Angel Hsing-Chi Hwang
Toward AI Matching Policies in Homeless Services: A Qualitative Study with Policymakers
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence researchers have proposed various data-driven algorithms to improve the processes that match individuals experiencing homelessness to scarce housing resources. It remains unclear whether and how these algorithms are received or adopted by practitioners and what their corresponding consequences are. Through semi-structured interviews with 13 policymakers in homeless services in Los Angeles, we investigate whether such change-makers are open to the idea of integrating AI into the housing resource matching process, identifying where they see potential gains and drawbacks from such a system in issues of efficiency, fairness, and transparency. Our qualitative analysis indicates that, even when aware of various complicating factors, policymakers welcome the idea of an AI matching tool if thoughtfully designed and used in tandem with human decision-makers. Though there is no consensus as to the exact design of such an AI system, insights from policymakers raise open questions and design considerations that can be enlightening for future researchers and practitioners who aim to build responsible algorithmic systems to support decision-making in low-resource scenarios.
"It was 80% me, 20% AI": Seeking Authenticity in Co-Writing with Large Language Models
Nov 20, 2024
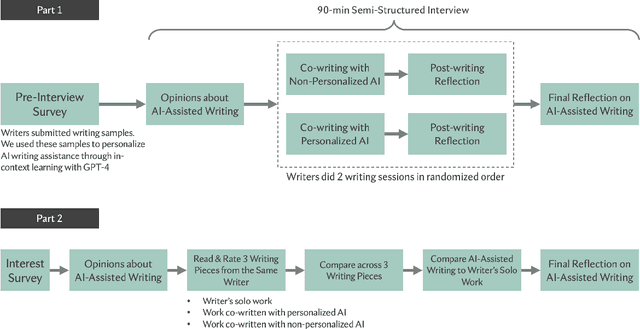


Abstract:Given the rising proliferation and diversity of AI writing assistance tools, especially those powered by large language models (LLMs), both writers and readers may have concerns about the impact of these tools on the authenticity of writing work. We examine whether and how writers want to preserve their authentic voice when co-writing with AI tools and whether personalization of AI writing support could help achieve this goal. We conducted semi-structured interviews with 19 professional writers, during which they co-wrote with both personalized and non-personalized AI writing-support tools. We supplemented writers' perspectives with opinions from 30 avid readers about the written work co-produced with AI collected through an online survey. Our findings illuminate conceptions of authenticity in human-AI co-creation, which focus more on the process and experience of constructing creators' authentic selves. While writers reacted positively to personalized AI writing tools, they believed the form of personalization needs to target writers' growth and go beyond the phase of text production. Overall, readers' responses showed less concern about human-AI co-writing. Readers could not distinguish AI-assisted work, personalized or not, from writers' solo-written work and showed positive attitudes toward writers experimenting with new technology for creative writing.
From Fake Perfects to Conversational Imperfects: Exploring Image-Generative AI as a Boundary Object for Participatory Design of Public Spaces
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:Designing public spaces requires balancing the interests of diverse stakeholders within a constrained physical and institutional space. Designers usually approach these problems through participatory methods but struggle to incorporate diverse perspectives into design outputs. The growing capabilities of image-generative artificial intelligence (IGAI) could support participatory design. Prior work in leveraging IGAI's capabilities in design has focused on augmenting the experience and performance of individual creators. We study how IGAI could facilitate participatory processes when designing public spaces, a complex collaborative task. We conducted workshops and IGAI-mediated interviews in a real-world participatory process to upgrade a park in Los Angeles. We found (1) a shift from focusing on accuracy to fostering richer conversations as the desirable outcome of adopting IGAI in participatory design, (2) that IGAI promoted more space-aware conversations, and (3) that IGAI-mediated conversations are subject to the abilities of the facilitators in managing the interaction between themselves, the AI, and stakeholders. We contribute by discussing practical implications for using IGAI in participatory design, including success metrics, relevant skills, and asymmetries between designers and stakeholders. We finish by proposing a series of open research questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge