Sungzoon Cho
PsyProbe: Proactive and Interpretable Dialogue through User State Modeling for Exploratory Counseling
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have enabled mental health dialogue systems, yet existing approaches remain predominantly reactive, lacking systematic user state modeling for proactive therapeutic exploration. We introduce PsyProbe, a dialogue system designed for the exploration phase of counseling that systematically tracks user psychological states through the PPPPPI framework (Presenting, Predisposing, Precipitating, Perpetuating, Protective, Impact) augmented with cognitive error detection. PsyProbe combines State Builder for extracting structured psychological profiles, Memory Construction for tracking information gaps, Strategy Planner for Motivational Interviewing behavioral codes, and Response Generator with Question Ideation and Critic/Revision modules to generate contextually appropriate, proactive questions. We evaluate PsyProbe with 27 participants in real-world Korean counseling scenarios, including automatic evaluation across ablation modes, user evaluation, and expert evaluation by a certified counselor. The full PsyProbe model consistently outperforms baseline and ablation modes in automatic evaluation. User evaluation demonstrates significantly increased engagement intention and improved naturalness compared to baseline. Expert evaluation shows that PsyProbe substantially improves core issue understanding and achieves question rates comparable to professional counselors, validating the effectiveness of systematic state modeling and proactive questioning for therapeutic exploration.
SpecExtend: A Drop-in Enhancement for Speculative Decoding of Long Sequences
May 27, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding is a widely adopted technique for accelerating inference in large language models (LLMs), but its performance degrades on long inputs due to increased attention cost and reduced draft accuracy. We introduce SpecExtend, a drop-in enhancement that improves the performance of speculative decoding on long sequences without any additional training. SpecExtend integrates efficient attention mechanisms such as FlashAttention and Hybrid Tree Attention into both the draft and target models, reducing latency across all stages. To improve draft accuracy and speed, we propose Cross-model Retrieval, a novel KV cache update strategy that uses the target model's attention scores to dynamically select relevant context for the draft model. Extensive evaluations on three long-context understanding datasets show that SpecExtend accelerates standard tree-based speculative decoding by up to 2.22x for inputs up to 16K tokens, providing an effective solution for speculative decoding of long sequences. The code is available at https://github.com/jycha98/SpecExtend .
Do You Keep an Eye on What I Ask? Mitigating Multimodal Hallucination via Attention-Guided Ensemble Decoding
May 23, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly expanded their utility in tasks like image captioning and visual question answering. However, they still struggle with object hallucination, where models generate descriptions that inaccurately reflect the visual content by including nonexistent objects or misrepresenting existing ones. While previous methods, such as data augmentation and training-free approaches, strive to tackle this issue, they still encounter scalability challenges and often depend on additional external modules. In this work, we propose Ensemble Decoding (ED), a novel strategy that splits the input image into sub-images and combines logit distributions by assigning weights through the attention map. Furthermore, we introduce ED adaptive plausibility constraint to calibrate logit distribution and FastED, a variant designed for speed-critical applications. Extensive experiments across hallucination benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
A Revisit to the Decoder for Camouflaged Object Detection
Mar 18, 2025
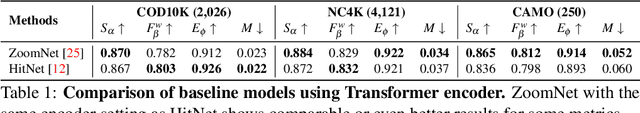
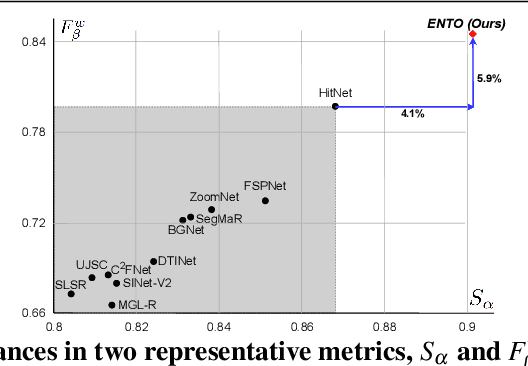
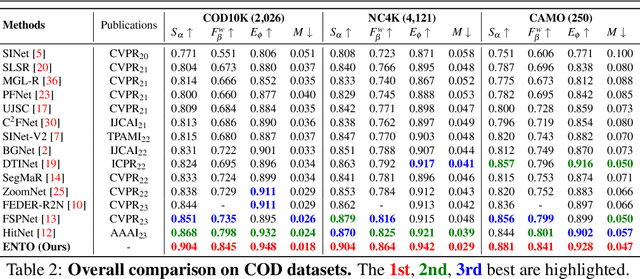
Abstract:Camouflaged object detection (COD) aims to generate a fine-grained segmentation map of camouflaged objects hidden in their background. Due to the hidden nature of camouflaged objects, it is essential for the decoder to be tailored to effectively extract proper features of camouflaged objects and extra-carefully generate their complex boundaries. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture that augments the prevalent decoding strategy in COD with Enrich Decoder and Retouch Decoder, which help to generate a fine-grained segmentation map. Specifically, the Enrich Decoder amplifies the channels of features that are important for COD using channel-wise attention. Retouch Decoder further refines the segmentation maps by spatially attending to important pixels, such as the boundary regions. With extensive experiments, we demonstrate that ENTO shows superior performance using various encoders, with the two novel components playing their unique roles that are mutually complementary.
* Published in BMVC 2024, 13 pages, 7 figures (Appendix: 5 pages, 2 figures)
LLM-guided Plan and Retrieval: A Strategic Alignment for Interpretable User Satisfaction Estimation in Dialogue
Mar 06, 2025
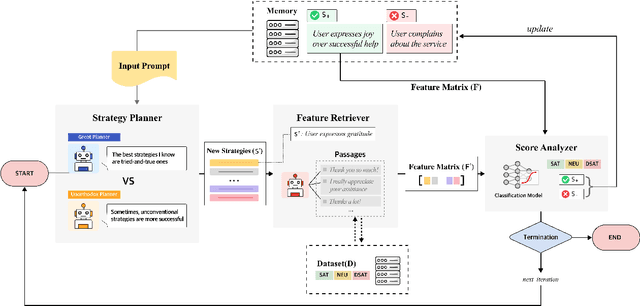

Abstract:Understanding user satisfaction with conversational systems, known as User Satisfaction Estimation (USE), is essential for assessing dialogue quality and enhancing user experiences. However, existing methods for USE face challenges due to limited understanding of underlying reasons for user dissatisfaction and the high costs of annotating user intentions. To address these challenges, we propose PRAISE (Plan and Retrieval Alignment for Interpretable Satisfaction Estimation), an interpretable framework for effective user satisfaction prediction. PRAISE operates through three key modules. The Strategy Planner develops strategies, which are natural language criteria for classifying user satisfaction. The Feature Retriever then incorporates knowledge on user satisfaction from Large Language Models (LLMs) and retrieves relevance features from utterances. Finally, the Score Analyzer evaluates strategy predictions and classifies user satisfaction. Experimental results demonstrate that PRAISE achieves state-of-the-art performance on three benchmarks for the USE task. Beyond its superior performance, PRAISE offers additional benefits. It enhances interpretability by providing instance-level explanations through effective alignment of utterances with strategies. Moreover, PRAISE operates more efficiently than existing approaches by eliminating the need for LLMs during the inference phase.
KMI: A Dataset of Korean Motivational Interviewing Dialogues for Psychotherapy
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:The increasing demand for mental health services has led to the rise of AI-driven mental health chatbots, though challenges related to privacy, data collection, and expertise persist. Motivational Interviewing (MI) is gaining attention as a theoretical basis for boosting expertise in the development of these chatbots. However, existing datasets are showing limitations for training chatbots, leading to a substantial demand for publicly available resources in the field of MI and psychotherapy. These challenges are even more pronounced in non-English languages, where they receive less attention. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that simulates MI sessions enriched with the expertise of professional therapists. We train an MI forecaster model that mimics the behavioral choices of professional therapists and employ Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate utterances through prompt engineering. Then, we present KMI, the first synthetic dataset theoretically grounded in MI, containing 1,000 high-quality Korean Motivational Interviewing dialogues. Through an extensive expert evaluation of the generated dataset and the dialogue model trained on it, we demonstrate the quality, expertise, and practicality of KMI. We also introduce novel metrics derived from MI theory in order to evaluate dialogues from the perspective of MI.
Measuring Recency Bias In Sequential Recommendation Systems
Sep 15, 2024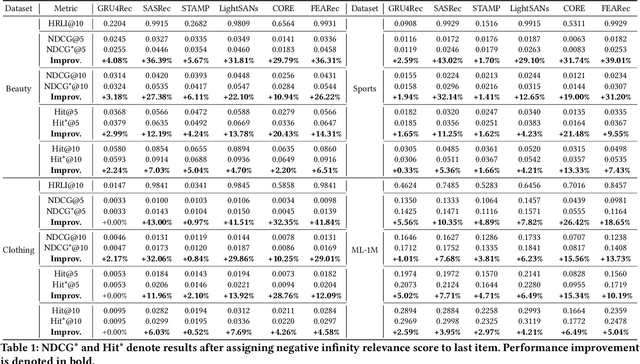
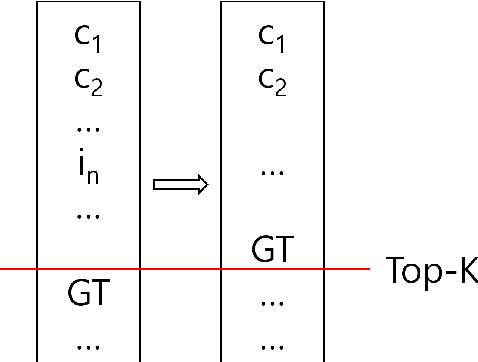
Abstract:Recency bias in a sequential recommendation system refers to the overly high emphasis placed on recent items within a user session. This bias can diminish the serendipity of recommendations and hinder the system's ability to capture users' long-term interests, leading to user disengagement. We propose a simple yet effective novel metric specifically designed to quantify recency bias. Our findings also demonstrate that high recency bias measured in our proposed metric adversely impacts recommendation performance too, and mitigating it results in improved recommendation performances across all models evaluated in our experiments, thus highlighting the importance of measuring recency bias.
Safe-Embed: Unveiling the Safety-Critical Knowledge of Sentence Encoders
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Despite the impressive capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in various tasks, their vulnerability to unsafe prompts remains a critical issue. These prompts can lead LLMs to generate responses on illegal or sensitive topics, posing a significant threat to their safe and ethical use. Existing approaches attempt to address this issue using classification models, but they have several drawbacks. With the increasing complexity of unsafe prompts, similarity search-based techniques that identify specific features of unsafe prompts provide a more robust and effective solution to this evolving problem. This paper investigates the potential of sentence encoders to distinguish safe from unsafe prompts, and the ability to classify various unsafe prompts according to a safety taxonomy. We introduce new pairwise datasets and the Categorical Purity (CP) metric to measure this capability. Our findings reveal both the effectiveness and limitations of existing sentence encoders, proposing directions to improve sentence encoders to operate as more robust safety detectors. Our code is available at https://github.com/JwdanielJung/Safe-Embed.
Pretraining Vision-Language Model for Difference Visual Question Answering in Longitudinal Chest X-rays
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Difference visual question answering (diff-VQA) is a challenging task that requires answering complex questions based on differences between a pair of images. This task is particularly important in reading chest X-ray images because radiologists often compare multiple images of the same patient taken at different times to track disease progression and changes in its severity in their clinical practice. However, previous works focused on designing specific network architectures for the diff-VQA task, missing opportunities to enhance the model's performance using a pretrained vision-language model (VLM). Here, we introduce a novel VLM called PLURAL, which is pretrained on natural and longitudinal chest X-ray data for the diff-VQA task. The model is developed using a step-by-step approach, starting with being pretrained on natural images and texts, followed by being trained using longitudinal chest X-ray data. The longitudinal data consist of pairs of X-ray images, along with question-answer sets and radiologist's reports that describe the changes in lung abnormalities and diseases over time. Our experimental results show that the PLURAL model outperforms state-of-the-art methods not only in diff-VQA for longitudinal X-rays but also in conventional VQA for a single X-ray image. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed VLM architecture and pretraining method in improving the model's performance.
MEMTO: Memory-guided Transformer for Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:Detecting anomalies in real-world multivariate time series data is challenging due to complex temporal dependencies and inter-variable correlations. Recently, reconstruction-based deep models have been widely used to solve the problem. However, these methods still suffer from an over-generalization issue and fail to deliver consistently high performance. To address this issue, we propose the MEMTO, a memory-guided Transformer using a reconstruction-based approach. It is designed to incorporate a novel memory module that can learn the degree to which each memory item should be updated in response to the input data. To stabilize the training procedure, we use a two-phase training paradigm which involves using K-means clustering for initializing memory items. Additionally, we introduce a bi-dimensional deviation-based detection criterion that calculates anomaly scores considering both input space and latent space. We evaluate our proposed method on five real-world datasets from diverse domains, and it achieves an average anomaly detection F1-score of 95.74%, significantly outperforming the previous state-of-the-art methods. We also conduct extensive experiments to empirically validate the effectiveness of our proposed model's key components.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge