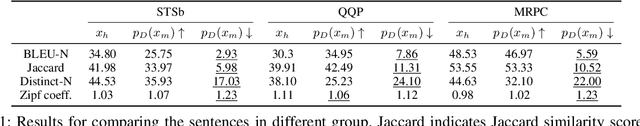
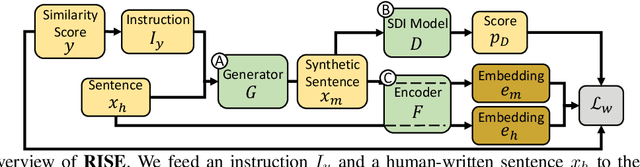

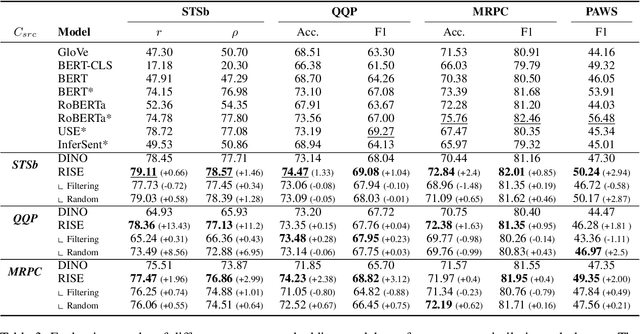
Abstract:Semantically meaningful sentence embeddings are important for numerous tasks in natural language processing. To obtain such embeddings, recent studies explored the idea of utilizing synthetically generated data from pretrained language models (PLMs) as a training corpus. However, PLMs often generate sentences much different from the ones written by human. We hypothesize that treating all these synthetic examples equally for training deep neural networks can have an adverse effect on learning semantically meaningful embeddings. To analyze this, we first train a classifier that identifies machine-written sentences, and observe that the linguistic features of the sentences identified as written by a machine are significantly different from those of human-written sentences. Based on this, we propose a novel approach that first trains the classifier to measure the importance of each sentence. The distilled information from the classifier is then used to train a reliable sentence embedding model. Through extensive evaluation on four real-world datasets, we demonstrate that our model trained on synthetic data generalizes well and outperforms the existing baselines. Our implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/ddehun/coling2022_reweighting_sts.
AVocaDo: Strategy for Adapting Vocabulary to Downstream Domain
Oct 26, 2021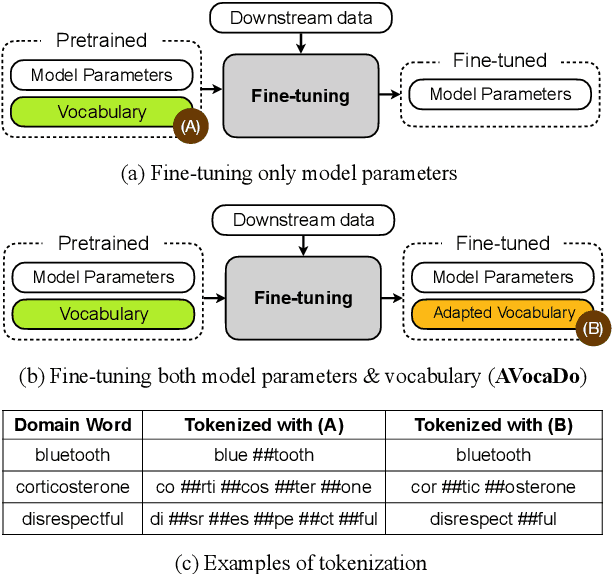
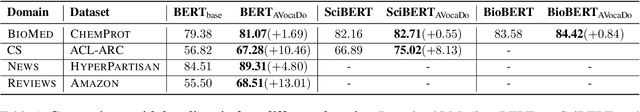
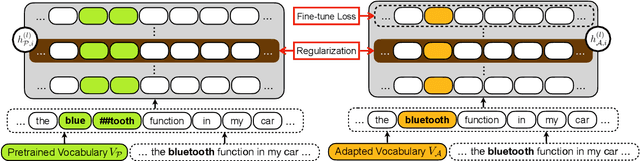
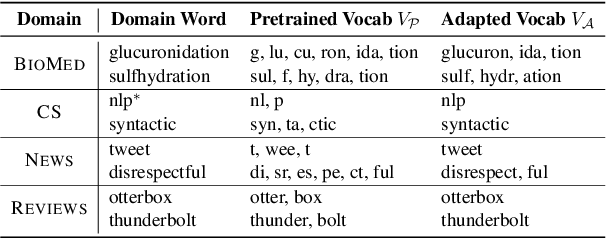
Abstract:During the fine-tuning phase of transfer learning, the pretrained vocabulary remains unchanged, while model parameters are updated. The vocabulary generated based on the pretrained data is suboptimal for downstream data when domain discrepancy exists. We propose to consider the vocabulary as an optimizable parameter, allowing us to update the vocabulary by expanding it with domain-specific vocabulary based on a tokenization statistic. Furthermore, we preserve the embeddings of the added words from overfitting to downstream data by utilizing knowledge learned from a pretrained language model with a regularization term. Our method achieved consistent performance improvements on diverse domains (i.e., biomedical, computer science, news, and reviews).
Meta-Learning for Low-Resource Unsupervised Neural MachineTranslation
Oct 18, 2020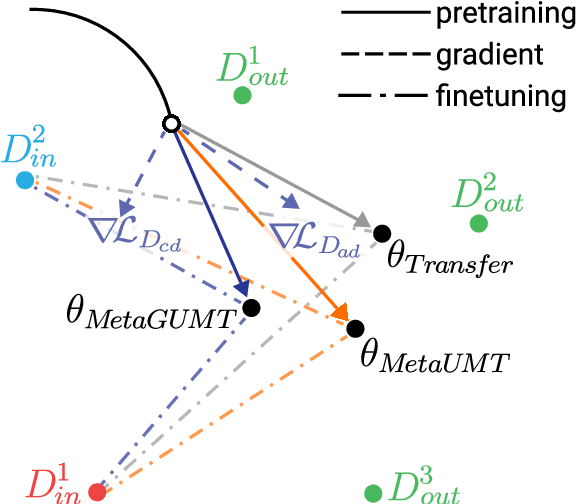
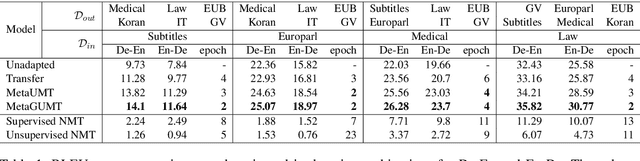
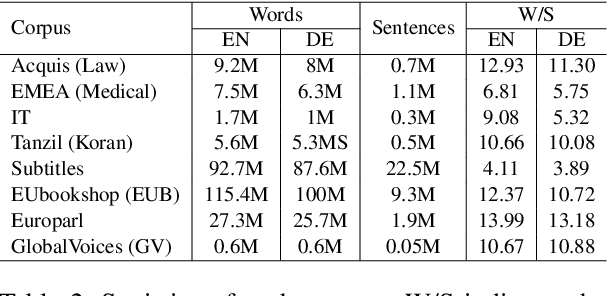

Abstract:Unsupervised machine translation, which utilizes unpaired monolingual corpora as training data, has achieved comparable performance against supervised machine translation. However, it still suffers from data-scarce domains. To address this issue, this paper presents a meta-learning algorithm for unsupervised neural machine translation (UNMT) that trains the model to adapt to another domain by utilizing only a small amount of training data. We assume that domain-general knowledge is a significant factor in handling data-scarce domains. Hence, we extend the meta-learning algorithm, which utilizes knowledge learned from high-resource domains to boost the performance of low-resource UNMT. Our model surpasses a transfer learning-based approach by up to 2-4 BLEU scores. Extensive experimental results show that our proposed algorithm is pertinent for fast adaptation and consistently outperforms other baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge