Samuel Dooley
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Transformers Boost the Performance of Decision Trees on Tabular Data across Sample Sizes
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) perform remarkably well on tabular datasets in zero- and few-shot settings, since they can extract meaning from natural language column headers that describe features and labels. Similarly, TabPFN, a recent non-LLM transformer pretrained on numerous tables for in-context learning, has demonstrated excellent performance for dataset sizes up to a thousand samples. In contrast, gradient-boosted decision trees (GBDTs) are typically trained from scratch on each dataset without benefiting from pretraining data and must learn the relationships between columns from their entries alone since they lack natural language understanding. LLMs and TabPFN excel on small tabular datasets where a strong prior is essential, yet they are not competitive with GBDTs on medium or large datasets, since their context lengths are limited. In this paper, we propose a simple and lightweight approach for fusing large language models and TabPFN with gradient-boosted decision trees, which allows scalable GBDTs to benefit from the natural language capabilities and pretraining of transformers. We name our fusion methods LLM-Boost and PFN-Boost, respectively. While matching or surpassing the performance of the transformer at sufficiently small dataset sizes and GBDTs at sufficiently large sizes, LLM-Boost and PFN-Boost outperform both standalone components on a wide range of dataset sizes in between. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance against numerous baselines and ensembling algorithms. We find that PFN-Boost achieves the best average performance among all methods we test for all but very small dataset sizes. We release our code at http://github.com/MayukaJ/LLM-Boost .
LiveBench: A Challenging, Contamination-Free LLM Benchmark
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Test set contamination, wherein test data from a benchmark ends up in a newer model's training set, is a well-documented obstacle for fair LLM evaluation and can quickly render benchmarks obsolete. To mitigate this, many recent benchmarks crowdsource new prompts and evaluations from human or LLM judges; however, these can introduce significant biases, and break down when scoring hard questions. In this work, we introduce a new benchmark for LLMs designed to be immune to both test set contamination and the pitfalls of LLM judging and human crowdsourcing. We release LiveBench, the first benchmark that (1) contains frequently-updated questions from recent information sources, (2) scores answers automatically according to objective ground-truth values, and (3) contains a wide variety of challenging tasks, spanning math, coding, reasoning, language, instruction following, and data analysis. To achieve this, LiveBench contains questions that are based on recently-released math competitions, arXiv papers, news articles, and datasets, and it contains harder, contamination-free versions of tasks from previous benchmarks such as Big-Bench Hard, AMPS, and IFEval. We evaluate many prominent closed-source models, as well as dozens of open-source models ranging from 0.5B to 110B in size. LiveBench is difficult, with top models achieving below 65% accuracy. We release all questions, code, and model answers. Questions will be added and updated on a monthly basis, and we will release new tasks and harder versions of tasks over time so that LiveBench can distinguish between the capabilities of LLMs as they improve in the future. We welcome community engagement and collaboration for expanding the benchmark tasks and models.
Large Language Models Must Be Taught to Know What They Don't Know
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:When using large language models (LLMs) in high-stakes applications, we need to know when we can trust their predictions. Some works argue that prompting high-performance LLMs is sufficient to produce calibrated uncertainties, while others introduce sampling methods that can be prohibitively expensive. In this work, we first argue that prompting on its own is insufficient to achieve good calibration and then show that fine-tuning on a small dataset of correct and incorrect answers can create an uncertainty estimate with good generalization and small computational overhead. We show that a thousand graded examples are sufficient to outperform baseline methods and that training through the features of a model is necessary for good performance and tractable for large open-source models when using LoRA. We also investigate the mechanisms that enable reliable LLM uncertainty estimation, finding that many models can be used as general-purpose uncertainty estimators, applicable not just to their own uncertainties but also the uncertainty of other models. Lastly, we show that uncertainty estimates inform human use of LLMs in human-AI collaborative settings through a user study.
Multi-objective Differentiable Neural Architecture Search
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Pareto front profiling in multi-objective optimization (MOO), i.e. finding a diverse set of Pareto optimal solutions, is challenging, especially with expensive objectives like neural network training. Typically, in MOO neural architecture search (NAS), we aim to balance performance and hardware metrics across devices. Prior NAS approaches simplify this task by incorporating hardware constraints into the objective function, but profiling the Pareto front necessitates a search for each constraint. In this work, we propose a novel NAS algorithm that encodes user preferences for the trade-off between performance and hardware metrics, and yields representative and diverse architectures across multiple devices in just one search run. To this end, we parameterize the joint architectural distribution across devices and multiple objectives via a hypernetwork that can be conditioned on hardware features and preference vectors, enabling zero-shot transferability to new devices. Extensive experiments with up to 19 hardware devices and 3 objectives showcase the effectiveness and scalability of our method. Finally, we show that, without additional costs, our method outperforms existing MOO NAS methods across qualitatively different search spaces and datasets, including MobileNetV3 on ImageNet-1k and a Transformer space on machine translation.
Smaug: Fixing Failure Modes of Preference Optimisation with DPO-Positive
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:Direct Preference Optimisation (DPO) is effective at significantly improving the performance of large language models (LLMs) on downstream tasks such as reasoning, summarisation, and alignment. Using pairs of preferred and dispreferred data, DPO models the \textit{relative} probability of picking one response over another. In this work, first we show theoretically that the standard DPO loss can lead to a \textit{reduction} of the model's likelihood of the preferred examples, as long as the relative probability between the preferred and dispreferred classes increases. We then show empirically that this phenomenon occurs when fine-tuning LLMs on common datasets, especially datasets in which the edit distance between pairs of completions is low. Using these insights, we design DPO-Positive (DPOP), a new loss function and training procedure which avoids this failure mode. Surprisingly, we also find that DPOP significantly outperforms DPO across a wide variety of datasets and downstream tasks, including datasets with high edit distances between completions. By fine-tuning with DPOP, we create and release Smaug-34B and Smaug-72B, which achieve state-of-the-art open-source performance. Notably, Smaug-72B is nearly 2\% better than any other open-source model on the HuggingFace Open LLM Leaderboard and becomes the first open-source LLM to surpass an average accuracy of 80\%.
ForecastPFN: Synthetically-Trained Zero-Shot Forecasting
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:The vast majority of time-series forecasting approaches require a substantial training dataset. However, many real-life forecasting applications have very little initial observations, sometimes just 40 or fewer. Thus, the applicability of most forecasting methods is restricted in data-sparse commercial applications. While there is recent work in the setting of very limited initial data (so-called `zero-shot' forecasting), its performance is inconsistent depending on the data used for pretraining. In this work, we take a different approach and devise ForecastPFN, the first zero-shot forecasting model trained purely on a novel synthetic data distribution. ForecastPFN is a prior-data fitted network, trained to approximate Bayesian inference, which can make predictions on a new time series dataset in a single forward pass. Through extensive experiments, we show that zero-shot predictions made by ForecastPFN are more accurate and faster compared to state-of-the-art forecasting methods, even when the other methods are allowed to train on hundreds of additional in-distribution data points.
Fairer and More Accurate Tabular Models Through NAS
Oct 18, 2023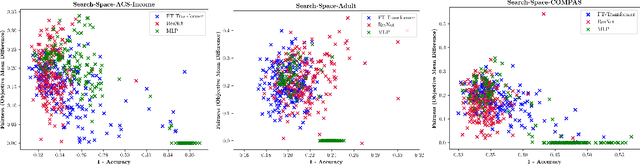
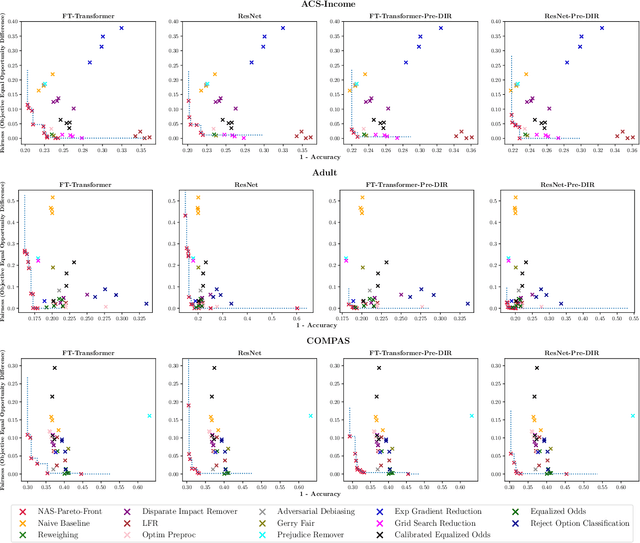
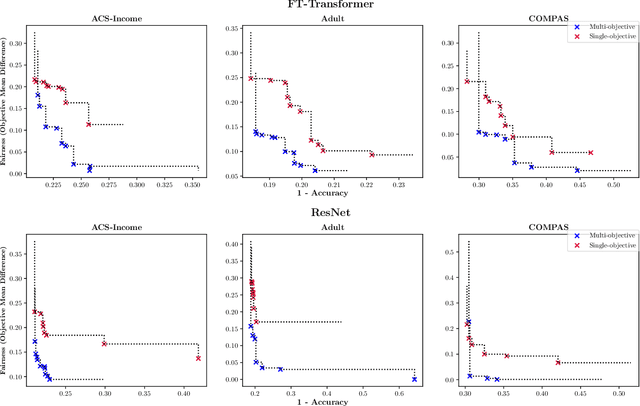
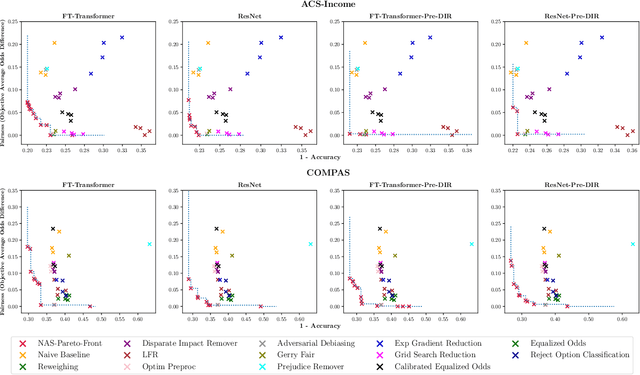
Abstract:Making models algorithmically fairer in tabular data has been long studied, with techniques typically oriented towards fixes which usually take a neural model with an undesirable outcome and make changes to how the data are ingested, what the model weights are, or how outputs are processed. We employ an emergent and different strategy where we consider updating the model's architecture and training hyperparameters to find an entirely new model with better outcomes from the beginning of the debiasing procedure. In this work, we propose using multi-objective Neural Architecture Search (NAS) and Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO) in the first application to the very challenging domain of tabular data. We conduct extensive exploration of architectural and hyperparameter spaces (MLP, ResNet, and FT-Transformer) across diverse datasets, demonstrating the dependence of accuracy and fairness metrics of model predictions on hyperparameter combinations. We show that models optimized solely for accuracy with NAS often fail to inherently address fairness concerns. We propose a novel approach that jointly optimizes architectural and training hyperparameters in a multi-objective constraint of both accuracy and fairness. We produce architectures that consistently Pareto dominate state-of-the-art bias mitigation methods either in fairness, accuracy or both, all of this while being Pareto-optimal over hyperparameters achieved through single-objective (accuracy) optimization runs. This research underscores the promise of automating fairness and accuracy optimization in deep learning models.
Data Contamination Through the Lens of Time
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Recent claims about the impressive abilities of large language models (LLMs) are often supported by evaluating publicly available benchmarks. Since LLMs train on wide swaths of the internet, this practice raises concerns of data contamination, i.e., evaluating on examples that are explicitly or implicitly included in the training data. Data contamination remains notoriously challenging to measure and mitigate, even with partial attempts like controlled experimentation of training data, canary strings, or embedding similarities. In this work, we conduct the first thorough longitudinal analysis of data contamination in LLMs by using the natural experiment of training cutoffs in GPT models to look at benchmarks released over time. Specifically, we consider two code/mathematical problem-solving datasets, Codeforces and Project Euler, and find statistically significant trends among LLM pass rate vs. GitHub popularity and release date that provide strong evidence of contamination. By open-sourcing our dataset, raw results, and evaluation framework, our work paves the way for rigorous analyses of data contamination in modern models. We conclude with a discussion of best practices and future steps for publicly releasing benchmarks in the age of LLMs that train on webscale data.
Giraffe: Adventures in Expanding Context Lengths in LLMs
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) that rely on attention mechanisms are typically trained with fixed context lengths which enforce upper limits on the length of input sequences that they can handle at evaluation time. To use these models on sequences longer than the train-time context length, one might employ techniques from the growing family of context length extrapolation methods -- most of which focus on modifying the system of positional encodings used in the attention mechanism to indicate where tokens or activations are located in the input sequence. We conduct a wide survey of existing methods of context length extrapolation on a base LLaMA or LLaMA 2 model, and introduce some of our own design as well -- in particular, a new truncation strategy for modifying the basis for the position encoding. We test these methods using three new evaluation tasks (FreeFormQA, AlteredNumericQA, and LongChat-Lines) as well as perplexity, which we find to be less fine-grained as a measure of long context performance of LLMs. We release the three tasks publicly as datasets on HuggingFace. We discover that linear scaling is the best method for extending context length, and show that further gains can be achieved by using longer scales at evaluation time. We also discover promising extrapolation capabilities in the truncated basis. To support further research in this area, we release three new 13B parameter long-context models which we call Giraffe: 4k and 16k context models trained from base LLaMA-13B, and a 32k context model trained from base LLaMA2-13B. We also release the code to replicate our results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge