Sami Mourad
AI Explainability 360: Impact and Design
Sep 24, 2021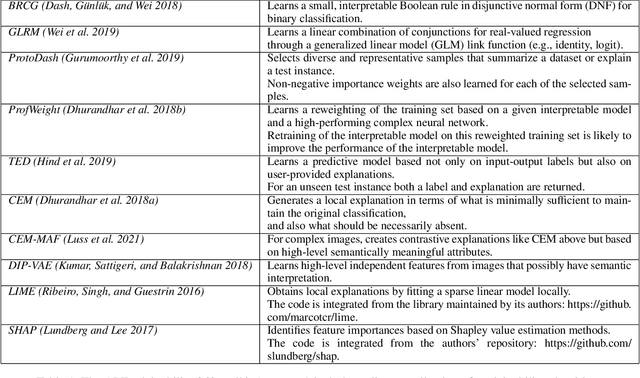

Abstract:As artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms become increasingly prevalent in society, multiple stakeholders are calling for these algorithms to provide explanations. At the same time, these stakeholders, whether they be affected citizens, government regulators, domain experts, or system developers, have different explanation needs. To address these needs, in 2019, we created AI Explainability 360 (Arya et al. 2020), an open source software toolkit featuring ten diverse and state-of-the-art explainability methods and two evaluation metrics. This paper examines the impact of the toolkit with several case studies, statistics, and community feedback. The different ways in which users have experienced AI Explainability 360 have resulted in multiple types of impact and improvements in multiple metrics, highlighted by the adoption of the toolkit by the independent LF AI & Data Foundation. The paper also describes the flexible design of the toolkit, examples of its use, and the significant educational material and documentation available to its users.
One Explanation Does Not Fit All: A Toolkit and Taxonomy of AI Explainability Techniques
Sep 14, 2019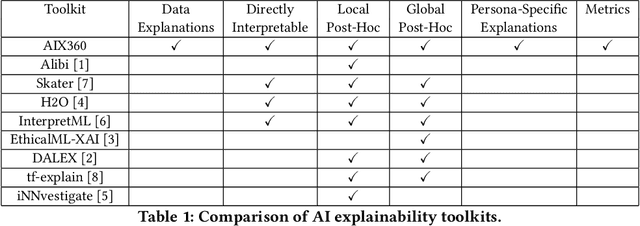
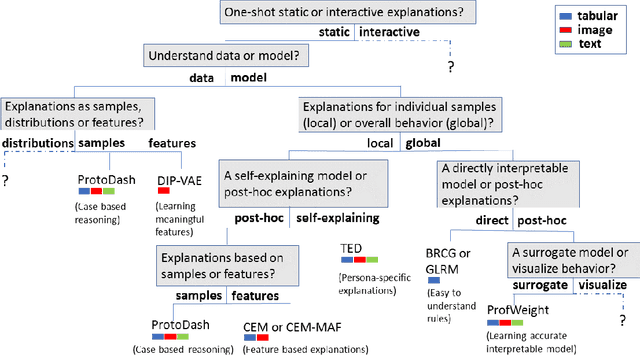
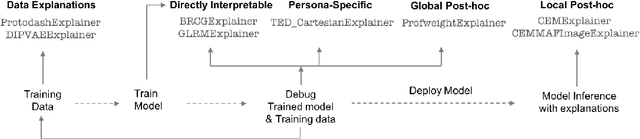
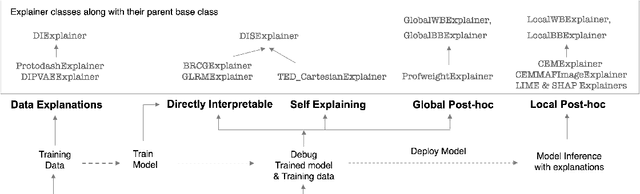
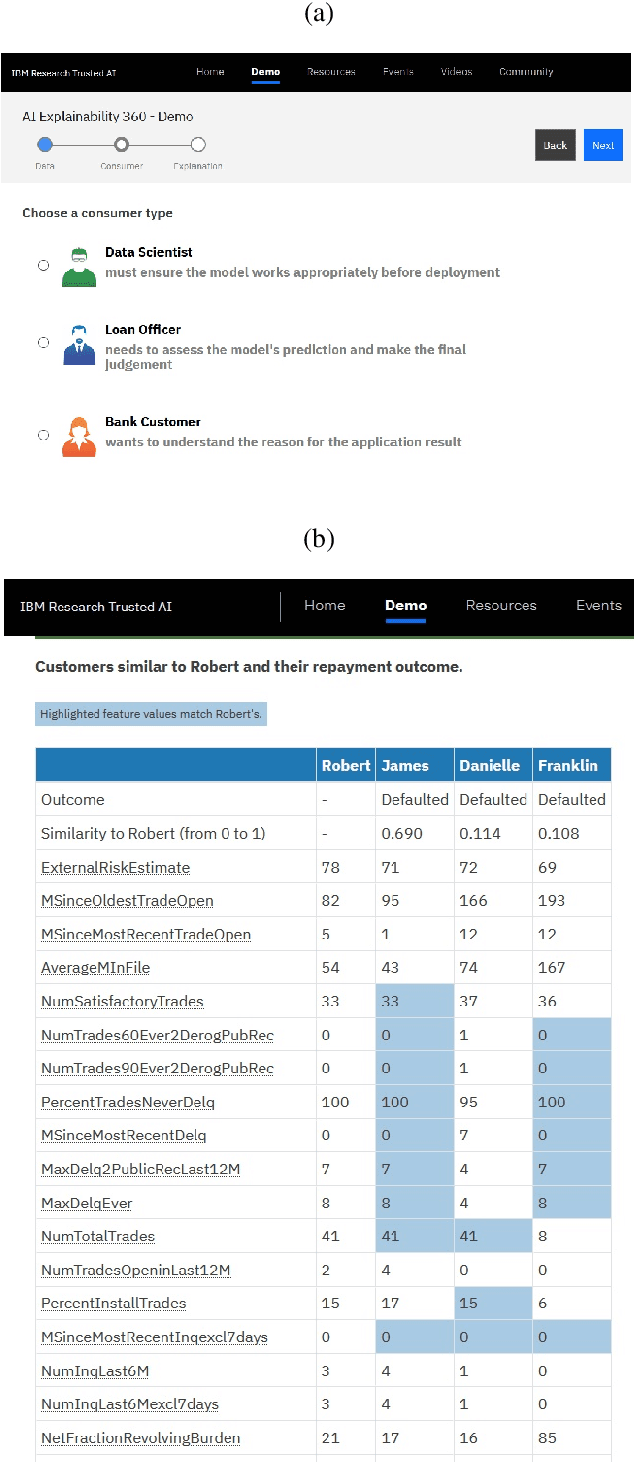
Abstract:As artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms make further inroads into society, calls are increasing from multiple stakeholders for these algorithms to explain their outputs. At the same time, these stakeholders, whether they be affected citizens, government regulators, domain experts, or system developers, present different requirements for explanations. Toward addressing these needs, we introduce AI Explainability 360 (http://aix360.mybluemix.net/), an open-source software toolkit featuring eight diverse and state-of-the-art explainability methods and two evaluation metrics. Equally important, we provide a taxonomy to help entities requiring explanations to navigate the space of explanation methods, not only those in the toolkit but also in the broader literature on explainability. For data scientists and other users of the toolkit, we have implemented an extensible software architecture that organizes methods according to their place in the AI modeling pipeline. We also discuss enhancements to bring research innovations closer to consumers of explanations, ranging from simplified, more accessible versions of algorithms, to tutorials and an interactive web demo to introduce AI explainability to different audiences and application domains. Together, our toolkit and taxonomy can help identify gaps where more explainability methods are needed and provide a platform to incorporate them as they are developed.
Learning Hierarchical Teaching in Cooperative Multiagent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 07, 2019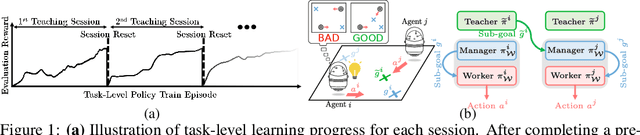
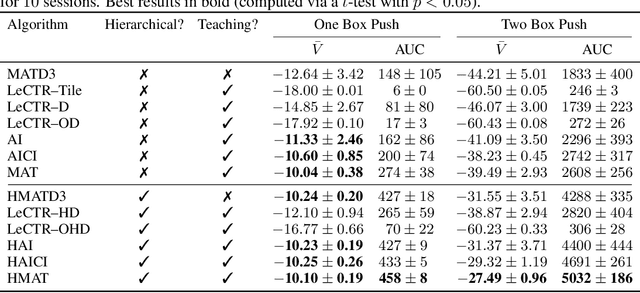
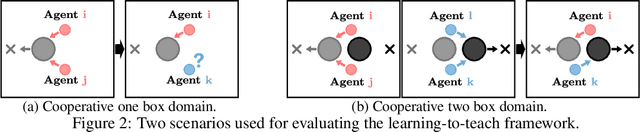

Abstract:Heterogeneous knowledge naturally arises among different agents in cooperative multiagent reinforcement learning. As such, learning can be greatly improved if agents can effectively pass their knowledge on to other agents. Existing work has demonstrated that peer-to-peer knowledge transfer, a process referred to as action advising, improves team-wide learning. In contrast to previous frameworks that advise at the level of primitive actions, we aim to learn high-level teaching policies that decide when and what high-level action (e.g., sub-goal) to advise a teammate. We introduce a new learning to teach framework, called hierarchical multiagent teaching (HMAT). The proposed framework solves difficulties faced by prior work on multiagent teaching when operating in domains with long horizons, delayed rewards, and continuous states/actions by leveraging temporal abstraction and deep function approximation. Our empirical evaluations show that HMAT accelerates team-wide learning progress in difficult environments that are more complex than those explored in previous work. HMAT also learns teaching policies that can be transferred to different teammates/tasks and can even teach teammates with heterogeneous action spaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge