Taebaek Hwang
KRETA: A Benchmark for Korean Reading and Reasoning in Text-Rich VQA Attuned to Diverse Visual Contexts
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Understanding and reasoning over text within visual contexts poses a significant challenge for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), given the complexity and diversity of real-world scenarios. To address this challenge, text-rich Visual Question Answering (VQA) datasets and benchmarks have emerged for high-resource languages like English. However, a critical gap persists for low-resource languages such as Korean, where the lack of comprehensive benchmarks hinders robust model evaluation and comparison. To bridge this gap, we introduce KRETA, a benchmark for Korean Reading and rEasoning in Text-rich VQA Attuned to diverse visual contexts. KRETA facilitates an in-depth evaluation of both visual text understanding and reasoning capabilities, while also supporting a multifaceted assessment across 15 domains and 26 image types. Additionally, we introduce a semi-automated VQA generation pipeline specifically optimized for text-rich settings, leveraging refined stepwise image decomposition and a rigorous seven-metric evaluation protocol to ensure data quality. While KRETA is tailored for Korean, we hope our adaptable and extensible pipeline will facilitate the development of similar benchmarks in other languages, thereby accelerating multilingual VLM research. The code and dataset for KRETA are available at https://github.com/tabtoyou/KRETA.
Do You Keep an Eye on What I Ask? Mitigating Multimodal Hallucination via Attention-Guided Ensemble Decoding
May 23, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly expanded their utility in tasks like image captioning and visual question answering. However, they still struggle with object hallucination, where models generate descriptions that inaccurately reflect the visual content by including nonexistent objects or misrepresenting existing ones. While previous methods, such as data augmentation and training-free approaches, strive to tackle this issue, they still encounter scalability challenges and often depend on additional external modules. In this work, we propose Ensemble Decoding (ED), a novel strategy that splits the input image into sub-images and combines logit distributions by assigning weights through the attention map. Furthermore, we introduce ED adaptive plausibility constraint to calibrate logit distribution and FastED, a variant designed for speed-critical applications. Extensive experiments across hallucination benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
CL3DOR: Contrastive Learning for 3D Large Multimodal Models via Odds Ratio on High-Resolution Point Clouds
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Recent research has demonstrated that Large Language Models (LLMs) are not limited to text-only tasks but can also function as multimodal models across various modalities, including audio, images, and videos. In particular, research on 3D Large Multimodal Models (3D LMMs) is making notable strides, driven by the potential of processing higher-dimensional data like point clouds. However, upon closer examination, we find that the visual and textual content within each sample of existing training datasets lacks both high informational granularity and clarity, which serve as a bottleneck for precise cross-modal understanding. To address these issues, we propose CL3DOR, Contrastive Learning for 3D large multimodal models via Odds ratio on high-Resolution point clouds, designed to ensure greater specificity and clarity in both visual and textual content. Specifically, we increase the density of point clouds per object and construct informative hard negative responses in the training dataset to penalize unwanted responses. To leverage hard negative responses, we incorporate the odds ratio as an auxiliary term for contrastive learning into the conventional language modeling loss. CL3DOR achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D scene understanding and reasoning benchmarks. Additionally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of CL3DOR's key components through extensive experiments.
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
SyncMask: Synchronized Attentional Masking for Fashion-centric Vision-Language Pretraining
Apr 01, 2024



Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have made significant strides in cross-modal understanding through large-scale paired datasets. However, in fashion domain, datasets often exhibit a disparity between the information conveyed in image and text. This issue stems from datasets containing multiple images of a single fashion item all paired with one text, leading to cases where some textual details are not visible in individual images. This mismatch, particularly when non-co-occurring elements are masked, undermines the training of conventional VLM objectives like Masked Language Modeling and Masked Image Modeling, thereby hindering the model's ability to accurately align fine-grained visual and textual features. Addressing this problem, we propose Synchronized attentional Masking (SyncMask), which generate masks that pinpoint the image patches and word tokens where the information co-occur in both image and text. This synchronization is accomplished by harnessing cross-attentional features obtained from a momentum model, ensuring a precise alignment between the two modalities. Additionally, we enhance grouped batch sampling with semi-hard negatives, effectively mitigating false negative issues in Image-Text Matching and Image-Text Contrastive learning objectives within fashion datasets. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, outperforming existing methods in three downstream tasks.
On Train-Test Class Overlap and Detection for Image Retrieval
Apr 01, 2024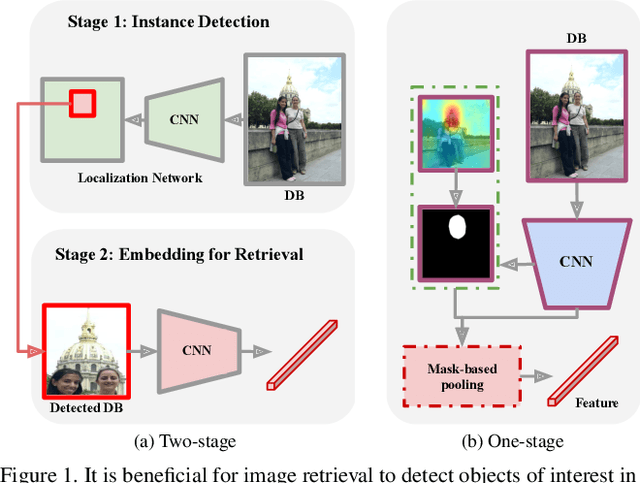



Abstract:How important is it for training and evaluation sets to not have class overlap in image retrieval? We revisit Google Landmarks v2 clean, the most popular training set, by identifying and removing class overlap with Revisited Oxford and Paris [34], the most popular evaluation set. By comparing the original and the new RGLDv2-clean on a benchmark of reproduced state-of-the-art methods, our findings are striking. Not only is there a dramatic drop in performance, but it is inconsistent across methods, changing the ranking.What does it take to focus on objects or interest and ignore background clutter when indexing? Do we need to train an object detector and the representation separately? Do we need location supervision? We introduce Single-stage Detect-to-Retrieve (CiDeR), an end-to-end, single-stage pipeline to detect objects of interest and extract a global image representation. We outperform previous state-of-the-art on both existing training sets and the new RGLDv2-clean. Our dataset is available at https://github.com/dealicious-inc/RGLDv2-clean.
Conditional Cross Attention Network for Multi-Space Embedding without Entanglement in Only a SINGLE Network
Jul 25, 2023



Abstract:Many studies in vision tasks have aimed to create effective embedding spaces for single-label object prediction within an image. However, in reality, most objects possess multiple specific attributes, such as shape, color, and length, with each attribute composed of various classes. To apply models in real-world scenarios, it is essential to be able to distinguish between the granular components of an object. Conventional approaches to embedding multiple specific attributes into a single network often result in entanglement, where fine-grained features of each attribute cannot be identified separately. To address this problem, we propose a Conditional Cross-Attention Network that induces disentangled multi-space embeddings for various specific attributes with only a single backbone. Firstly, we employ a cross-attention mechanism to fuse and switch the information of conditions (specific attributes), and we demonstrate its effectiveness through a diverse visualization example. Secondly, we leverage the vision transformer for the first time to a fine-grained image retrieval task and present a simple yet effective framework compared to existing methods. Unlike previous studies where performance varied depending on the benchmark dataset, our proposed method achieved consistent state-of-the-art performance on the FashionAI, DARN, DeepFashion, and Zappos50K benchmark datasets.
GRIT-VLP: Grouped Mini-batch Sampling for Efficient Vision and Language Pre-training
Aug 08, 2022Abstract:Most of the currently existing vision and language pre-training (VLP) methods have mainly focused on how to extract and align vision and text features. In contrast to the mainstream VLP methods, we highlight that two routinely applied steps during pre-training have crucial impact on the performance of the pre-trained model: in-batch hard negative sampling for image-text matching (ITM) and assigning the large masking probability for the masked language modeling (MLM). After empirically showing the unexpected effectiveness of above two steps, we systematically devise our GRIT-VLP, which adaptively samples mini-batches for more effective mining of hard negative samples for ITM while maintaining the computational cost for pre-training. Our method consists of three components: 1) GRouped mIni-baTch sampling (GRIT) strategy that collects similar examples in a mini-batch, 2) ITC consistency loss for improving the mining ability, and 3) enlarged masking probability for MLM. Consequently, we show our GRIT-VLP achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on various downstream tasks with much less computational cost. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our model is essentially in par with ALBEF, the previous state-of-the-art, only with one-third of training epochs on the same training data. Code is available at https://github.com/jaeseokbyun/GRIT-VLP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge