Bao Hoang
Distributed Harmonization: Federated Clustered Batch Effect Adjustment and Generalization
May 23, 2024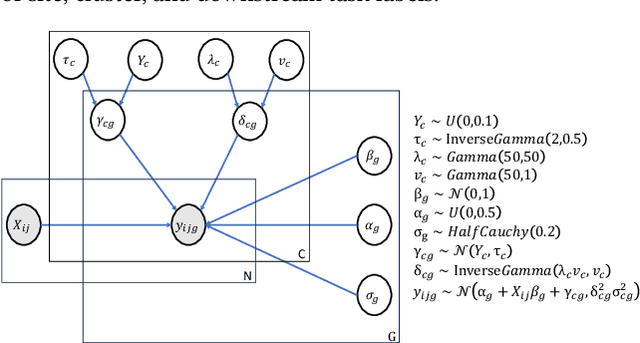

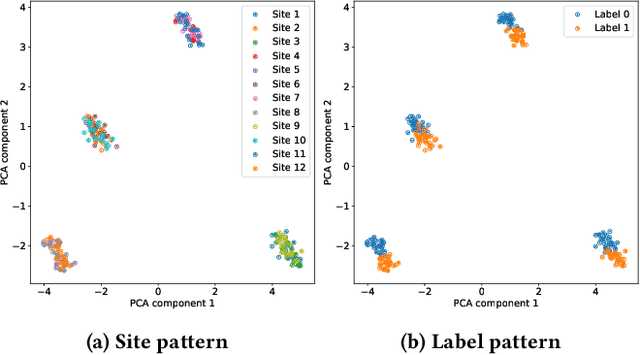

Abstract:Independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) data is essential to many data analysis and modeling techniques. In the medical domain, collecting data from multiple sites or institutions is a common strategy that guarantees sufficient clinical diversity, determined by the decentralized nature of medical data. However, data from various sites are easily biased by the local environment or facilities, thereby violating the i.i.d. rule. A common strategy is to harmonize the site bias while retaining important biological information. The ComBat is among the most popular harmonization approaches and has recently been extended to handle distributed sites. However, when faced with situations involving newly joined sites in training or evaluating data from unknown/unseen sites, ComBat lacks compatibility and requires retraining with data from all the sites. The retraining leads to significant computational and logistic overhead that is usually prohibitive. In this work, we develop a novel Cluster ComBat harmonization algorithm, which leverages cluster patterns of the data in different sites and greatly advances the usability of ComBat harmonization. We use extensive simulation and real medical imaging data from ADNI to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach.
Towards Stability of Parameter-free Optimization
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Hyperparameter tuning, particularly the selection of an appropriate learning rate in adaptive gradient training methods, remains a challenge. To tackle this challenge, in this paper, we propose a novel parameter-free optimizer, AdamG (Adam with the golden step size), designed to automatically adapt to diverse optimization problems without manual tuning. The core technique underlying AdamG is our golden step size derived for the AdaGrad-Norm algorithm, which is expected to help AdaGrad-Norm preserve the tuning-free convergence and approximate the optimal step size in expectation w.r.t. various optimization scenarios. To better evaluate tuning-free performance, we propose a novel evaluation criterion, stability, to comprehensively assess the efficacy of parameter-free optimizers in addition to classical performance criteria. Empirical results demonstrate that compared with other parameter-free baselines, AdamG achieves superior performance, which is consistently on par with Adam using a manually tuned learning rate across various optimization tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge