PePe: Personalized Post-editing Model utilizing User-generated Post-edits
Paper and Code
Sep 21, 2022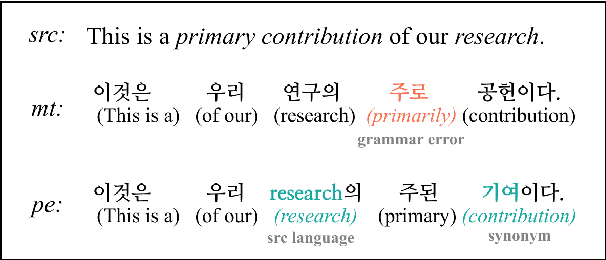
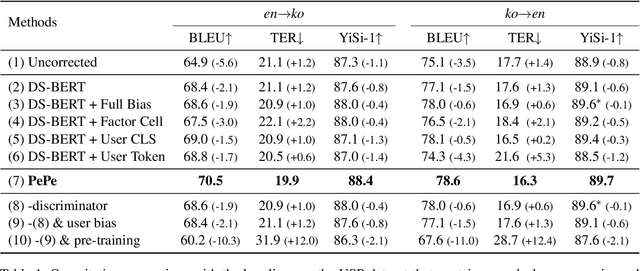
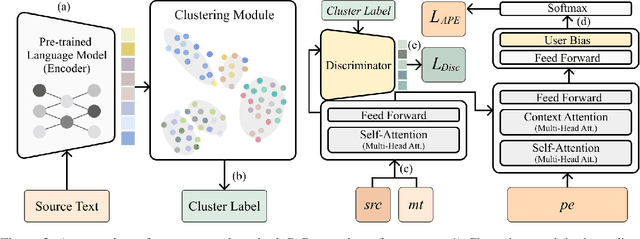
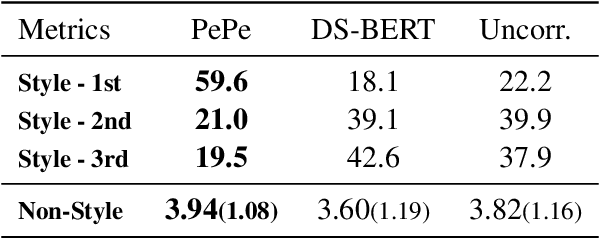
Incorporating personal preference is crucial in advanced machine translation tasks. Despite the recent advancement of machine translation, it remains a demanding task to properly reflect personal style. In this paper, we introduce a personalized automatic post-editing framework to address this challenge, which effectively generates sentences considering distinct personal behaviors. To build this framework, we first collect post-editing data that connotes the user preference from a live machine translation system. Specifically, real-world users enter source sentences for translation and edit the machine-translated outputs according to the user's preferred style. We then propose a model that combines a discriminator module and user-specific parameters on the APE framework. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other baseline models on four different metrics (i.e., BLEU, TER, YiSi-1, and human evaluation).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge