Siyuan Zhuang
The Danger of Overthinking: Examining the Reasoning-Action Dilemma in Agentic Tasks
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) represent a breakthrough in AI problem-solving capabilities, but their effectiveness in interactive environments can be limited. This paper introduces and analyzes overthinking in LRMs. A phenomenon where models favor extended internal reasoning chains over environmental interaction. Through experiments on software engineering tasks using SWE Bench Verified, we observe three recurring patterns: Analysis Paralysis, Rogue Actions, and Premature Disengagement. We propose a framework to study these behaviors, which correlates with human expert assessments, and analyze 4018 trajectories. We observe that higher overthinking scores correlate with decreased performance, with reasoning models exhibiting stronger tendencies toward overthinking compared to non-reasoning models. Our analysis reveals that simple efforts to mitigate overthinking in agentic environments, such as selecting the solution with the lower overthinking score, can improve model performance by almost 30% while reducing computational costs by 43%. These results suggest that mitigating overthinking has strong practical implications. We suggest that by leveraging native function-calling capabilities and selective reinforcement learning overthinking tendencies could be mitigated. We also open-source our evaluation framework and dataset to facilitate research in this direction at https://github.com/AlexCuadron/Overthinking.
A Statistical Framework for Ranking LLM-Based Chatbots
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have transformed natural language processing, with frameworks like Chatbot Arena providing pioneering platforms for evaluating these models. By facilitating millions of pairwise comparisons based on human judgments, Chatbot Arena has become a cornerstone in LLM evaluation, offering rich datasets for ranking models in open-ended conversational tasks. Building upon this foundation, we propose a statistical framework that incorporates key advancements to address specific challenges in pairwise comparison analysis. First, we introduce a factored tie model that enhances the ability to handle ties -- an integral aspect of human-judged comparisons -- significantly improving the model's fit to observed data. Second, we extend the framework to model covariance between competitors, enabling deeper insights into performance relationships and facilitating intuitive groupings into performance tiers. Third, we resolve optimization challenges arising from parameter non-uniqueness by introducing novel constraints, ensuring stable and interpretable parameter estimation. Through rigorous evaluation and extensive experimentation, our framework demonstrates substantial improvements over existing methods in modeling pairwise comparison data. To support reproducibility and practical adoption, we release leaderbot, an open-source Python package implementing our models and analyses.
JudgeBench: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLM-based Judges
Oct 16, 2024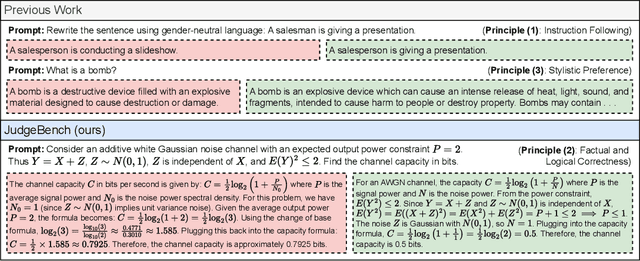
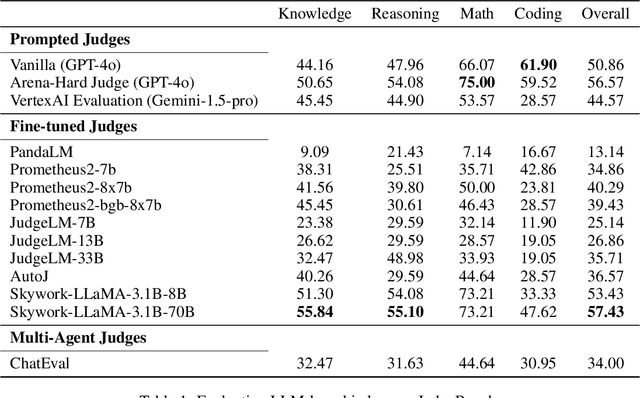
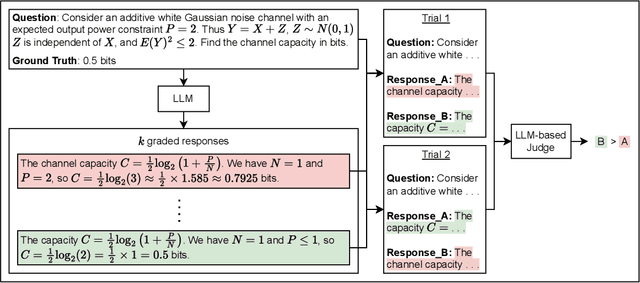
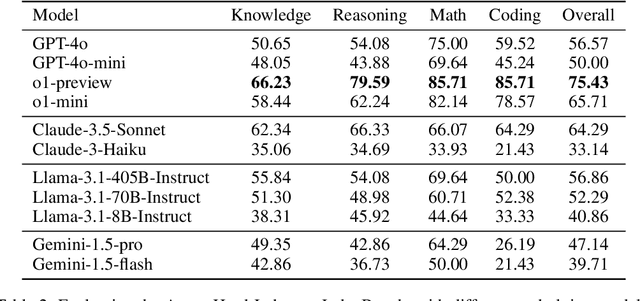
Abstract:LLM-based judges have emerged as a scalable alternative to human evaluation and are increasingly used to assess, compare, and improve models. However, the reliability of LLM-based judges themselves is rarely scrutinized. As LLMs become more advanced, their responses grow more sophisticated, requiring stronger judges to evaluate them. Existing benchmarks primarily focus on a judge's alignment with human preferences, but often fail to account for more challenging tasks where crowdsourced human preference is a poor indicator of factual and logical correctness. To address this, we propose a novel evaluation framework to objectively evaluate LLM-based judges. Based on this framework, we propose JudgeBench, a benchmark for evaluating LLM-based judges on challenging response pairs spanning knowledge, reasoning, math, and coding. JudgeBench leverages a novel pipeline for converting existing difficult datasets into challenging response pairs with preference labels reflecting objective correctness. Our comprehensive evaluation on a collection of prompted judges, fine-tuned judges, multi-agent judges, and reward models shows that JudgeBench poses a significantly greater challenge than previous benchmarks, with many strong models (e.g., GPT-4o) performing just slightly better than random guessing. Overall, JudgeBench offers a reliable platform for assessing increasingly advanced LLM-based judges. Data and code are available at https://github.com/ScalerLab/JudgeBench .
LMSYS-Chat-1M: A Large-Scale Real-World LLM Conversation Dataset
Sep 30, 2023



Abstract:Studying how people interact with large language models (LLMs) in real-world scenarios is increasingly important due to their widespread use in various applications. In this paper, we introduce LMSYS-Chat-1M, a large-scale dataset containing one million real-world conversations with 25 state-of-the-art LLMs. This dataset is collected from 210K unique IP addresses in the wild on our Vicuna demo and Chatbot Arena website. We offer an overview of the dataset's content, including its curation process, basic statistics, and topic distribution, highlighting its diversity, originality, and scale. We demonstrate its versatility through four use cases: developing content moderation models that perform similarly to GPT-4, building a safety benchmark, training instruction-following models that perform similarly to Vicuna, and creating challenging benchmark questions. We believe that this dataset will serve as a valuable resource for understanding and advancing LLM capabilities. The dataset is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/lmsys/lmsys-chat-1m.
Efficient Memory Management for Large Language Model Serving with PagedAttention
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:High throughput serving of large language models (LLMs) requires batching sufficiently many requests at a time. However, existing systems struggle because the key-value cache (KV cache) memory for each request is huge and grows and shrinks dynamically. When managed inefficiently, this memory can be significantly wasted by fragmentation and redundant duplication, limiting the batch size. To address this problem, we propose PagedAttention, an attention algorithm inspired by the classical virtual memory and paging techniques in operating systems. On top of it, we build vLLM, an LLM serving system that achieves (1) near-zero waste in KV cache memory and (2) flexible sharing of KV cache within and across requests to further reduce memory usage. Our evaluations show that vLLM improves the throughput of popular LLMs by 2-4$\times$ with the same level of latency compared to the state-of-the-art systems, such as FasterTransformer and Orca. The improvement is more pronounced with longer sequences, larger models, and more complex decoding algorithms. vLLM's source code is publicly available at https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm
Judging LLM-as-a-judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena
Jun 09, 2023



Abstract:Evaluating large language model (LLM) based chat assistants is challenging due to their broad capabilities and the inadequacy of existing benchmarks in measuring human preferences. To address this, we explore using strong LLMs as judges to evaluate these models on more open-ended questions. We examine the usage and limitations of LLM-as-a-judge, such as position and verbosity biases and limited reasoning ability, and propose solutions to migrate some of them. We then verify the agreement between LLM judges and human preferences by introducing two benchmarks: MT-bench, a multi-turn question set; and Chatbot Arena, a crowdsourced battle platform. Our results reveal that strong LLM judges like GPT-4 can match both controlled and crowdsourced human preferences well, achieving over 80\% agreement, the same level of agreement between humans. Hence, LLM-as-a-judge is a scalable and explainable way to approximate human preferences, which are otherwise very expensive to obtain. Additionally, we show our benchmark and traditional benchmarks complement each other by evaluating several variants of LLaMA/Vicuna. We will publicly release 80 MT-bench questions, 3K expert votes, and 30K conversations with human preferences from Chatbot Arena.
TeraPipe: Token-Level Pipeline Parallelism for Training Large-Scale Language Models
Feb 16, 2021



Abstract:Model parallelism has become a necessity for training modern large-scale deep language models. In this work, we identify a new and orthogonal dimension from existing model parallel approaches: it is possible to perform pipeline parallelism within a single training sequence for Transformer-based language models thanks to its autoregressive property. This enables a more fine-grained pipeline compared with previous work. With this key idea, we design TeraPipe, a high-performance token-level pipeline parallel algorithm for synchronous model-parallel training of Transformer-based language models. We develop a novel dynamic programming-based algorithm to calculate the optimal pipelining execution scheme given a specific model and cluster configuration. We show that TeraPipe can speed up the training by 5.0x for the largest GPT-3 model with 175 billion parameters on an AWS cluster with 48 p3.16xlarge instances compared with state-of-the-art model-parallel methods.
Hoplite: Efficient Collective Communication for Task-Based Distributed Systems
Feb 13, 2020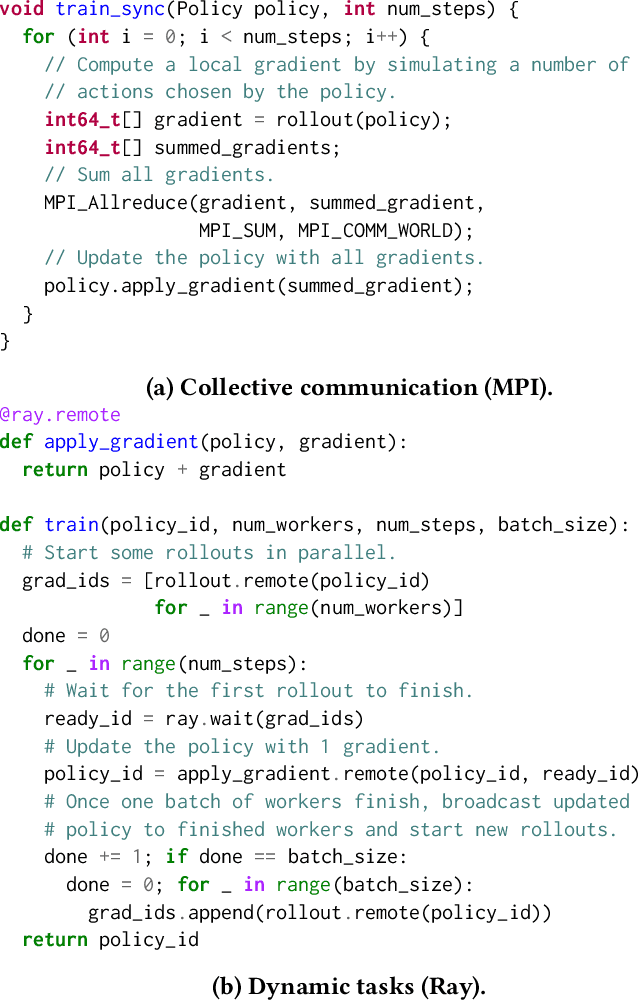

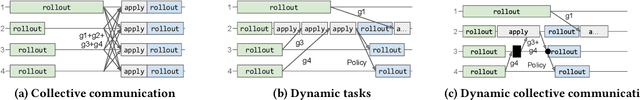
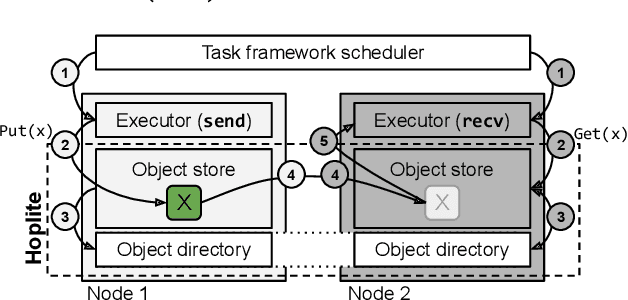
Abstract:Collective communication systems such as MPI offer high performance group communication primitives at the cost of application flexibility. Today, an increasing number of distributed applications (e.g, reinforcement learning) require flexibility in expressing dynamic and asynchronous communication patterns. To accommodate these applications, task-based distributed computing frameworks (e.g., Ray, Dask, Hydro) have become popular as they allow applications to dynamically specify communication by invoking tasks, or functions, at runtime. This design makes efficient collective communication challenging because (1) the group of communicating processes is chosen at runtime, and (2) processes may not all be ready at the same time. We design and implement Hoplite, a communication layer for task-based distributed systems that achieves high performance collective communication without compromising application flexibility. The key idea of Hoplite is to use distributed protocols to compute a data transfer schedule on the fly. This enables the same optimizations used in traditional collective communication, but for applications that specify the communication incrementally. We show that Hoplite can achieve similar performance compared with a traditional collective communication library, MPICH. We port a popular distributed computing framework, Ray, on atop of Hoplite. We show that Hoplite can speed up asynchronous parameter server and distributed reinforcement learning workloads that are difficult to execute efficiently with traditional collective communication by up to 8.1x and 3.9x, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge