Shan Cao
Deep Learning for Detecting and Early Predicting Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease from Spirogram Time Series: A UK Biobank Study
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung condition that causes airflow obstruction. The existing methods can only detect patients who already have COPD based on obvious features shown in the spirogram (In this article, the spirogram specifically involves measuring Volume-Flow curve time series). Early prediction of COPD risk is vital for monitoring COPD disease progression, slowing it down, or even preventing its onset. However, these methods fail to early predict an individual's probability of COPD in the future based on subtle features in the spirogram. To address this gap, for the first time, we propose DeepSpiro, a method based on deep learning for early prediction of future COPD risk. DeepSpiro consists of four parts. First, we construct Volume-Flow curves guided by Time-Volume instability smoothing (SpiroSmoother) to enhance the stability of the original Volume-Flow curves precisely. Second, we extract critical features from the evolution of varied-length key patches (SpiroEncoder) to capture the key temporal evolution from original high-dimensional dynamic sequences to a unified low-dimensional temporal representation. Third, we explain the model based on temporal attention and heterogeneous feature fusion (SpiroExplainer), which integrates information from heterogeneous data such as spirogram and demographic information. Fourth, we predict the risk of COPD based on the evolution of key patch concavity (SpiroPredictor), enabling accurate prediction of the risk of disease in high-risk patients who are not yet diagnosed, for up to 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 years, and beyond. We conduct experiments on the UK Biobank dataset. Results show that DeepSpiro achieves an AUC value of 0.8328 in the task of detecting COPD. In early prediction tasks, high-risk and low-risk groups show significant differences in the future, with a p-value of <0.001.
A Hierarchical Dataflow-Driven Heterogeneous Architecture for Wireless Baseband Processing
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Wireless baseband processing (WBP) is a key element of wireless communications, with a series of signal processing modules to improve data throughput and counter channel fading. Conventional hardware solutions, such as digital signal processors (DSPs) and more recently, graphic processing units (GPUs), provide various degrees of parallelism, yet they both fail to take into account the cyclical and consecutive character of WBP. Furthermore, the large amount of data in WBPs cannot be processed quickly in symmetric multiprocessors (SMPs) due to the unpredictability of memory latency. To address this issue, we propose a hierarchical dataflow-driven architecture to accelerate WBP. A pack-and-ship approach is presented under a non-uniform memory access (NUMA) architecture to allow the subordinate tiles to operate in a bundled access and execute manner. We also propose a multi-level dataflow model and the related scheduling scheme to manage and allocate the heterogeneous hardware resources. Experiment results demonstrate that our prototype achieves $2\times$ and $2.3\times$ speedup in terms of normalized throughput and single-tile clock cycles compared with GPU and DSP counterparts in several critical WBP benchmarks. Additionally, a link-level throughput of $288$ Mbps can be achieved with a $45$-core configuration.
A Non-Invasive Interpretable NAFLD Diagnostic Method Combining TCM Tongue Features
Sep 06, 2023



Abstract:Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a clinicopathological syndrome characterized by hepatic steatosis resulting from the exclusion of alcohol and other identifiable liver-damaging factors. It has emerged as a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Currently, the conventional methods for NAFLD detection are expensive and not suitable for users to perform daily diagnostics. To address this issue, this study proposes a non-invasive and interpretable NAFLD diagnostic method, the required user-provided indicators are only Gender, Age, Height, Weight, Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, and tongue image. This method involves merging patients' physiological indicators with tongue features, which are then input into a fusion network named SelectorNet. SelectorNet combines attention mechanisms with feature selection mechanisms, enabling it to autonomously learn the ability to select important features. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves an accuracy of 77.22\% using only non-invasive data, and it also provides compelling interpretability matrices. This study contributes to the early diagnosis of NAFLD and the intelligent advancement of TCM tongue diagnosis. The project in this paper is available at: https://github.com/cshan-github/SelectorNet.
TongueSAM: An Universal Tongue Segmentation Model Based on SAM with Zero-Shot
Aug 12, 2023Abstract:Tongue segmentation serves as the primary step in automated TCM tongue diagnosis, which plays a significant role in the diagnostic results. Currently, numerous deep learning based methods have achieved promising results. However, most of these methods exhibit mediocre performance on tongues different from the training set. To address this issue, this paper proposes a universal tongue segmentation model named TongueSAM based on SAM (Segment Anything Model). SAM is a large-scale pretrained interactive segmentation model known for its powerful zero-shot generalization capability. Applying SAM to tongue segmentation enables the segmentation of various types of tongue images with zero-shot. In this study, a Prompt Generator based on object detection is integrated into SAM to enable an end-to-end automated tongue segmentation method. Experiments demonstrate that TongueSAM achieves exceptional performance across various of tongue segmentation datasets, particularly under zero-shot. TongueSAM can be directly applied to other datasets without fine-tuning. As far as we know, this is the first application of large-scale pretrained model for tongue segmentation. The project and pretrained model of TongueSAM be publiced in :https://github.com/cshan-github/TongueSAM.
Multi-Task and Multi-Modal Learning for RGB Dynamic Gesture Recognition
Oct 29, 2021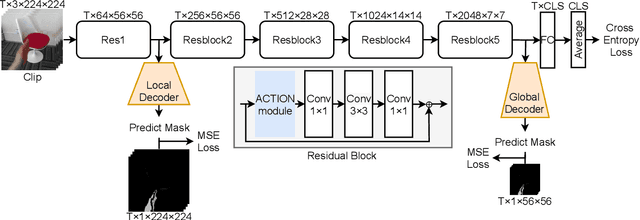
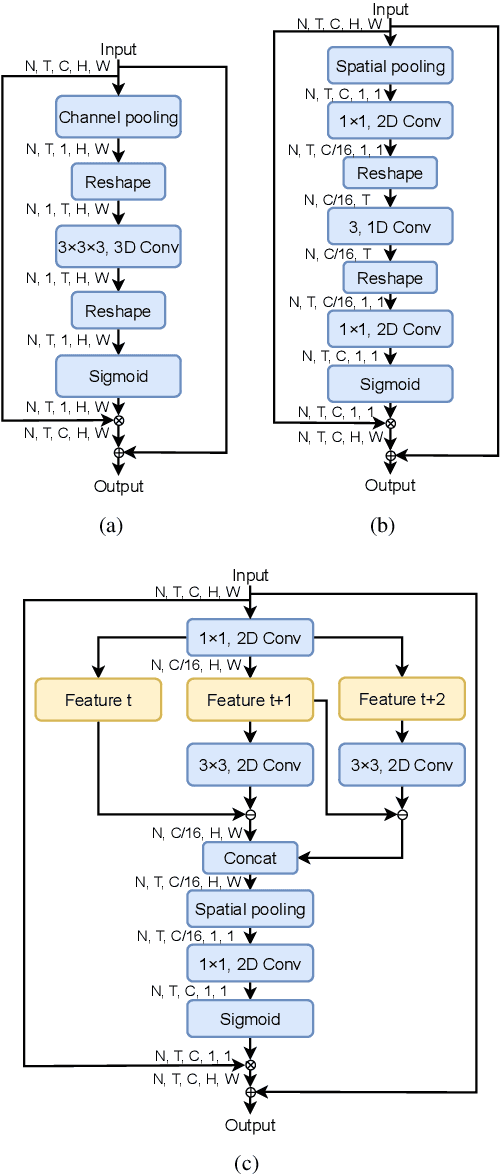


Abstract:Gesture recognition is getting more and more popular due to various application possibilities in human-machine interaction. Existing multi-modal gesture recognition systems take multi-modal data as input to improve accuracy, but such methods require more modality sensors, which will greatly limit their application scenarios. Therefore we propose an end-to-end multi-task learning framework in training 2D convolutional neural networks. The framework can use the depth modality to improve accuracy during training and save costs by using only RGB modality during inference. Our framework is trained to learn a representation for multi-task learning: gesture segmentation and gesture recognition. Depth modality contains the prior information for the location of the gesture. Therefore it can be used as the supervision for gesture segmentation. A plug-and-play module named Multi-Scale-Decoder is designed to realize gesture segmentation, which contains two sub-decoder. It is used in the lower stage and higher stage respectively, and can help the network pay attention to key target areas, ignore irrelevant information, and extract more discriminant features. Additionally, the MSD module and depth modality are only used in the training stage to improve gesture recognition performance. Only RGB modality and network without MSD are required during inference. Experimental results on three public gesture recognition datasets show that our proposed method provides superior performance compared with existing gesture recognition frameworks. Moreover, using the proposed plug-and-play MSD in other 2D CNN-based frameworks also get an excellent accuracy improvement.
IFR: Iterative Fusion Based Recognizer For Low Quality Scene Text Recognition
Aug 13, 2021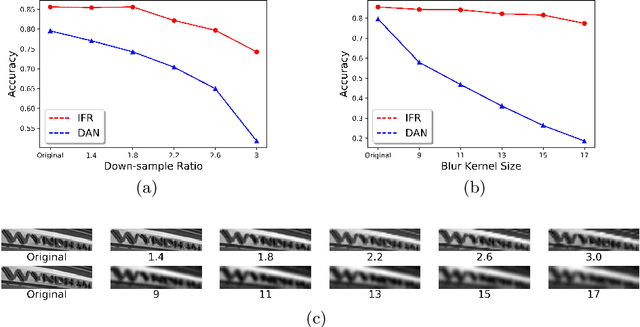
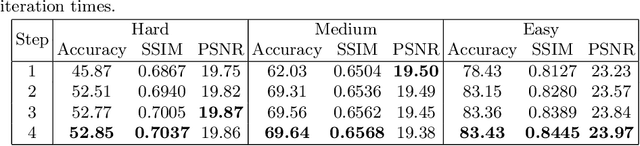
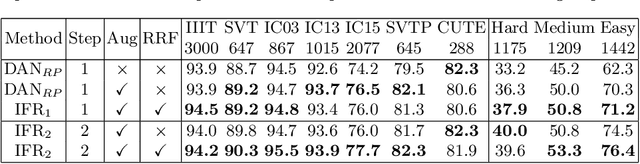
Abstract:Although recent works based on deep learning have made progress in improving recognition accuracy on scene text recognition, how to handle low-quality text images in end-to-end deep networks remains a research challenge. In this paper, we propose an Iterative Fusion based Recognizer (IFR) for low quality scene text recognition, taking advantage of refined text images input and robust feature representation. IFR contains two branches which focus on scene text recognition and low quality scene text image recovery respectively. We utilize an iterative collaboration between two branches, which can effectively alleviate the impact of low quality input. A feature fusion module is proposed to strengthen the feature representation of the two branches, where the features from the Recognizer are Fused with image Restoration branch, referred to as RRF. Without changing the recognition network structure, extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results show that the proposed method significantly outperforms the baseline methods in boosting the recognition accuracy of benchmark datasets and low resolution images in TextZoom dataset.
SGTBN: Generating Dense Depth Maps from Single-Line LiDAR
Jun 24, 2021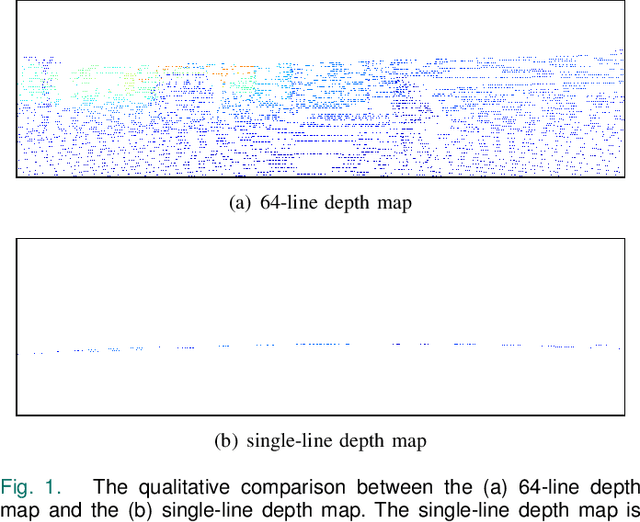
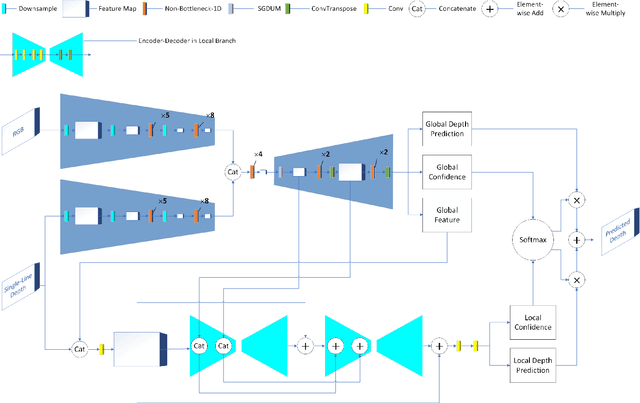
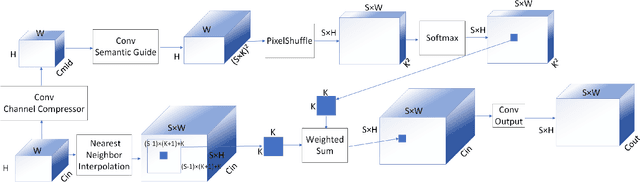
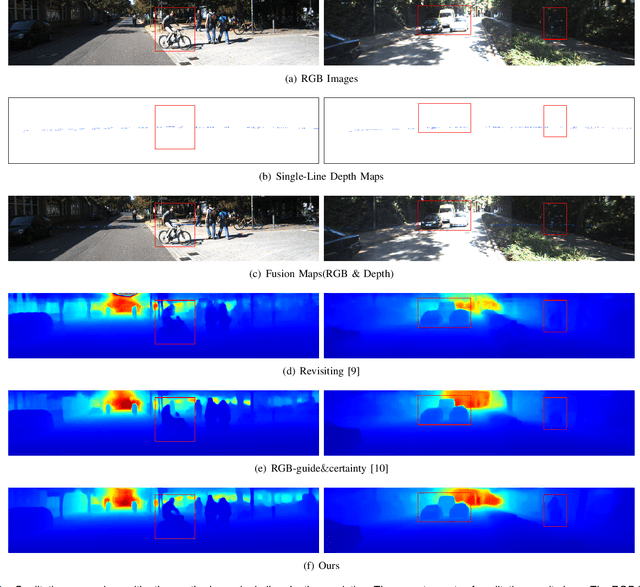
Abstract:Depth completion aims to generate a dense depth map from the sparse depth map and aligned RGB image. However, current depth completion methods use extremely expensive 64-line LiDAR(about $100,000) to obtain sparse depth maps, which will limit their application scenarios. Compared with the 64-line LiDAR, the single-line LiDAR is much less expensive and much more robust. Therefore, we propose a method to tackle the problem of single-line depth completion, in which we aim to generate a dense depth map from the single-line LiDAR info and the aligned RGB image. A single-line depth completion dataset is proposed based on the existing 64-line depth completion dataset(KITTI). A network called Semantic Guided Two-Branch Network(SGTBN) which contains global and local branches to extract and fuse global and local info is proposed for this task. A Semantic guided depth upsampling module is used in our network to make full use of the semantic info in RGB images. Except for the usual MSE loss, we add the virtual normal loss to increase the constraint of high-order 3D geometry in our network. Our network outperforms the state-of-the-art in the single-line depth completion task. Besides, compared with the monocular depth estimation, our method also has significant advantages in precision and model size.
Arbitrary-Shaped Text Detection withAdaptive Text Region Representation
Apr 01, 2021
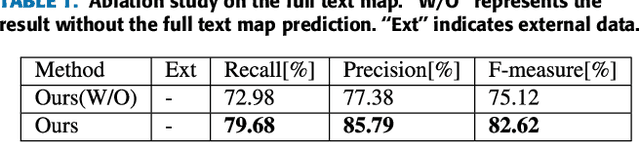

Abstract:Text detection/localization, as an important task in computer vision, has witnessed substantialadvancements in methodology and performance with convolutional neural networks. However, the vastmajority of popular methods use rectangles or quadrangles to describe text regions. These representationshave inherent drawbacks, especially relating to dense adjacent text and loose regional text boundaries,which usually cause difficulty detecting arbitrarily shaped text. In this paper, we propose a novel text regionrepresentation method, with a robust pipeline, which can precisely detect dense adjacent text instances witharbitrary shapes. We consider a text instance to be composed of an adaptive central text region mask anda corresponding expanding ratio between the central text region and the full text region. More specifically,our pipeline generates adaptive central text regions and corresponding expanding ratios with a proposedtraining strategy, followed by a new proposed post-processing algorithm which expands central text regionsto the complete text instance with the corresponding expanding ratios. We demonstrated that our new textregion representation is effective, and that the pipeline can precisely detect closely adjacent text instances ofarbitrary shapes. Experimental results on common datasets demonstrate superior performance o
Tracking Based Semi-Automatic Annotation for Scene Text Videos
Mar 29, 2021
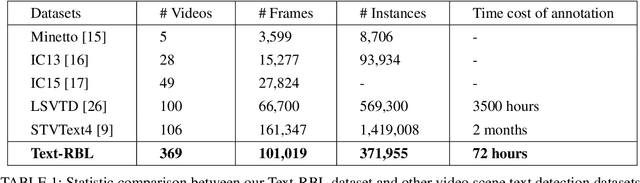

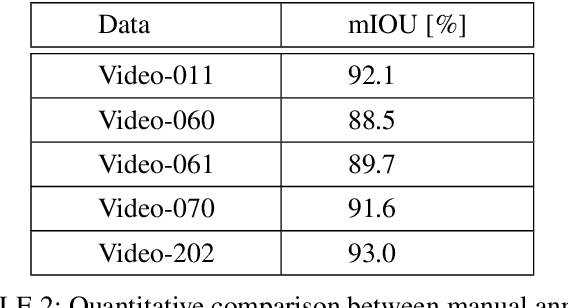
Abstract:Recently, video scene text detection has received increasing attention due to its comprehensive applications. However, the lack of annotated scene text video datasets has become one of the most important problems, which hinders the development of video scene text detection. The existing scene text video datasets are not large-scale due to the expensive cost caused by manual labeling. In addition, the text instances in these datasets are too clear to be a challenge. To address the above issues, we propose a tracking based semi-automatic labeling strategy for scene text videos in this paper. We get semi-automatic scene text annotation by labeling manually for the first frame and tracking automatically for the subsequent frames, which avoid the huge cost of manual labeling. Moreover, a paired low-quality scene text video dataset named Text-RBL is proposed, consisting of raw videos, blurry videos, and low-resolution videos, labeled by the proposed convenient semi-automatic labeling strategy. Through an averaging operation and bicubic down-sampling operation over the raw videos, we can efficiently obtain blurry videos and low-resolution videos paired with raw videos separately. To verify the effectiveness of Text-RBL, we propose a baseline model combined with the text detector and tracker for video scene text detection. Moreover, a failure detection scheme is designed to alleviate the baseline model drift issue caused by complex scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Text-RBL with paired low-quality videos labeled by the semi-automatic method can significantly improve the performance of the text detector in low-quality scenes.
A Dataset and Benchmark Towards Multi-Modal Face Anti-Spoofing Under Surveillance Scenarios
Mar 29, 2021



Abstract:Face Anti-spoofing (FAS) is a challenging problem due to complex serving scenarios and diverse face presentation attack patterns. Especially when captured images are low-resolution, blurry, and coming from different domains, the performance of FAS will degrade significantly. The existing multi-modal FAS datasets rarely pay attention to the cross-domain problems under deployment scenarios, which is not conducive to the study of model performance. To solve these problems, we explore the fine-grained differences between multi-modal cameras and construct a cross-domain multi-modal FAS dataset under surveillance scenarios called GREAT-FASD-S. Besides, we propose an Attention based Face Anti-spoofing network with Feature Augment (AFA) to solve the FAS towards low-quality face images. It consists of the depthwise separable attention module (DAM) and the multi-modal based feature augment module (MFAM). Our model can achieve state-of-the-art performance on the CASIA-SURF dataset and our proposed GREAT-FASD-S dataset.
* Published in: IEEE Access
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge