Jaeseok Byun
Reducing Task Discrepancy of Text Encoders for Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) aims to retrieve a target image based on a reference image and conditioning text, enabling controllable searches. Due to the expensive dataset construction cost for CIR triplets, a zero-shot (ZS) CIR setting has been actively studied to eliminate the need for human-collected triplet datasets. The mainstream of ZS-CIR employs an efficient projection module that projects a CLIP image embedding to the CLIP text token embedding space, while fixing the CLIP encoders. Using the projected image embedding, these methods generate image-text composed features by using the pre-trained text encoder. However, their CLIP image and text encoders suffer from the task discrepancy between the pre-training task (text $\leftrightarrow$ image) and the target CIR task (image + text $\leftrightarrow$ image). Conceptually, we need expensive triplet samples to reduce the discrepancy, but we use cheap text triplets instead and update the text encoder. To that end, we introduce the Reducing Task Discrepancy of text encoders for Composed Image Retrieval (RTD), a plug-and-play training scheme for the text encoder that enhances its capability using a novel target-anchored text contrastive learning. We also propose two additional techniques to improve the proposed learning scheme: a hard negatives-based refined batch sampling strategy and a sophisticated concatenation scheme. Integrating RTD into the state-of-the-art projection-based ZS-CIR methods significantly improves performance across various datasets and backbones, demonstrating its efficiency and generalizability.
Converting and Smoothing False Negatives for Vision-Language Pre-training
Dec 11, 2023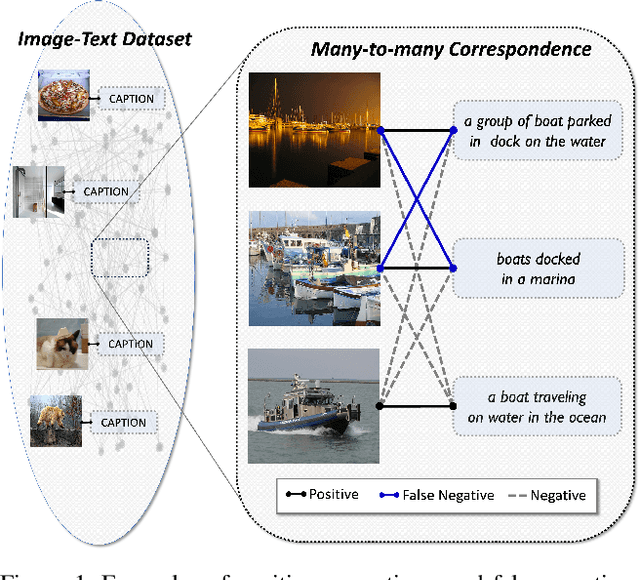



Abstract:We consider the critical issue of false negatives in Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP), a challenge that arises from the inherent many-to-many correspondence of image-text pairs in large-scale web-crawled datasets. The presence of false negatives can impede achieving optimal performance and even lead to learning failures. To address this challenge, we propose a method called COSMO (COnverting and SMOoothing false negatives) that manages the false negative issues, especially powerful in hard negative sampling. Building upon the recently developed GRouped mIni-baTch sampling (GRIT) strategy, our approach consists of two pivotal components: 1) an efficient connection mining process that identifies and converts false negatives into positives, and 2) label smoothing for the image-text contrastive loss (ITC). Our comprehensive experiments verify the effectiveness of COSMO across multiple downstream tasks, emphasizing the crucial role of addressing false negatives in VLP, potentially even surpassing the importance of addressing false positives. In addition, the compatibility of COSMO with the recent BLIP-family model is also demonstrated.
GRIT-VLP: Grouped Mini-batch Sampling for Efficient Vision and Language Pre-training
Aug 08, 2022Abstract:Most of the currently existing vision and language pre-training (VLP) methods have mainly focused on how to extract and align vision and text features. In contrast to the mainstream VLP methods, we highlight that two routinely applied steps during pre-training have crucial impact on the performance of the pre-trained model: in-batch hard negative sampling for image-text matching (ITM) and assigning the large masking probability for the masked language modeling (MLM). After empirically showing the unexpected effectiveness of above two steps, we systematically devise our GRIT-VLP, which adaptively samples mini-batches for more effective mining of hard negative samples for ITM while maintaining the computational cost for pre-training. Our method consists of three components: 1) GRouped mIni-baTch sampling (GRIT) strategy that collects similar examples in a mini-batch, 2) ITC consistency loss for improving the mining ability, and 3) enlarged masking probability for MLM. Consequently, we show our GRIT-VLP achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on various downstream tasks with much less computational cost. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our model is essentially in par with ALBEF, the previous state-of-the-art, only with one-third of training epochs on the same training data. Code is available at https://github.com/jaeseokbyun/GRIT-VLP.
FBI-Denoiser: Fast Blind Image Denoiser for Poisson-Gaussian Noise
May 23, 2021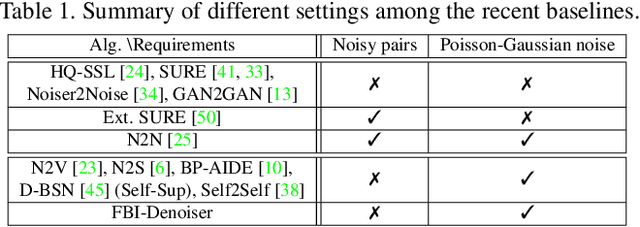
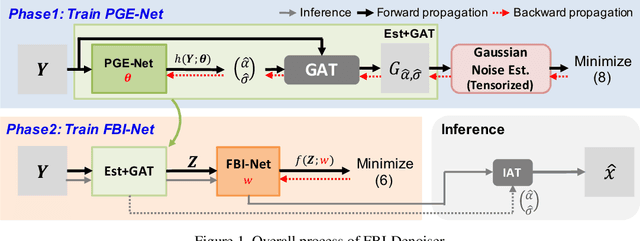
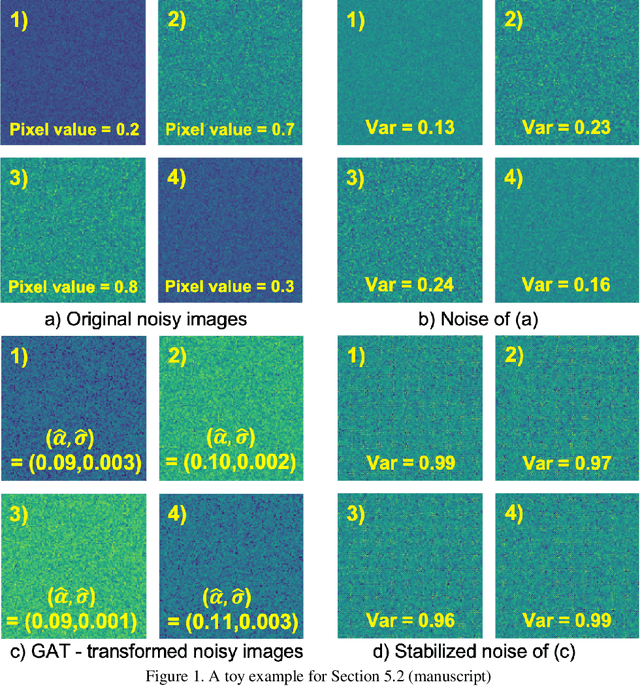
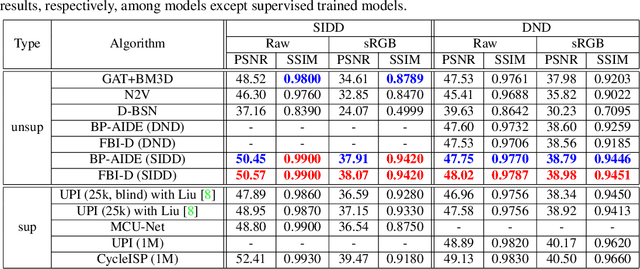
Abstract:We consider the challenging blind denoising problem for Poisson-Gaussian noise, in which no additional information about clean images or noise level parameters is available. Particularly, when only "single" noisy images are available for training a denoiser, the denoising performance of existing methods was not satisfactory. Recently, the blind pixelwise affine image denoiser (BP-AIDE) was proposed and significantly improved the performance in the above setting, to the extent that it is competitive with denoisers which utilized additional information. However, BP-AIDE seriously suffered from slow inference time due to the inefficiency of noise level estimation procedure and that of the blind-spot network (BSN) architecture it used. To that end, we propose Fast Blind Image Denoiser (FBI-Denoiser) for Poisson-Gaussian noise, which consists of two neural network models; 1) PGE-Net that estimates Poisson-Gaussian noise parameters 2000 times faster than the conventional methods and 2) FBI-Net that realizes a much more efficient BSN for pixelwise affine denoiser in terms of the number of parameters and inference speed. Consequently, we show that our FBI-Denoiser blindly trained solely based on single noisy images can achieve the state-of-the-art performance on several real-world noisy image benchmark datasets with much faster inference time (x 10), compared to BP-AIDE. The official code of our method is available at https://github.com/csm9493/FBI-Denoiser.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge