Aleksandra Mojsilović
A Methodology for Creating AI FactSheets
Jun 28, 2020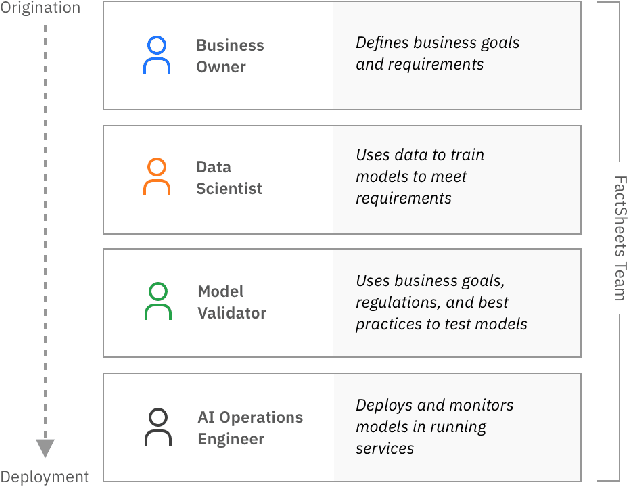

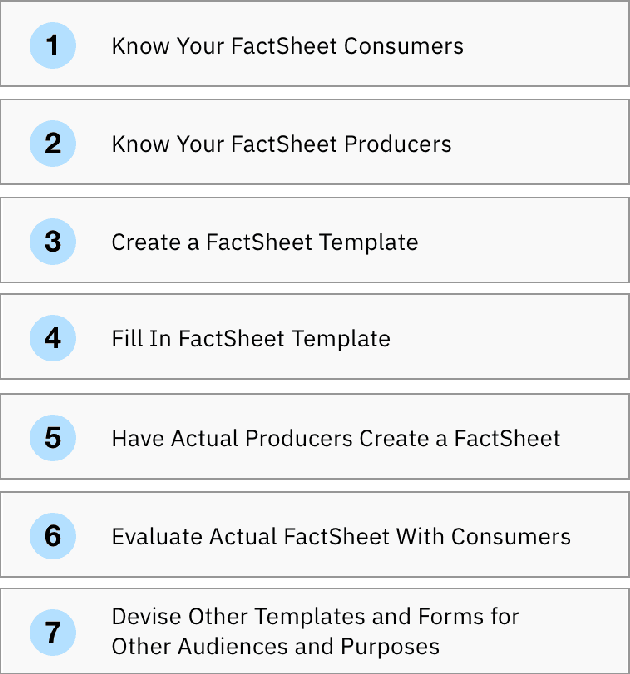
Abstract:As AI models and services are used in a growing number of highstakes areas, a consensus is forming around the need for a clearer record of how these models and services are developed to increase trust. Several proposals for higher quality and more consistent AI documentation have emerged to address ethical and legal concerns and general social impacts of such systems. However, there is little published work on how to create this documentation. This is the first work to describe a methodology for creating the form of AI documentation we call FactSheets. We have used this methodology to create useful FactSheets for nearly two dozen models. This paper describes this methodology and shares the insights we have gathered. Within each step of the methodology, we describe the issues to consider and the questions to explore with the relevant people in an organization who will be creating and consuming the AI facts in a FactSheet. This methodology will accelerate the broader adoption of transparent AI documentation.
One Explanation Does Not Fit All: A Toolkit and Taxonomy of AI Explainability Techniques
Sep 14, 2019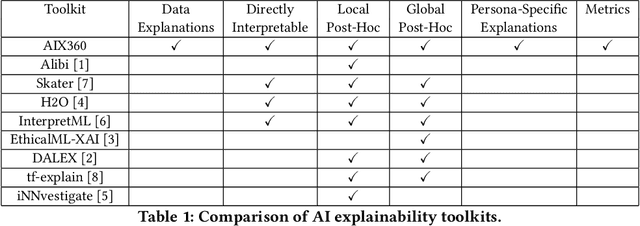
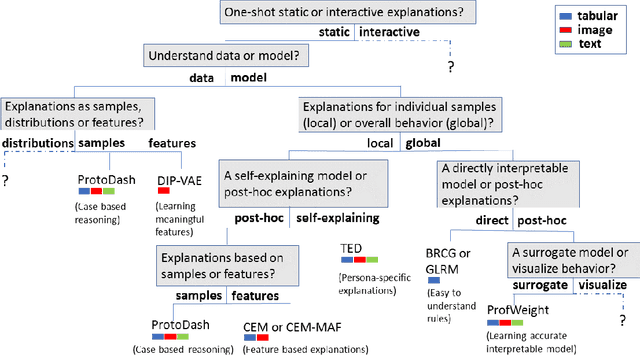
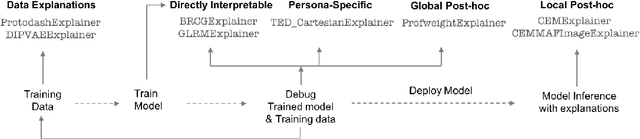
Abstract:As artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms make further inroads into society, calls are increasing from multiple stakeholders for these algorithms to explain their outputs. At the same time, these stakeholders, whether they be affected citizens, government regulators, domain experts, or system developers, present different requirements for explanations. Toward addressing these needs, we introduce AI Explainability 360 (http://aix360.mybluemix.net/), an open-source software toolkit featuring eight diverse and state-of-the-art explainability methods and two evaluation metrics. Equally important, we provide a taxonomy to help entities requiring explanations to navigate the space of explanation methods, not only those in the toolkit but also in the broader literature on explainability. For data scientists and other users of the toolkit, we have implemented an extensible software architecture that organizes methods according to their place in the AI modeling pipeline. We also discuss enhancements to bring research innovations closer to consumers of explanations, ranging from simplified, more accessible versions of algorithms, to tutorials and an interactive web demo to introduce AI explainability to different audiences and application domains. Together, our toolkit and taxonomy can help identify gaps where more explainability methods are needed and provide a platform to incorporate them as they are developed.
Teaching AI to Explain its Decisions Using Embeddings and Multi-Task Learning
Jun 05, 2019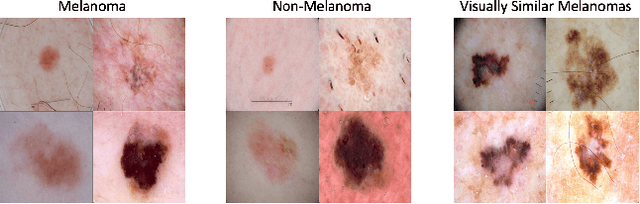
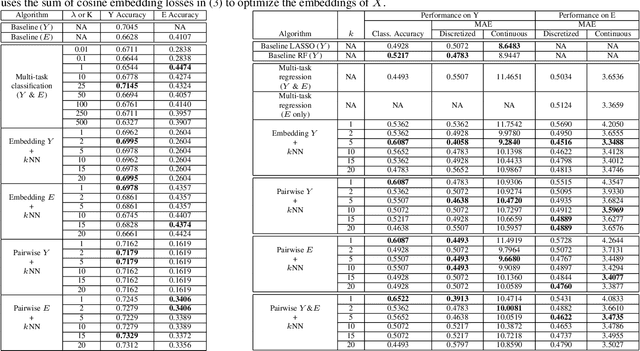
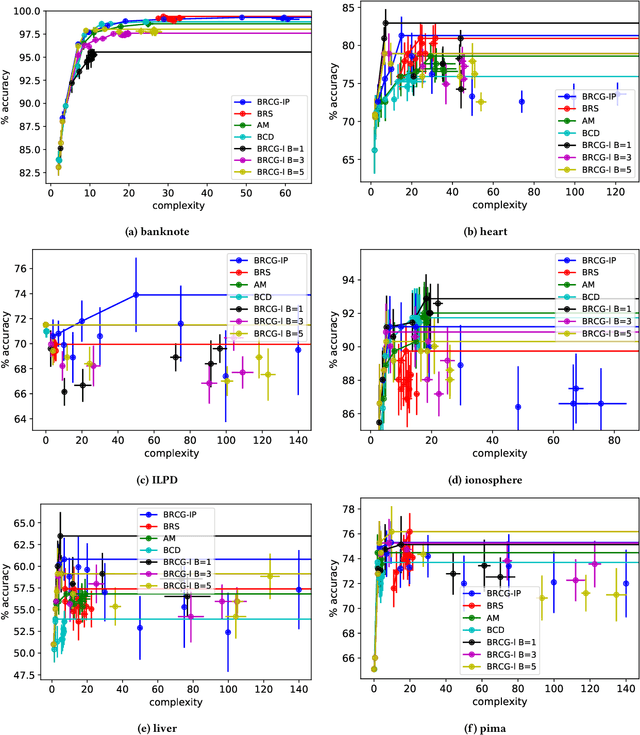
Abstract:Using machine learning in high-stakes applications often requires predictions to be accompanied by explanations comprehensible to the domain user, who has ultimate responsibility for decisions and outcomes. Recently, a new framework for providing explanations, called TED, has been proposed to provide meaningful explanations for predictions. This framework augments training data to include explanations elicited from domain users, in addition to features and labels. This approach ensures that explanations for predictions are tailored to the complexity expectations and domain knowledge of the consumer. In this paper, we build on this foundational work, by exploring more sophisticated instantiations of the TED framework and empirically evaluate their effectiveness in two diverse domains, chemical odor and skin cancer prediction. Results demonstrate that meaningful explanations can be reliably taught to machine learning algorithms, and in some cases, improving modeling accuracy.
Understanding Innovation to Drive Sustainable Development
Jun 15, 2016



Abstract:Innovation is among the key factors driving a country's economic and social growth. But what are the factors that make a country innovative? How do they differ across different parts of the world and different stages of development? In this work done in collaboration with the World Economic Forum (WEF), we analyze the scores obtained through executive opinion surveys that constitute the WEF's Global Competitiveness Index in conjunction with other country-level metrics and indicators to identify actionable levers of innovation. The findings can help country leaders and organizations shape the policies to drive developmental activities and increase the capacity of innovation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge