Sherif Abdulatif
Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
Class-Aware PillarMix: Can Mixed Sample Data Augmentation Enhance 3D Object Detection with Radar Point Clouds?
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Due to the significant effort required for data collection and annotation in 3D perception tasks, mixed sample data augmentation (MSDA) has been widely studied to generate diverse training samples by mixing existing data. Recently, many MSDA techniques have been developed for point clouds, but they mainly target LiDAR data, leaving their application to radar point clouds largely unexplored. In this paper, we examine the feasibility of applying existing MSDA methods to radar point clouds and identify several challenges in adapting these techniques. These obstacles stem from the radar's irregular angular distribution, deviations from a single-sensor polar layout in multi-radar setups, and point sparsity. To address these issues, we propose Class-Aware PillarMix (CAPMix), a novel MSDA approach that applies MixUp at the pillar level in 3D point clouds, guided by class labels. Unlike methods that rely a single mix ratio to the entire sample, CAPMix assigns an independent ratio to each pillar, boosting sample diversity. To account for the density of different classes, we use class-specific distributions: for dense objects (e.g., large vehicles), we skew ratios to favor points from another sample, while for sparse objects (e.g., pedestrians), we sample more points from the original. This class-aware mixing retains critical details and enriches each sample with new information, ultimately generating more diverse training data. Experimental results demonstrate that our method not only significantly boosts performance but also outperforms existing MSDA approaches across two datasets (Bosch Street and K-Radar). We believe that this straightforward yet effective approach will spark further investigation into MSDA techniques for radar data.
Exploring Domain Shift on Radar-Based 3D Object Detection Amidst Diverse Environmental Conditions
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:The rapid evolution of deep learning and its integration with autonomous driving systems have led to substantial advancements in 3D perception using multimodal sensors. Notably, radar sensors show greater robustness compared to cameras and lidar under adverse weather and varying illumination conditions. This study delves into the often-overlooked yet crucial issue of domain shift in 4D radar-based object detection, examining how varying environmental conditions, such as different weather patterns and road types, impact 3D object detection performance. Our findings highlight distinct domain shifts across various weather scenarios, revealing unique dataset sensitivities that underscore the critical role of radar point cloud generation. Additionally, we demonstrate that transitioning between different road types, especially from highways to urban settings, introduces notable domain shifts, emphasizing the necessity for diverse data collection across varied road environments. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive analysis of domain shift effects on 4D radar-based object detection. We believe this empirical study contributes to understanding the complex nature of domain shifts in radar data and suggests paths forward for data collection strategy in the face of environmental variability.
CMGAN: Conformer-Based Metric-GAN for Monaural Speech Enhancement
Sep 23, 2022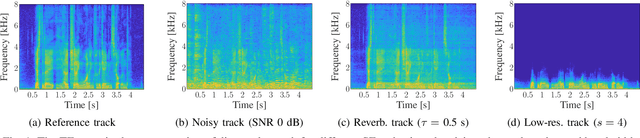
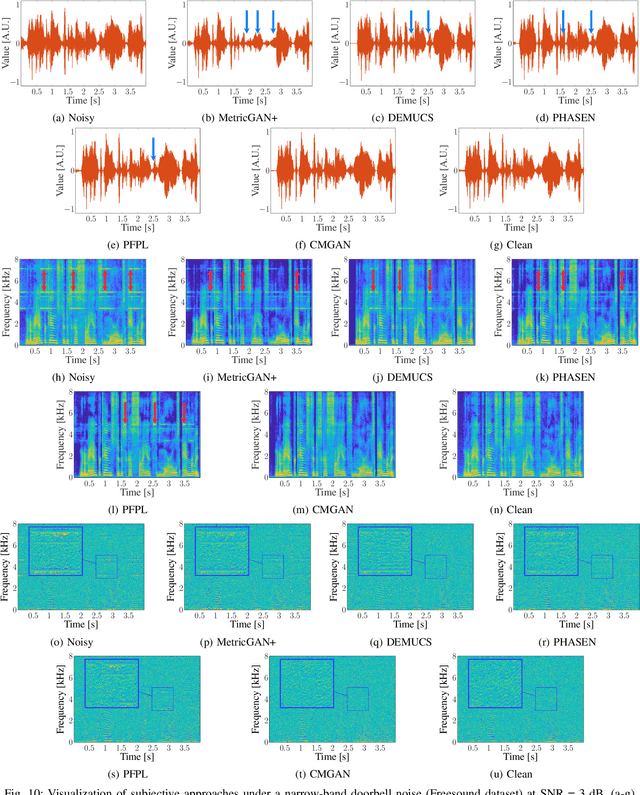
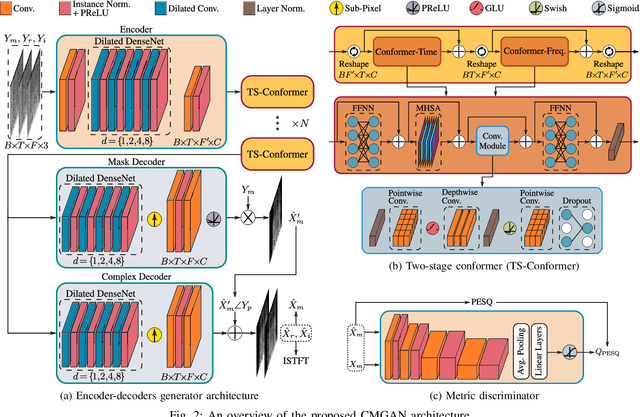
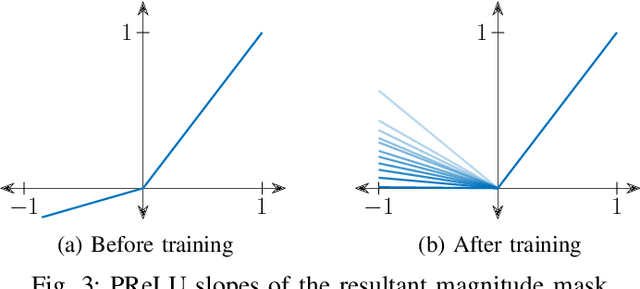
Abstract:Convolution-augmented transformers (Conformers) are recently proposed in various speech-domain applications, such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech separation, as they can capture both local and global dependencies. In this paper, we propose a conformer-based metric generative adversarial network (CMGAN) for speech enhancement (SE) in the time-frequency (TF) domain. The generator encodes the magnitude and complex spectrogram information using two-stage conformer blocks to model both time and frequency dependencies. The decoder then decouples the estimation into a magnitude mask decoder branch to filter out unwanted distortions and a complex refinement branch to further improve the magnitude estimation and implicitly enhance the phase information. Additionally, we include a metric discriminator to alleviate metric mismatch by optimizing the generator with respect to a corresponding evaluation score. Objective and subjective evaluations illustrate that CMGAN is able to show superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in three speech enhancement tasks (denoising, dereverberation and super-resolution). For instance, quantitative denoising analysis on Voice Bank+DEMAND dataset indicates that CMGAN outperforms various previous models with a margin, i.e., PESQ of 3.41 and SSNR of 11.10 dB.
CMGAN: Conformer-based Metric GAN for Speech Enhancement
Mar 28, 2022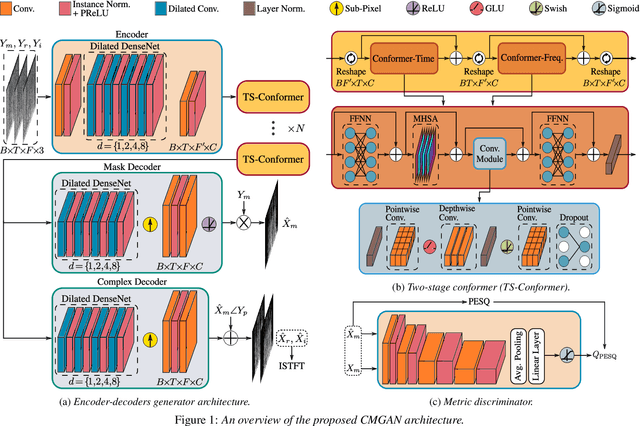
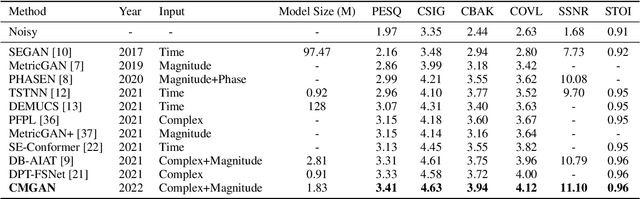
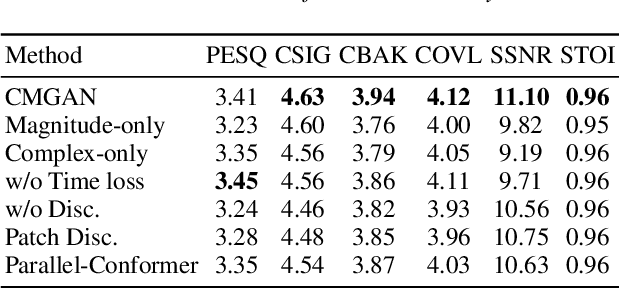
Abstract:Recently, convolution-augmented transformer (Conformer) has achieved promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and time-domain speech enhancement (SE), as it can capture both local and global dependencies in the speech signal. In this paper, we propose a conformer-based metric generative adversarial network (CMGAN) for SE in the time-frequency (TF) domain. In the generator, we utilize two-stage conformer blocks to aggregate all magnitude and complex spectrogram information by modeling both time and frequency dependencies. The estimation of magnitude and complex spectrogram is decoupled in the decoder stage and then jointly incorporated to reconstruct the enhanced speech. In addition, a metric discriminator is employed to further improve the quality of the enhanced estimated speech by optimizing the generator with respect to a corresponding evaluation score. Quantitative analysis on Voice Bank+DEMAND dataset indicates the capability of CMGAN in outperforming various previous models with a margin, i.e., PESQ of 3.41 and SSNR of 11.10 dB.
A MIMO Radar-based Few-Shot Learning Approach for Human-ID
Oct 16, 2021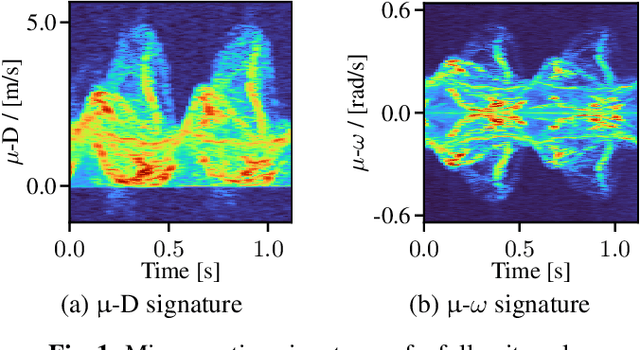
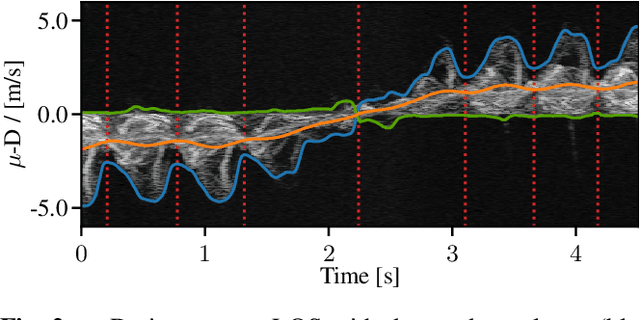


Abstract:Radar for deep learning-based human identification has become a research area of increasing interest. It has been shown that micro-Doppler (\(\upmu\)-D) can reflect the walking behavior through capturing the periodic limbs' micro-motions. One of the main aspects is maximizing the number of included classes while considering the real-time and training dataset size constraints. In this paper, a multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) radar is used to formulate micro-motion spectrograms of the elevation angular velocity (\(\upmu\)-\(\omega\)). The effectiveness of concatenating this newly-formulated spectrogram with the commonly used \(\upmu\)-D is investigated. To accommodate for non-constrained real walking motion, an adaptive cycle segmentation framework is utilized and a metric learning network is trained on half gait cycles (\(\approx\) 0.5 s). Studies on the effects of various numbers of classes (5--20), different dataset sizes, and varying observation time windows 1--2 s are conducted. A non-constrained walking dataset of 22 subjects is collected with different aspect angles with respect to the radar. The proposed few-shot learning (FSL) approach achieves a classification error of 11.3 % with only 2 min of training data per subject.
Uncertainty-Based Biological Age Estimation of Brain MRI Scans
Mar 15, 2021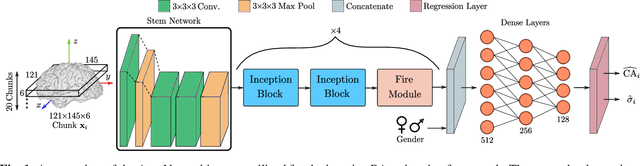
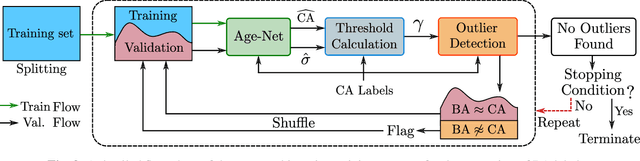
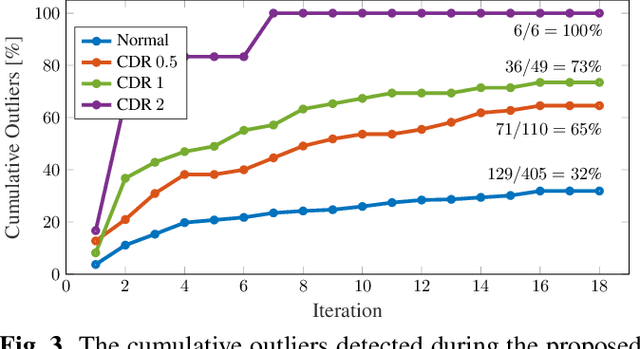
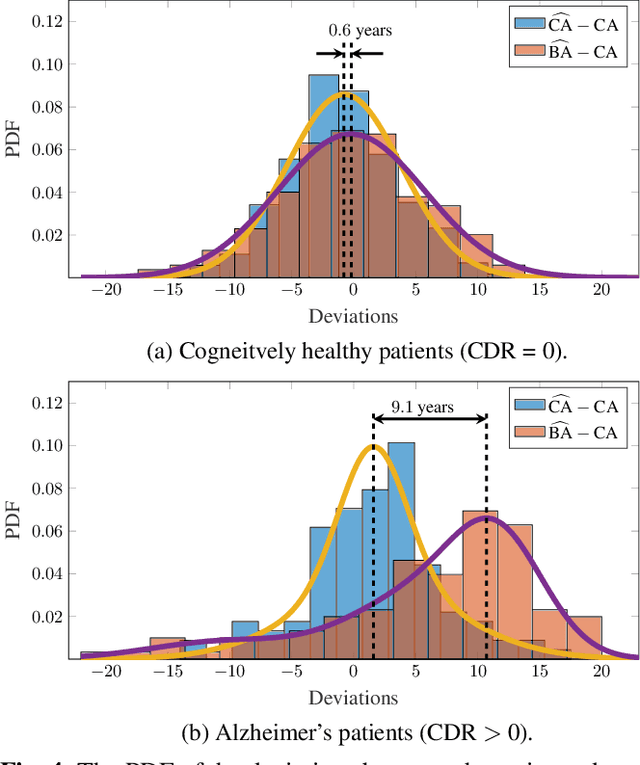
Abstract:Age is an essential factor in modern diagnostic procedures. However, assessment of the true biological age (BA) remains a daunting task due to the lack of reference ground-truth labels. Current BA estimation approaches are either restricted to skeletal images or rely on non-imaging modalities that yield a whole-body BA assessment. However, various organ systems may exhibit different aging characteristics due to lifestyle and genetic factors. In this initial study, we propose a new framework for organ-specific BA estimation utilizing 3D magnetic resonance image (MRI) scans. As a first step, this framework predicts the chronological age (CA) together with the corresponding patient-dependent aleatoric uncertainty. An iterative training algorithm is then utilized to segregate atypical aging patients from the given population based on the predicted uncertainty scores. In this manner, we hypothesize that training a new model on the remaining population should approximate the true BA behavior. We apply the proposed methodology on a brain MRI dataset containing healthy individuals as well as Alzheimer's patients. We demonstrate the correlation between the predicted BAs and the expected cognitive deterioration in Alzheimer's patients.
Investigating Cross-Domain Losses for Speech Enhancement
Oct 20, 2020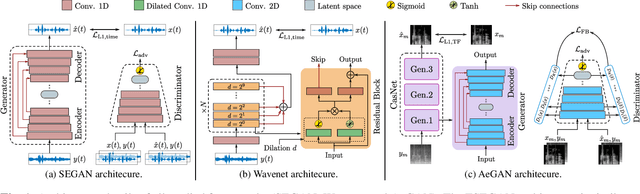
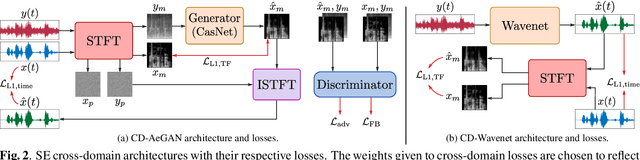
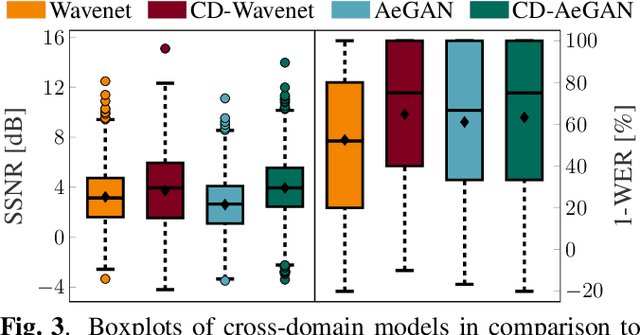
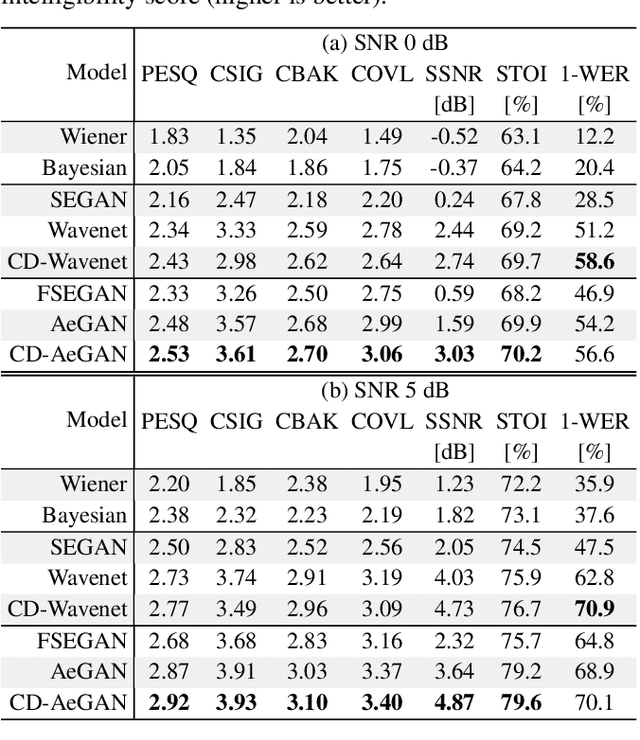
Abstract:Recent years have seen a surge in the number of available frameworks for speech enhancement (SE) and recognition. Whether model-based or constructed via deep learning, these frameworks often rely in isolation on either time-domain signals or time-frequency (TF) representations of speech data. In this study, we investigate the advantages of each set of approaches by separately examining their impact on speech intelligibility and quality. Furthermore, we combine the fragmented benefits of time-domain and TF speech representations by introducing two new cross-domain SE frameworks. A quantitative comparative analysis against recent model-based and deep learning SE approaches is performed to illustrate the merit of the proposed frameworks.
Age-Net: An MRI-Based Iterative Framework for Biological Age Estimation
Sep 22, 2020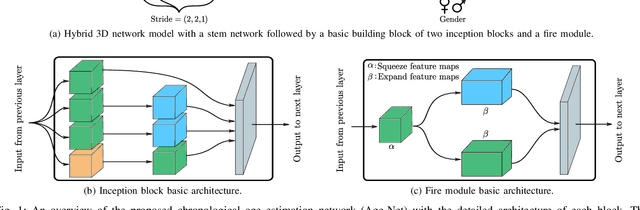
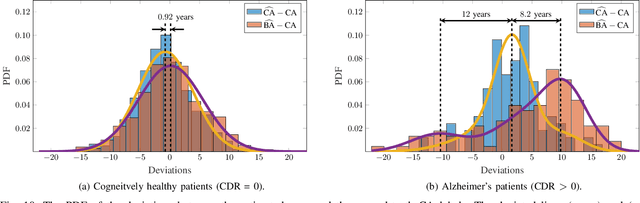
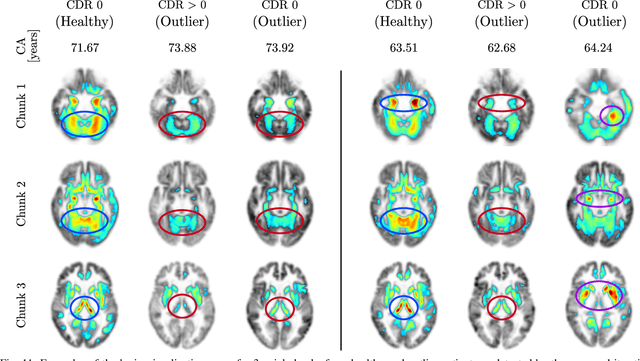
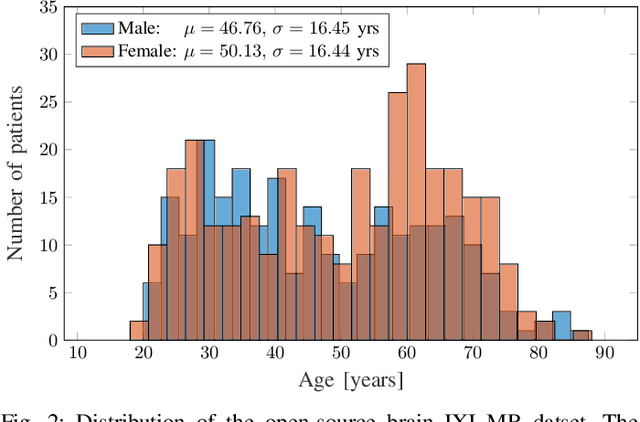
Abstract:The concept of biological age (BA) - although important in clinical practice - is hard to grasp mainly due to lack of a clearly defined reference standard. For specific applications, especially in pediatrics, medical image data are used for BA estimation in a routine clinical context. Beyond this young age group, BA estimation is restricted to whole-body assessment using non-imaging indicators such as blood biomarkers, genetic and cellular data. However, various organ systems may exhibit different aging characteristics due to lifestyle and genetic factors. Thus, a whole-body assessment of the BA does not reflect the deviations of aging behavior between organs. To this end, we propose a new imaging-based framework for organ-specific BA estimation. As a first step, we introduce a chronological age (CA) estimation framework using deep convolutional neural networks (Age-Net). We quantitatively assess the performance of this framework in comparison to existing CA estimation approaches. Furthermore, we expand upon Age-Net with a novel iterative data-cleaning algorithm to segregate atypical-aging patients (BA $\not \approx$ CA) from the given population. In this manner, we hypothesize that the remaining population should approximate the true BA behaviour. For this initial study, we apply the proposed methodology on a brain magnetic resonance image (MRI) dataset containing healthy individuals as well as Alzheimer's patients with different dementia ratings. We demonstrate the correlation between the predicted BAs and the expected cognitive deterioration in Alzheimer's patients. A statistical and visualization-based analysis has provided evidence regarding the potential and current challenges of the proposed methodology.
SELD-TCN: Sound Event Localization & Detection via Temporal Convolutional Networks
Mar 03, 2020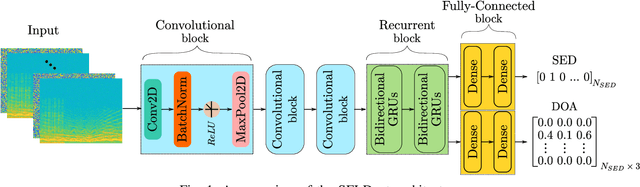
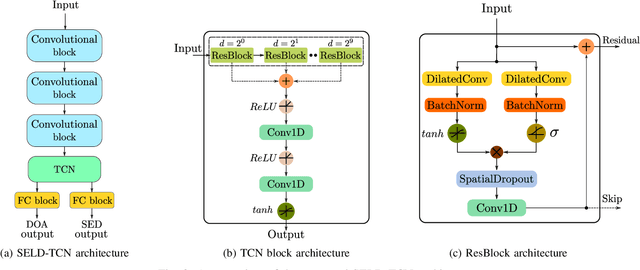
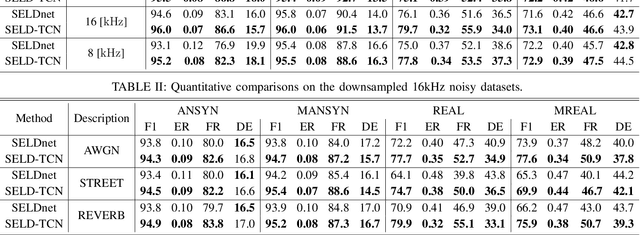
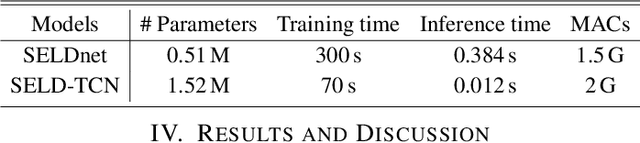
Abstract:The understanding of the surrounding environment plays a critical role in autonomous robotic systems, such as self-driving cars. Extensive research has been carried out concerning visual perception. Yet, to obtain a more complete perception of the environment, autonomous systems of the future should also take acoustic information into account. Recent sound event localization and detection (SELD) frameworks utilize convolutional recurrent neural networks (CRNNs). However, considering the recurrent nature of CRNNs, it becomes challenging to implement them efficiently on embedded hardware. Not only are their computations strenuous to parallelize, but they also require high memory bandwidth and large memory buffers. In this work, we develop a more robust and hardware-friendly novel architecture based on a temporal convolutional network(TCN). The proposed framework (SELD-TCN) outperforms the state-of-the-art SELDnet performance on four different datasets. Moreover, SELD-TCN achieves 4x faster training time per epoch and 40x faster inference time on an ordinary graphics processing unit (GPU).
Perceptual Speech Enhancement via Generative Adversarial Networks
Oct 21, 2019

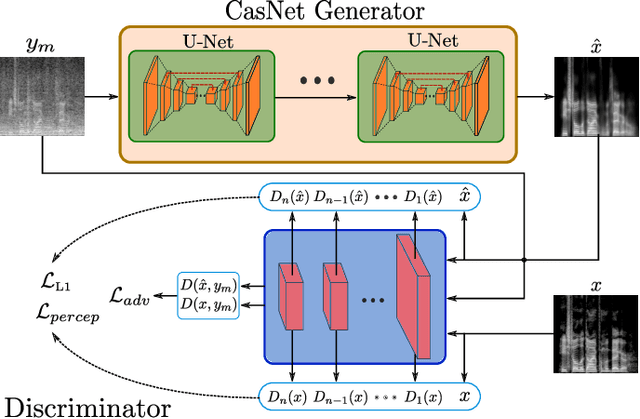

Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems are of vital importance nowadays in commonplace tasks such as speech-to-text processing and language translation. This created the need of an ASR system that can operate in realistic crowded environments. Thus, speech enhancement is now considered as a fundamental building block in newly developed ASR systems. In this paper, a generative adversarial network (GAN) based framework is investigated for the task of speech enhancement of audio tracks. A new architecture based on CasNet generator and additional perceptual loss is incorporated to get realistically denoised speech phonetics. Finally, the proposed framework is shown to quantitatively outperform other GAN-based speech enhancement approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge