Soha Hassoun
UNIGE
SpecBridge: Bridging Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Representations via Cross-Modal Alignment
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Small-molecule identification from tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) remains a bottleneck in untargeted settings where spectral libraries are incomplete. While deep learning offers a solution, current approaches typically fall into two extremes: explicit generative models that construct molecular graphs atom-by-atom, or joint contrastive models that learn cross-modal subspaces from scratch. We introduce SpecBridge, a novel implicit alignment framework that treats structure identification as a geometric alignment problem. SpecBridge fine-tunes a self-supervised spectral encoder (DreaMS) to project directly into the latent space of a frozen molecular foundation model (ChemBERTa), and then performs retrieval by cosine similarity to a fixed bank of precomputed molecular embeddings. Across MassSpecGym, Spectraverse, and MSnLib benchmarks, SpecBridge improves top-1 retrieval accuracy by roughly 20-25% relative to strong neural baselines, while keeping the number of trainable parameters small. These results suggest that aligning to frozen foundation models is a practical, stable alternative to designing new architectures from scratch. The code for SpecBridge is released at https://github.com/HassounLab/SpecBridge.
General Intelligence-based Fragmentation (GIF): A framework for peak-labeled spectra simulation
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Despite growing reference libraries and advanced computational tools, progress in the field of metabolomics remains constrained by low rates of annotating measured spectra. The recent developments of large language models (LLMs) have led to strong performance across a wide range of generation and reasoning tasks, spurring increased interest in LLMs' application to domain-specific scientific challenges, such as mass spectra annotation. Here, we present a novel framework, General Intelligence-based Fragmentation (GIF), that guides pretrained LLMs through spectra simulation using structured prompting and reasoning. GIF utilizes tagging, structured inputs/outputs, system prompts, instruction-based prompts, and iterative refinement. Indeed, GIF offers a structured alternative to ad hoc prompting, underscoring the need for systematic guidance of LLMs on complex scientific tasks. Using GIF, we evaluate current generalist LLMs' ability to use reasoning towards fragmentation and to perform intensity prediction after fine-tuning. We benchmark performance on a novel QA dataset, the MassSpecGym QA-sim dataset, that we derive from the MassSpecGym dataset. Through these implementations of GIF, we find that GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini achieve a cosine similarity of 0.36 and 0.35 between the simulated and true spectra, respectively, outperforming other pretrained models including GPT-5, Llama-3.1, and ChemDFM, despite GPT-5's recency and ChemDFM's domain specialization. GIF outperforms several deep learning baselines. Our evaluation of GIF highlights the value of using LLMs not only for spectra simulation but for enabling human-in-the-loop workflows and structured, explainable reasoning in molecular fragmentation.
MetaboT: AI-based agent for natural language-based interaction with metabolomics knowledge graphs
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Mass spectrometry metabolomics generates vast amounts of data requiring advanced methods for interpretation. Knowledge graphs address these challenges by structuring mass spectrometry data, metabolite information, and their relationships into a connected network (Gaudry et al. 2024). However, effective use of a knowledge graph demands an in-depth understanding of its ontology and its query language syntax. To overcome this, we designed MetaboT, an AI system utilizing large language models (LLMs) to translate user questions into SPARQL semantic query language for operating on knowledge graphs (Steve Harris 2013). We demonstrate its effectiveness using the Experimental Natural Products Knowledge Graph (ENPKG), a large-scale public knowledge graph for plant natural products (Gaudry et al. 2024).MetaboT employs specialized AI agents for handling user queries and interacting with the knowledge graph by breaking down complex tasks into discrete components, each managed by a specialised agent (Fig. 1a). The multi-agent system is constructed using the LangChain and LangGraph libraries, which facilitate the integration of LLMs with external tools and information sources (LangChain, n.d.). The query generation process follows a structured workflow. First, the Entry Agent determines if the question is new or a follow-up to previous interactions. New questions are forwarded to the Validator Agent, which verifies if the question is related to the knowledge graph. Then, the valid question is sent to the Supervisor Agent, which identifies if the question requires chemical conversions or standardized identifiers. In this case it delegates the question to the Knowledge Graph Agent, which can use tools to extract necessary details, such as URIs or taxonomies of chemical names, from the user query. Finally, an agent responsible for crafting the SPARQL queries equipped with the ontology of the knowledge graph uses the provided identifiers to generate the query. Then, the system executes the generated query against the metabolomics knowledge graph and returns structured results to the user (Fig. 1b). To assess the performance of MetaboT we have curated 50 metabolomics-related questions and their expected answers. In addition to submitting these questions to MetaboT, we evaluated a baseline by submitting them to a standard LLM (GPT-4o) with a prompt that incorporated the knowledge graph ontology but did not provide specific entity IDs. This baseline achieved only 8.16% accuracy, compared to MetaboT's 83.67%, underscoring the necessity of our multi-agent system for accurately retrieving entities and generating correct SPARQL queries. MetaboT demonstrates promising performance as a conversational question-answering assistant, enabling researchers to retrieve structured metabolomics data through natural language queries. By automating the generation and execution of SPARQL queries, it removes technical barriers that have traditionally hindered access to knowledge graphs. Importantly, MetaboT leverages the capabilities of LLMs while maintaining experimentally grounded query generation, ensuring that outputs remain aligned with domain-specific standards and data structures. This approach facilitates data-driven discoveries by bridging the gap between complex semantic technologies and user-friendly interaction. MetaboT is accessible at [https://metabot.holobiomicslab.eu/], and its source code is available at [https://github.com/HolobiomicsLab/MetaboT].
Large Language Model is Secretly a Protein Sequence Optimizer
Jan 16, 2025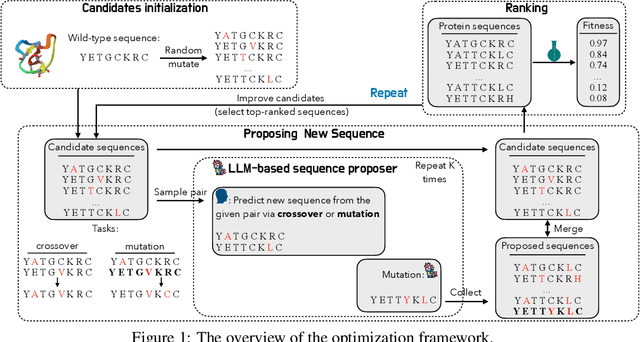
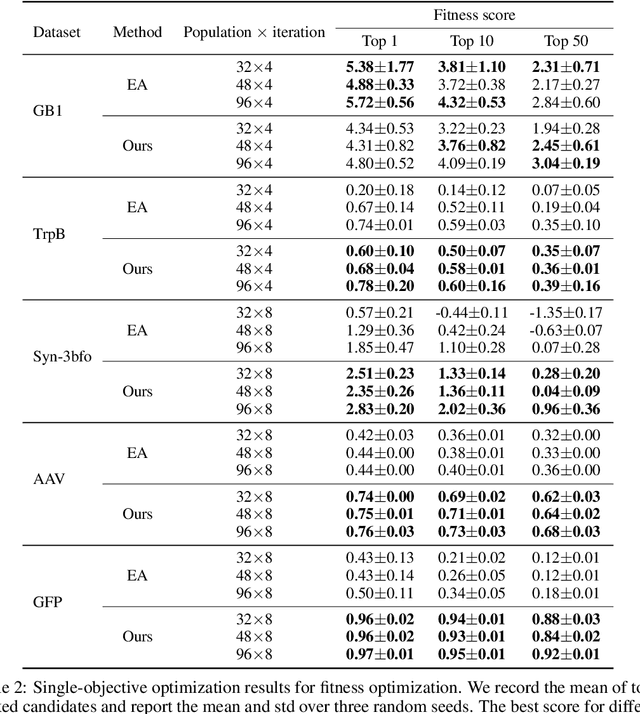
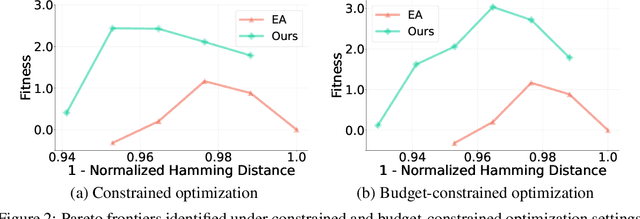
Abstract:We consider the protein sequence engineering problem, which aims to find protein sequences with high fitness levels, starting from a given wild-type sequence. Directed evolution has been a dominating paradigm in this field which has an iterative process to generate variants and select via experimental feedback. We demonstrate large language models (LLMs), despite being trained on massive texts, are secretly protein sequence optimizers. With a directed evolutionary method, LLM can perform protein engineering through Pareto and experiment-budget constrained optimization, demonstrating success on both synthetic and experimental fitness landscapes.
MADGEN -- Mass-Spec attends to De Novo Molecular generation
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:The annotation (assigning structural chemical identities) of MS/MS spectra remains a significant challenge due to the enormous molecular diversity in biological samples and the limited scope of reference databases. Currently, the vast majority of spectral measurements remain in the "dark chemical space" without structural annotations. To improve annotation, we propose MADGEN (Mass-spec Attends to De Novo Molecular GENeration), a scaffold-based method for de novo molecular structure generation guided by mass spectrometry data. MADGEN operates in two stages: scaffold retrieval and spectra-conditioned molecular generation starting with the scaffold. In the first stage, given an MS/MS spectrum, we formulate scaffold retrieval as a ranking problem and employ contrastive learning to align mass spectra with candidate molecular scaffolds. In the second stage, starting from the retrieved scaffold, we employ the MS/MS spectrum to guide an attention-based generative model to generate the final molecule. Our approach constrains the molecular generation search space, reducing its complexity and improving generation accuracy. We evaluate MADGEN on three datasets (NIST23, CANOPUS, and MassSpecGym) and evaluate MADGEN's performance with a predictive scaffold retriever and with an oracle retriever. We demonstrate the effectiveness of using attention to integrate spectral information throughout the generation process to achieve strong results with the oracle retriever.
Graph Generative Pre-trained Transformer
Jan 02, 2025Abstract:Graph generation is a critical task in numerous domains, including molecular design and social network analysis, due to its ability to model complex relationships and structured data. While most modern graph generative models utilize adjacency matrix representations, this work revisits an alternative approach that represents graphs as sequences of node set and edge set. We advocate for this approach due to its efficient encoding of graphs and propose a novel representation. Based on this representation, we introduce the Graph Generative Pre-trained Transformer (G2PT), an auto-regressive model that learns graph structures via next-token prediction. To further exploit G2PT's capabilities as a general-purpose foundation model, we explore fine-tuning strategies for two downstream applications: goal-oriented generation and graph property prediction. We conduct extensive experiments across multiple datasets. Results indicate that G2PT achieves superior generative performance on both generic graph and molecule datasets. Furthermore, G2PT exhibits strong adaptability and versatility in downstream tasks from molecular design to property prediction.
JESTR: Joint Embedding Space Technique for Ranking Candidate Molecules for the Annotation of Untargeted Metabolomics Data
Nov 25, 2024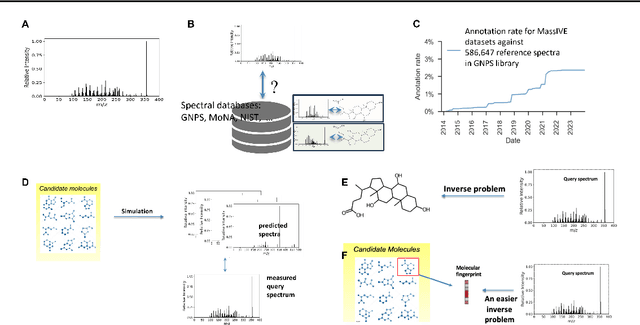
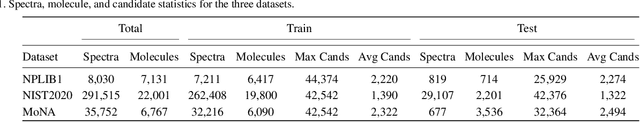
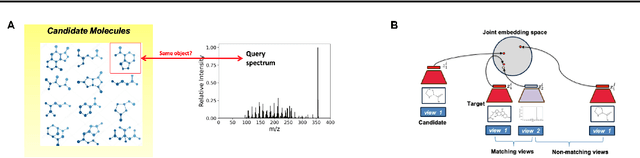
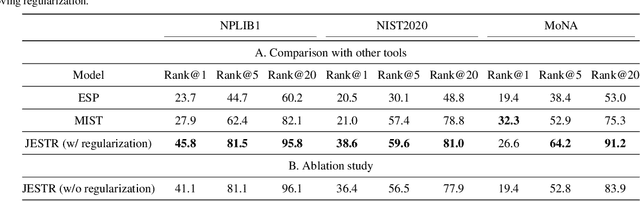
Abstract:Motivation: A major challenge in metabolomics is annotation: assigning molecular structures to mass spectral fragmentation patterns. Despite recent advances in molecule-to-spectra and in spectra-to-molecular fingerprint prediction (FP), annotation rates remain low. Results: We introduce in this paper a novel paradigm (JESTR) for annotation. Unlike prior approaches that explicitly construct molecular fingerprints or spectra, JESTR leverages the insight that molecules and their corresponding spectra are views of the same data and effectively embeds their representations in a joint space. Candidate structures are ranked based on cosine similarity between the embeddings of query spectrum and each candidate. We evaluate JESTR against mol-to-spec and spec-to-FP annotation tools on three datasets. On average, for rank@[1-5], JESTR outperforms other tools by 23.6%-71.6%. We further demonstrate the strong value of regularization with candidate molecules during training, boosting rank@1 performance by 11.4% and enhancing the model's ability to discern between target and candidate molecules. Through JESTR, we offer a novel promising avenue towards accurate annotation, therefore unlocking valuable insights into the metabolome.
MassSpecGym: A benchmark for the discovery and identification of molecules
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:The discovery and identification of molecules in biological and environmental samples is crucial for advancing biomedical and chemical sciences. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) is the leading technique for high-throughput elucidation of molecular structures. However, decoding a molecular structure from its mass spectrum is exceptionally challenging, even when performed by human experts. As a result, the vast majority of acquired MS/MS spectra remain uninterpreted, thereby limiting our understanding of the underlying (bio)chemical processes. Despite decades of progress in machine learning applications for predicting molecular structures from MS/MS spectra, the development of new methods is severely hindered by the lack of standard datasets and evaluation protocols. To address this problem, we propose MassSpecGym -- the first comprehensive benchmark for the discovery and identification of molecules from MS/MS data. Our benchmark comprises the largest publicly available collection of high-quality labeled MS/MS spectra and defines three MS/MS annotation challenges: \textit{de novo} molecular structure generation, molecule retrieval, and spectrum simulation. It includes new evaluation metrics and a generalization-demanding data split, therefore standardizing the MS/MS annotation tasks and rendering the problem accessible to the broad machine learning community. MassSpecGym is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/pluskal-lab/MassSpecGym}.
On Separate Normalization in Self-supervised Transformers
Sep 22, 2023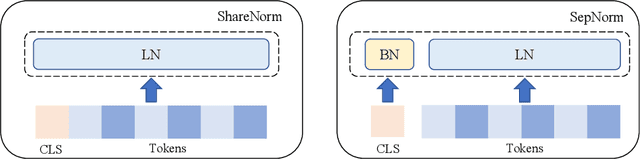
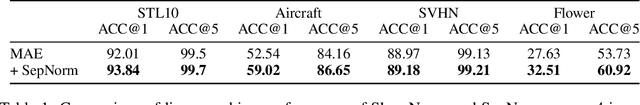
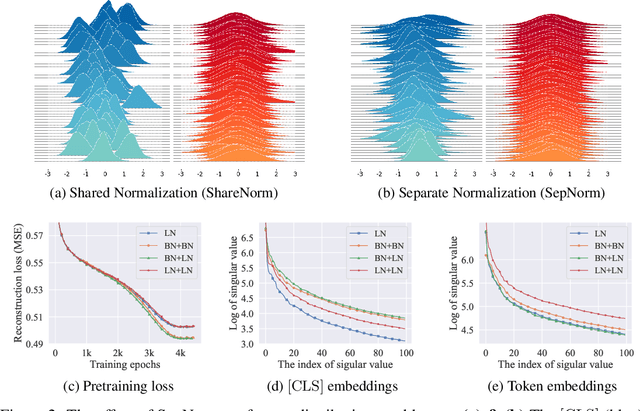
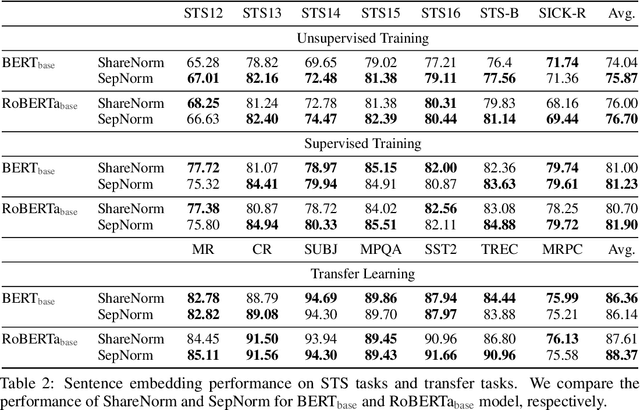
Abstract:Self-supervised training methods for transformers have demonstrated remarkable performance across various domains. Previous transformer-based models, such as masked autoencoders (MAE), typically utilize a single normalization layer for both the [CLS] symbol and the tokens. We propose in this paper a simple modification that employs separate normalization layers for the tokens and the [CLS] symbol to better capture their distinct characteristics and enhance downstream task performance. Our method aims to alleviate the potential negative effects of using the same normalization statistics for both token types, which may not be optimally aligned with their individual roles. We empirically show that by utilizing a separate normalization layer, the [CLS] embeddings can better encode the global contextual information and are distributed more uniformly in its anisotropic space. When replacing the conventional normalization layer with the two separate layers, we observe an average 2.7% performance improvement over the image, natural language, and graph domains.
Ensemble Spectral Prediction (ESP) Model for Metabolite Annotation
Mar 25, 2022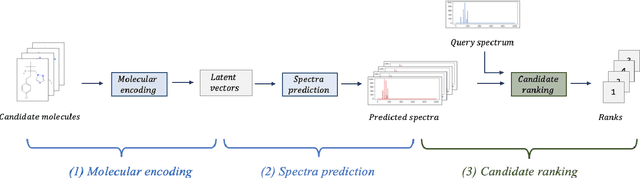
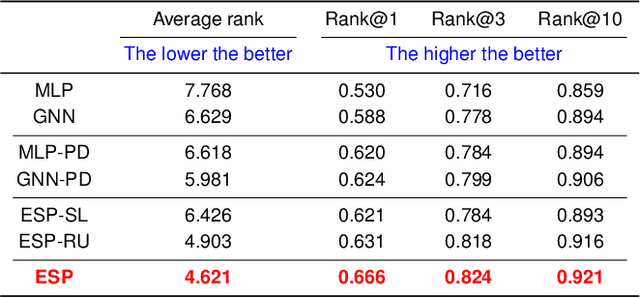
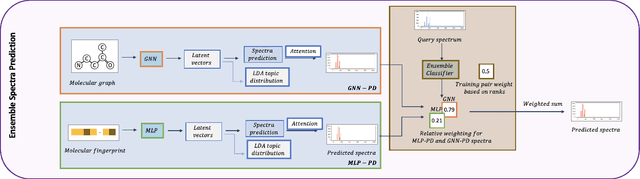
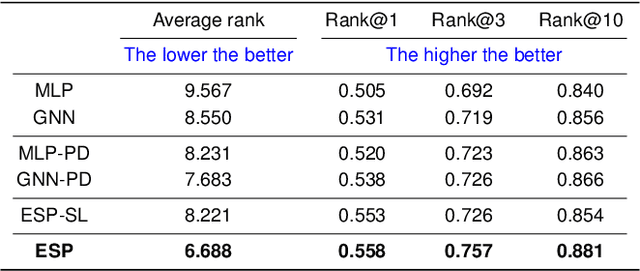
Abstract:A key challenge in metabolomics is annotating measured spectra from a biological sample with chemical identities. Currently, only a small fraction of measurements can be assigned identities. Two complementary computational approaches have emerged to address the annotation problem: mapping candidate molecules to spectra, and mapping query spectra to molecular candidates. In essence, the candidate molecule with the spectrum that best explains the query spectrum is recommended as the target molecule. Despite candidate ranking being fundamental in both approaches, no prior works utilized rank learning tasks in determining the target molecule. We propose a novel machine learning model, Ensemble Spectral Prediction (ESP), for metabolite annotation. ESP takes advantage of prior neural network-based annotation models that utilize multilayer perceptron (MLP) networks and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). Based on the ranking results of the MLP and GNN-based models, ESP learns a weighting for the outputs of MLP and GNN spectral predictors to generate a spectral prediction for a query molecule. Importantly, training data is stratified by molecular formula to provide candidate sets during model training. Further, baseline MLP and GNN models are enhanced by considering peak dependencies through multi-head attention mechanism and multi-tasking on spectral topic distributions. ESP improves average rank by 41% and 30% over the MLP and GNN baselines, respectively, demonstrating remarkable performance gain over state-of-the-art neural network approaches. We show that annotation performance, for ESP and other models, is a strong function of the number of molecules in the candidate set and their similarity to the target molecule.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge