Q. Vera Liao
Fostering Appropriate Reliance on Large Language Models: The Role of Explanations, Sources, and Inconsistencies
Feb 12, 2025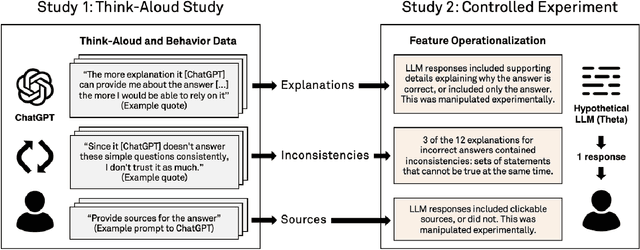
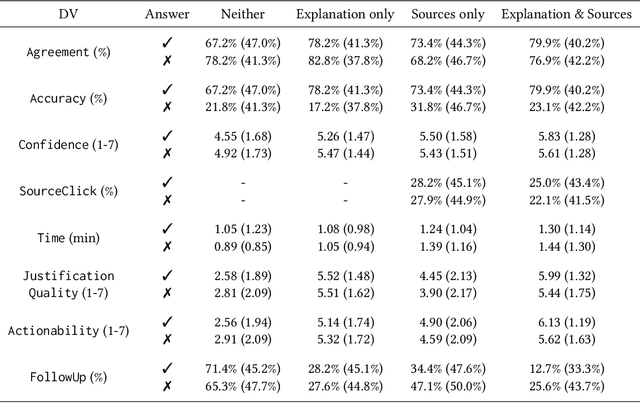
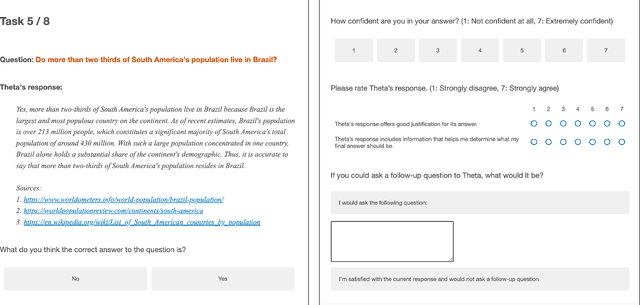

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can produce erroneous responses that sound fluent and convincing, raising the risk that users will rely on these responses as if they were correct. Mitigating such overreliance is a key challenge. Through a think-aloud study in which participants use an LLM-infused application to answer objective questions, we identify several features of LLM responses that shape users' reliance: explanations (supporting details for answers), inconsistencies in explanations, and sources. Through a large-scale, pre-registered, controlled experiment (N=308), we isolate and study the effects of these features on users' reliance, accuracy, and other measures. We find that the presence of explanations increases reliance on both correct and incorrect responses. However, we observe less reliance on incorrect responses when sources are provided or when explanations exhibit inconsistencies. We discuss the implications of these findings for fostering appropriate reliance on LLMs.
"It was 80% me, 20% AI": Seeking Authenticity in Co-Writing with Large Language Models
Nov 20, 2024
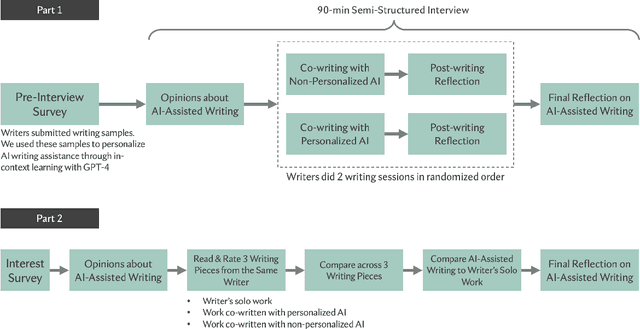


Abstract:Given the rising proliferation and diversity of AI writing assistance tools, especially those powered by large language models (LLMs), both writers and readers may have concerns about the impact of these tools on the authenticity of writing work. We examine whether and how writers want to preserve their authentic voice when co-writing with AI tools and whether personalization of AI writing support could help achieve this goal. We conducted semi-structured interviews with 19 professional writers, during which they co-wrote with both personalized and non-personalized AI writing-support tools. We supplemented writers' perspectives with opinions from 30 avid readers about the written work co-produced with AI collected through an online survey. Our findings illuminate conceptions of authenticity in human-AI co-creation, which focus more on the process and experience of constructing creators' authentic selves. While writers reacted positively to personalized AI writing tools, they believed the form of personalization needs to target writers' growth and go beyond the phase of text production. Overall, readers' responses showed less concern about human-AI co-writing. Readers could not distinguish AI-assisted work, personalized or not, from writers' solo-written work and showed positive attitudes toward writers experimenting with new technology for creative writing.
ECBD: Evidence-Centered Benchmark Design for NLP
Jun 13, 2024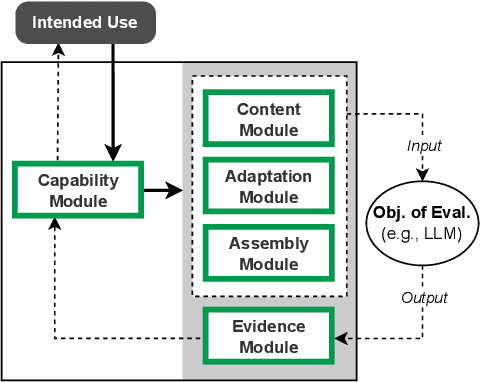
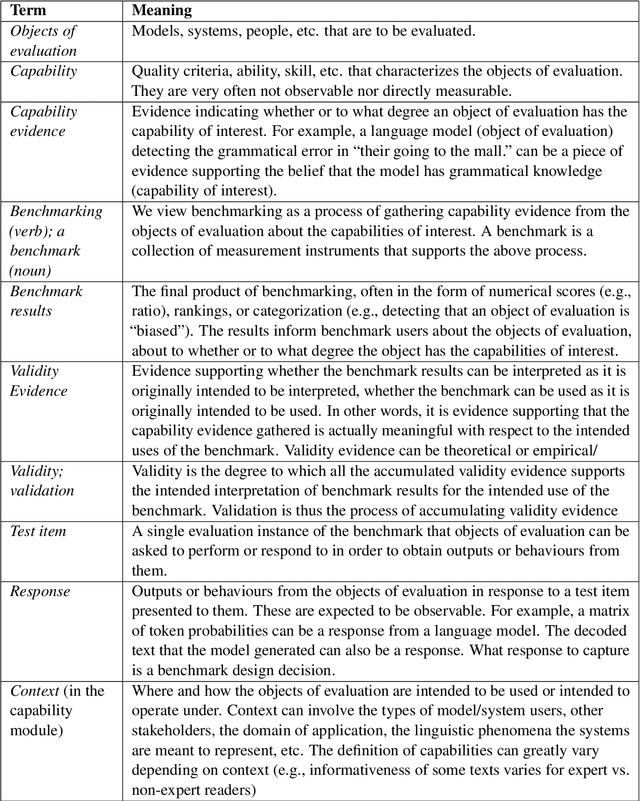

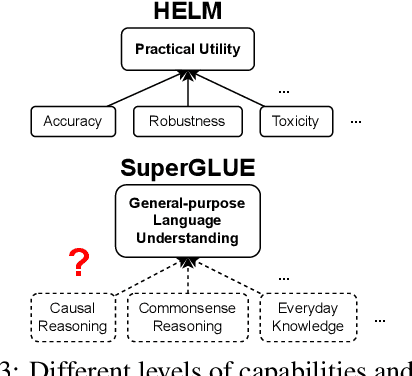
Abstract:Benchmarking is seen as critical to assessing progress in NLP. However, creating a benchmark involves many design decisions (e.g., which datasets to include, which metrics to use) that often rely on tacit, untested assumptions about what the benchmark is intended to measure or is actually measuring. There is currently no principled way of analyzing these decisions and how they impact the validity of the benchmark's measurements. To address this gap, we draw on evidence-centered design in educational assessments and propose Evidence-Centered Benchmark Design (ECBD), a framework which formalizes the benchmark design process into five modules. ECBD specifies the role each module plays in helping practitioners collect evidence about capabilities of interest. Specifically, each module requires benchmark designers to describe, justify, and support benchmark design choices -- e.g., clearly specifying the capabilities the benchmark aims to measure or how evidence about those capabilities is collected from model responses. To demonstrate the use of ECBD, we conduct case studies with three benchmarks: BoolQ, SuperGLUE, and HELM. Our analysis reveals common trends in benchmark design and documentation that could threaten the validity of benchmarks' measurements.
"I'm Not Sure, But": Examining the Impact of Large Language Models' Uncertainty Expression on User Reliance and Trust
May 01, 2024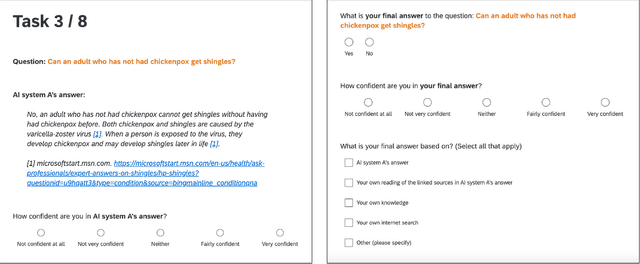
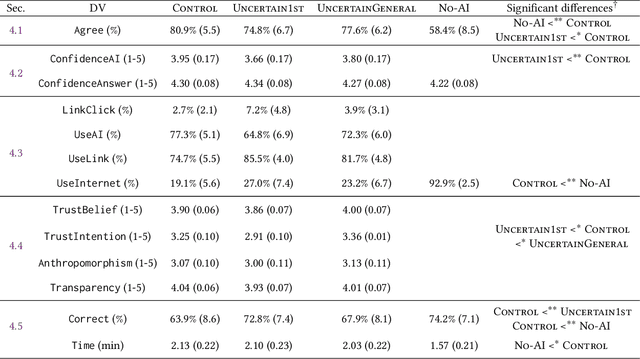
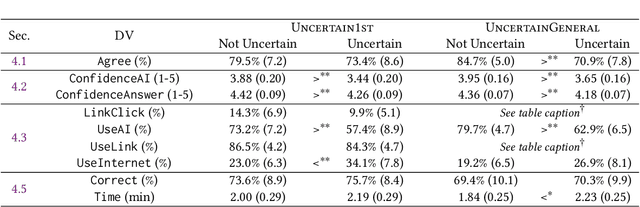
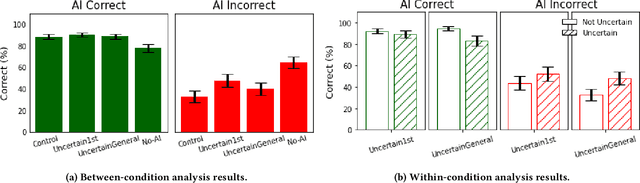
Abstract:Widely deployed large language models (LLMs) can produce convincing yet incorrect outputs, potentially misleading users who may rely on them as if they were correct. To reduce such overreliance, there have been calls for LLMs to communicate their uncertainty to end users. However, there has been little empirical work examining how users perceive and act upon LLMs' expressions of uncertainty. We explore this question through a large-scale, pre-registered, human-subject experiment (N=404) in which participants answer medical questions with or without access to responses from a fictional LLM-infused search engine. Using both behavioral and self-reported measures, we examine how different natural language expressions of uncertainty impact participants' reliance, trust, and overall task performance. We find that first-person expressions (e.g., "I'm not sure, but...") decrease participants' confidence in the system and tendency to agree with the system's answers, while increasing participants' accuracy. An exploratory analysis suggests that this increase can be attributed to reduced (but not fully eliminated) overreliance on incorrect answers. While we observe similar effects for uncertainty expressed from a general perspective (e.g., "It's not clear, but..."), these effects are weaker and not statistically significant. Our findings suggest that using natural language expressions of uncertainty may be an effective approach for reducing overreliance on LLMs, but that the precise language used matters. This highlights the importance of user testing before deploying LLMs at scale.
Generative Echo Chamber? Effects of LLM-Powered Search Systems on Diverse Information Seeking
Feb 10, 2024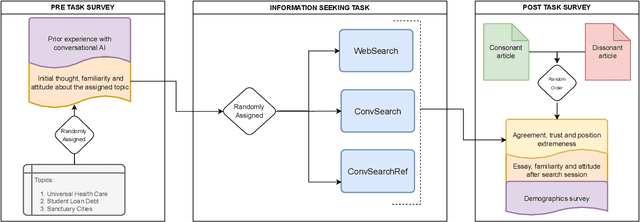



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) powered conversational search systems have already been used by hundreds of millions of people, and are believed to bring many benefits over conventional search. However, while decades of research and public discourse interrogated the risk of search systems in increasing selective exposure and creating echo chambers -- limiting exposure to diverse opinions and leading to opinion polarization, little is known about such a risk of LLM-powered conversational search. We conduct two experiments to investigate: 1) whether and how LLM-powered conversational search increases selective exposure compared to conventional search; 2) whether and how LLMs with opinion biases that either reinforce or challenge the user's view change the effect. Overall, we found that participants engaged in more biased information querying with LLM-powered conversational search, and an opinionated LLM reinforcing their views exacerbated this bias. These results present critical implications for the development of LLMs and conversational search systems, and the policy governing these technologies.
AI Transparency in the Age of LLMs: A Human-Centered Research Roadmap
Jun 02, 2023
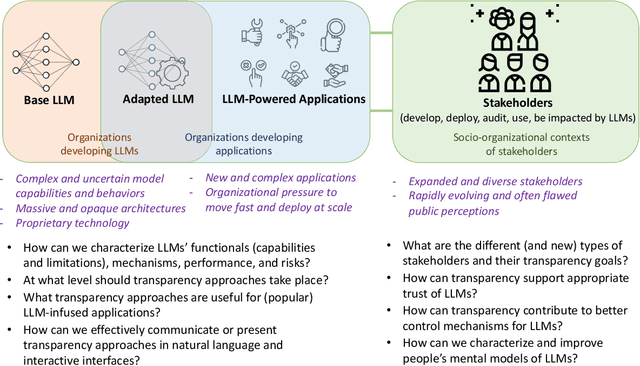
Abstract:The rise of powerful large language models (LLMs) brings about tremendous opportunities for innovation but also looming risks for individuals and society at large. We have reached a pivotal moment for ensuring that LLMs and LLM-infused applications are developed and deployed responsibly. However, a central pillar of responsible AI -- transparency -- is largely missing from the current discourse around LLMs. It is paramount to pursue new approaches to provide transparency for LLMs, and years of research at the intersection of AI and human-computer interaction (HCI) highlight that we must do so with a human-centered perspective: Transparency is fundamentally about supporting appropriate human understanding, and this understanding is sought by different stakeholders with different goals in different contexts. In this new era of LLMs, we must develop and design approaches to transparency by considering the needs of stakeholders in the emerging LLM ecosystem, the novel types of LLM-infused applications being built, and the new usage patterns and challenges around LLMs, all while building on lessons learned about how people process, interact with, and make use of information. We reflect on the unique challenges that arise in providing transparency for LLMs, along with lessons learned from HCI and responsible AI research that has taken a human-centered perspective on AI transparency. We then lay out four common approaches that the community has taken to achieve transparency -- model reporting, publishing evaluation results, providing explanations, and communicating uncertainty -- and call out open questions around how these approaches may or may not be applied to LLMs. We hope this provides a starting point for discussion and a useful roadmap for future research.
Rethinking Model Evaluation as Narrowing the Socio-Technical Gap
Jun 01, 2023
Abstract:The recent development of generative and large language models (LLMs) poses new challenges for model evaluation that the research community and industry are grappling with. While the versatile capabilities of these models ignite excitement, they also inevitably make a leap toward homogenization: powering a wide range of applications with a single, often referred to as ``general-purpose'', model. In this position paper, we argue that model evaluation practices must take on a critical task to cope with the challenges and responsibilities brought by this homogenization: providing valid assessments for whether and how much human needs in downstream use cases can be satisfied by the given model (\textit{socio-technical gap}). By drawing on lessons from the social sciences, human-computer interaction (HCI), and the interdisciplinary field of explainable AI (XAI), we urge the community to develop evaluation methods based on real-world socio-requirements and embrace diverse evaluation methods with an acknowledgment of trade-offs between realism to socio-requirements and pragmatic costs. By mapping HCI and current NLG evaluation methods, we identify opportunities for new evaluation methods for LLMs to narrow the socio-technical gap and pose open questions.
Evaluating NLG Evaluation Metrics: A Measurement Theory Perspective
May 24, 2023Abstract:We address the fundamental challenge in Natural Language Generation (NLG) model evaluation, the design and validation of evaluation metrics. Recognizing the limitations of existing metrics and issues with human judgment, we propose using measurement theory, the foundation of test design, as a framework for conceptualizing and evaluating the validity and reliability of NLG evaluation metrics. This approach offers a systematic method for defining "good" metrics, developing robust metrics, and assessing metric performance. In this paper, we introduce core concepts in measurement theory in the context of NLG evaluation and key methods to evaluate the performance of NLG metrics. Through this framework, we aim to promote the design, evaluation, and interpretation of valid and reliable metrics, ultimately contributing to the advancement of robust and effective NLG models in real-world settings.
Supporting Qualitative Analysis with Large Language Models: Combining Codebook with GPT-3 for Deductive Coding
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:Qualitative analysis of textual contents unpacks rich and valuable information by assigning labels to the data. However, this process is often labor-intensive, particularly when working with large datasets. While recent AI-based tools demonstrate utility, researchers may not have readily available AI resources and expertise, let alone be challenged by the limited generalizability of those task-specific models. In this study, we explored the use of large language models (LLMs) in supporting deductive coding, a major category of qualitative analysis where researchers use pre-determined codebooks to label the data into a fixed set of codes. Instead of training task-specific models, a pre-trained LLM could be used directly for various tasks without fine-tuning through prompt learning. Using a curiosity-driven questions coding task as a case study, we found, by combining GPT-3 with expert-drafted codebooks, our proposed approach achieved fair to substantial agreements with expert-coded results. We lay out challenges and opportunities in using LLMs to support qualitative coding and beyond.
Why is AI not a Panacea for Data Workers? An Interview Study on Human-AI Collaboration in Data Storytelling
Apr 17, 2023


Abstract:Data storytelling plays an important role in data workers' daily jobs since it boosts team collaboration and public communication. However, to make an appealing data story, data workers spend tremendous efforts on various tasks, including outlining and styling the story. Recently, a growing research trend has been exploring how to assist data storytelling with advanced artificial intelligence (AI). However, existing studies may focus on individual tasks in the workflow of data storytelling and do not reveal a complete picture of humans' preference for collaborating with AI. To better understand real-world needs, we interviewed eighteen data workers from both industry and academia to learn where and how they would like to collaborate with AI. Surprisingly, though the participants showed excitement about collaborating with AI, many of them also expressed reluctance and pointed out nuanced reasons. Based on their responses, we first characterize stages and tasks in the practical data storytelling workflows and the desired roles of AI. Then the preferred collaboration patterns in different tasks are identified. Next, we summarize the interviewees' reasons why and why not they would like to collaborate with AI. Finally, we provide suggestions for human-AI collaborative data storytelling to hopefully shed light on future related research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge