Shuyang Yu
Neural Parameter Search for Slimmer Fine-Tuned Models and Better Transfer
May 24, 2025Abstract:Foundation models and their checkpoints have significantly advanced deep learning, boosting performance across various applications. However, fine-tuned models often struggle outside their specific domains and exhibit considerable redundancy. Recent studies suggest that combining a pruned fine-tuned model with the original pre-trained model can mitigate forgetting, reduce interference when merging model parameters across tasks, and improve compression efficiency. In this context, developing an effective pruning strategy for fine-tuned models is crucial. Leveraging the advantages of the task vector mechanism, we preprocess fine-tuned models by calculating the differences between them and the original model. Recognizing that different task vector subspaces contribute variably to model performance, we introduce a novel method called Neural Parameter Search (NPS-Pruning) for slimming down fine-tuned models. This method enhances pruning efficiency by searching through neural parameters of task vectors within low-rank subspaces. Our method has three key applications: enhancing knowledge transfer through pairwise model interpolation, facilitating effective knowledge fusion via model merging, and enabling the deployment of compressed models that retain near-original performance while significantly reducing storage costs. Extensive experiments across vision, NLP, and multi-modal benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our approach, resulting in substantial performance gains. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/duguodong7/NPS-Pruning.
Fast Online Adaptive Neural MPC via Meta-Learning
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Data-driven model predictive control (MPC) has demonstrated significant potential for improving robot control performance in the presence of model uncertainties. However, existing approaches often require extensive offline data collection and computationally intensive training, limiting their ability to adapt online. To address these challenges, this paper presents a fast online adaptive MPC framework that leverages neural networks integrated with Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML). Our approach focuses on few-shot adaptation of residual dynamics - capturing the discrepancy between nominal and true system behavior - using minimal online data and gradient steps. By embedding these meta-learned residual models into a computationally efficient L4CasADi-based MPC pipeline, the proposed method enables rapid model correction, enhances predictive accuracy, and improves real-time control performance. We validate the framework through simulation studies on a Van der Pol oscillator, a Cart-Pole system, and a 2D quadrotor. Results show significant gains in adaptation speed and prediction accuracy over both nominal MPC and nominal MPC augmented with a freshly initialized neural network, underscoring the effectiveness of our approach for real-time adaptive robot control.
Disentangling Task Interference within Neurons: Model Merging in Alignment with Neuronal Mechanisms
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning pre-trained models on targeted datasets enhances task-specific performance but often comes at the expense of generalization. Model merging techniques, which integrate multiple fine-tuned models into a single multi-task model through task arithmetic at various levels: model, layer, or parameter, offer a promising solution. However, task interference remains a fundamental challenge, leading to performance degradation and suboptimal merged models. Existing approaches largely overlook the fundamental role of individual neurons and their connectivity, resulting in a lack of interpretability in both the merging process and the merged models. In this work, we present the first study on the impact of neuronal alignment in model merging. We decompose task-specific representations into two complementary neuronal subspaces that regulate neuron sensitivity and input adaptability. Leveraging this decomposition, we introduce NeuroMerging, a novel merging framework developed to mitigate task interference within neuronal subspaces, enabling training-free model fusion across diverse tasks. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that NeuroMerging achieves superior performance compared to existing methods on multi-task benchmarks across both vision and natural language domains. Our findings highlight the importance of aligning neuronal mechanisms in model merging, offering new insights into mitigating task interference and improving knowledge fusion.
Dynamic Uncertainty Ranking: Enhancing In-Context Learning for Long-Tail Knowledge in LLMs
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can learn vast amounts of knowledge from diverse domains during pre-training. However, long-tail knowledge from specialized domains is often scarce and underrepresented, rarely appearing in the models' memorization. Prior work has shown that in-context learning (ICL) with retriever augmentation can help LLMs better capture long-tail knowledge, reducing their reliance on pre-trained data. Despite these advances, we observe that LLM predictions for long-tail questions remain uncertain to variations in retrieved samples. To take advantage of the uncertainty in ICL for guiding LLM predictions toward correct answers on long-tail samples, we propose a reinforcement learning-based dynamic uncertainty ranking method for ICL that accounts for the varying impact of each retrieved sample on LLM predictions. Our approach prioritizes more informative and stable samples while demoting misleading ones, updating rankings based on the feedback from the LLM w.r.t. each retrieved sample. To enhance training efficiency and reduce query costs, we introduce a learnable dynamic ranking threshold, adjusted when the model encounters negative prediction shifts. Experimental results on various question-answering datasets from different domains show that our method outperforms the best baseline by $2.76\%$, with a notable $5.96\%$ boost in accuracy on long-tail questions that elude zero-shot inference.
Parameter Competition Balancing for Model Merging
Oct 03, 2024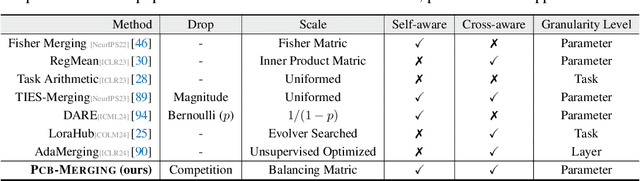
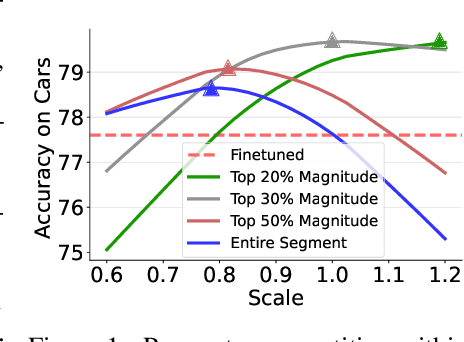
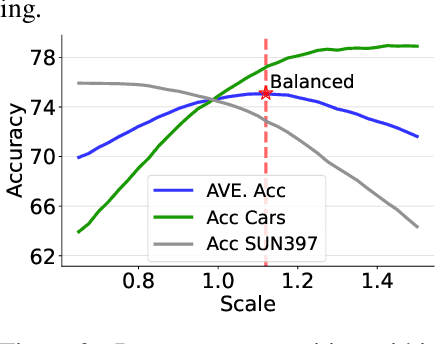
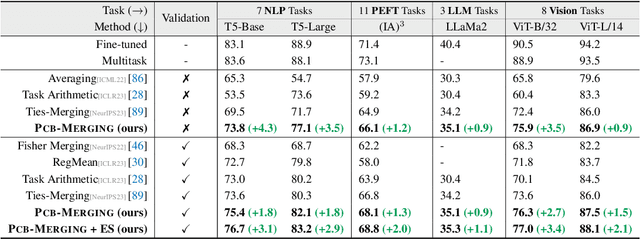
Abstract:While fine-tuning pretrained models has become common practice, these models often underperform outside their specific domains. Recently developed model merging techniques enable the direct integration of multiple models, each fine-tuned for distinct tasks, into a single model. This strategy promotes multitasking capabilities without requiring retraining on the original datasets. However, existing methods fall short in addressing potential conflicts and complex correlations between tasks, especially in parameter-level adjustments, posing a challenge in effectively balancing parameter competition across various tasks. This paper introduces an innovative technique named PCB-Merging (Parameter Competition Balancing), a lightweight and training-free technique that adjusts the coefficients of each parameter for effective model merging. PCB-Merging employs intra-balancing to gauge parameter significance within individual tasks and inter-balancing to assess parameter similarities across different tasks. Parameters with low importance scores are dropped, and the remaining ones are rescaled to form the final merged model. We assessed our approach in diverse merging scenarios, including cross-task, cross-domain, and cross-training configurations, as well as out-of-domain generalization. The experimental results reveal that our approach achieves substantial performance enhancements across multiple modalities, domains, model sizes, number of tasks, fine-tuning forms, and large language models, outperforming existing model merging methods. The code is publicly available at: \url{https://github.com/duguodong7/pcb-merging}.
Knowledge Fusion By Evolving Weights of Language Models
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Fine-tuning pre-trained language models, particularly large language models, demands extensive computing resources and can result in varying performance outcomes across different domains and datasets. This paper examines the approach of integrating multiple models from diverse training scenarios into a unified model. This unified model excels across various data domains and exhibits the ability to generalize well on out-of-domain data. We propose a knowledge fusion method named Evolver, inspired by evolutionary algorithms, which does not need further training or additional training data. Specifically, our method involves aggregating the weights of different language models into a population and subsequently generating offspring models through mutation and crossover operations. These offspring models are then evaluated against their parents, allowing for the preservation of those models that show enhanced performance on development datasets. Importantly, our model evolving strategy can be seamlessly integrated with existing model merging frameworks, offering a versatile tool for model enhancement. Experimental results on mainstream language models (i.e., encoder-only, decoder-only, encoder-decoder) reveal that Evolver outperforms previous state-of-the-art models by large margins. The code is publicly available at {https://github.com/duguodong7/model-evolution}.
CADE: Cosine Annealing Differential Evolution for Spiking Neural Network
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs) have gained prominence for their potential in neuromorphic computing and energy-efficient artificial intelligence, yet optimizing them remains a formidable challenge for gradient-based methods due to their discrete, spike-based computation. This paper attempts to tackle the challenges by introducing Cosine Annealing Differential Evolution (CADE), designed to modulate the mutation factor (F) and crossover rate (CR) of differential evolution (DE) for the SNN model, i.e., Spiking Element Wise (SEW) ResNet. Extensive empirical evaluations were conducted to analyze CADE. CADE showed a balance in exploring and exploiting the search space, resulting in accelerated convergence and improved accuracy compared to existing gradient-based and DE-based methods. Moreover, an initialization method based on a transfer learning setting was developed, pretraining on a source dataset (i.e., CIFAR-10) and fine-tuning the target dataset (i.e., CIFAR-100), to improve population diversity. It was found to further enhance CADE for SNN. Remarkably, CADE elevates the performance of the highest accuracy SEW model by an additional 0.52 percentage points, underscoring its effectiveness in fine-tuning and enhancing SNNs. These findings emphasize the pivotal role of a scheduler for F and CR adjustment, especially for DE-based SNN. Source Code on Github: https://github.com/Tank-Jiang/CADE4SNN.
Towards Stability of Parameter-free Optimization
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Hyperparameter tuning, particularly the selection of an appropriate learning rate in adaptive gradient training methods, remains a challenge. To tackle this challenge, in this paper, we propose a novel parameter-free optimizer, AdamG (Adam with the golden step size), designed to automatically adapt to diverse optimization problems without manual tuning. The core technique underlying AdamG is our golden step size derived for the AdaGrad-Norm algorithm, which is expected to help AdaGrad-Norm preserve the tuning-free convergence and approximate the optimal step size in expectation w.r.t. various optimization scenarios. To better evaluate tuning-free performance, we propose a novel evaluation criterion, stability, to comprehensively assess the efficacy of parameter-free optimizers in addition to classical performance criteria. Empirical results demonstrate that compared with other parameter-free baselines, AdamG achieves superior performance, which is consistently on par with Adam using a manually tuned learning rate across various optimization tasks.
Safe and Robust Watermark Injection with a Single OoD Image
Sep 04, 2023



Abstract:Training a high-performance deep neural network requires large amounts of data and computational resources. Protecting the intellectual property (IP) and commercial ownership of a deep model is challenging yet increasingly crucial. A major stream of watermarking strategies implants verifiable backdoor triggers by poisoning training samples, but these are often unrealistic due to data privacy and safety concerns and are vulnerable to minor model changes such as fine-tuning. To overcome these challenges, we propose a safe and robust backdoor-based watermark injection technique that leverages the diverse knowledge from a single out-of-distribution (OoD) image, which serves as a secret key for IP verification. The independence of training data makes it agnostic to third-party promises of IP security. We induce robustness via random perturbation of model parameters during watermark injection to defend against common watermark removal attacks, including fine-tuning, pruning, and model extraction. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed watermarking approach is not only time- and sample-efficient without training data, but also robust against the watermark removal attacks above.
Revisiting Data-Free Knowledge Distillation with Poisoned Teachers
Jun 04, 2023



Abstract:Data-free knowledge distillation (KD) helps transfer knowledge from a pre-trained model (known as the teacher model) to a smaller model (known as the student model) without access to the original training data used for training the teacher model. However, the security of the synthetic or out-of-distribution (OOD) data required in data-free KD is largely unknown and under-explored. In this work, we make the first effort to uncover the security risk of data-free KD w.r.t. untrusted pre-trained models. We then propose Anti-Backdoor Data-Free KD (ABD), the first plug-in defensive method for data-free KD methods to mitigate the chance of potential backdoors being transferred. We empirically evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed ABD in diminishing transferred backdoor knowledge while maintaining compatible downstream performances as the vanilla KD. We envision this work as a milestone for alarming and mitigating the potential backdoors in data-free KD. Codes are released at https://github.com/illidanlab/ABD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge