Renqiang Luo
Bridging Semantic Understanding and Popularity Bias with LLMs
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Semantic understanding of popularity bias is a crucial yet underexplored challenge in recommender systems, where popular items are often favored at the expense of niche content. Most existing debiasing methods treat the semantic understanding of popularity bias as a matter of diversity enhancement or long-tail coverage, neglecting the deeper semantic layer that embodies the causal origins of the bias itself. Consequently, such shallow interpretations limit both their debiasing effectiveness and recommendation accuracy. In this paper, we propose FairLRM, a novel framework that bridges the gap in the semantic understanding of popularity bias with Recommendation via Large Language Model (RecLLM). FairLRM decomposes popularity bias into item-side and user-side components, using structured instruction-based prompts to enhance the model's comprehension of both global item distributions and individual user preferences. Unlike traditional methods that rely on surface-level features such as "diversity" or "debiasing", FairLRM improves the model's ability to semantically interpret and address the underlying bias. Through empirical evaluation, we show that FairLRM significantly enhances both fairness and recommendation accuracy, providing a more semantically aware and trustworthy approach to enhance the semantic understanding of popularity bias. The implementation is available at https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairLRM.
FairGE: Fairness-Aware Graph Encoding in Incomplete Social Networks
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Graph Transformers (GTs) are increasingly applied to social network analysis, yet their deployment is often constrained by fairness concerns. This issue is particularly critical in incomplete social networks, where sensitive attributes are frequently missing due to privacy and ethical restrictions. Existing solutions commonly generate these incomplete attributes, which may introduce additional biases and further compromise user privacy. To address this challenge, FairGE (Fair Graph Encoding) is introduced as a fairness-aware framework for GTs in incomplete social networks. Instead of generating sensitive attributes, FairGE encodes fairness directly through spectral graph theory. By leveraging the principal eigenvector to represent structural information and padding incomplete sensitive attributes with zeros to maintain independence, FairGE ensures fairness without data reconstruction. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that the method suppresses the influence of non-principal spectral components, thereby enhancing fairness. Extensive experiments on seven real-world social network datasets confirm that FairGE achieves at least a 16% improvement in both statistical parity and equality of opportunity compared with state-of-the-art baselines. The source code is shown in https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairGE.
FairGU: Fairness-aware Graph Unlearning in Social Network
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Graph unlearning has emerged as a critical mechanism for supporting sustainable and privacy-preserving social networks, enabling models to remove the influence of deleted nodes and thereby better safeguard user information. However, we observe that existing graph unlearning techniques insufficiently protect sensitive attributes, often leading to degraded algorithmic fairness compared with traditional graph learning methods. To address this gap, we introduce FairGU, a fairness-aware graph unlearning framework designed to preserve both utility and fairness during the unlearning process. FairGU integrates a dedicated fairness-aware module with effective data protection strategies, ensuring that sensitive attributes are neither inadvertently amplified nor structurally exposed when nodes are removed. Through extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets, we demonstrate that FairGU consistently outperforms state-of-the-art graph unlearning methods and fairness-enhanced graph learning baselines in terms of both accuracy and fairness metrics. Our findings highlight a previously overlooked risk in current unlearning practices and establish FairGU as a robust and equitable solution for the next generation of socially sustainable networked systems. The codes are available at https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairGU.
When to Invoke: Refining LLM Fairness with Toxicity Assessment
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for toxicity assessment in online moderation systems, where fairness across demographic groups is essential for equitable treatment. However, LLMs often produce inconsistent toxicity judgements for subtle expressions, particularly those involving implicit hate speech, revealing underlying biases that are difficult to correct through standard training. This raises a key question that existing approaches often overlook: when should corrective mechanisms be invoked to ensure fair and reliable assessments? To address this, we propose FairToT, an inference-time framework that enhances LLM fairness through prompt-guided toxicity assessment. FairToT identifies cases where demographic-related variation is likely to occur and determines when additional assessment should be applied. In addition, we introduce two interpretable fairness indicators that detect such cases and improve inference consistency without modifying model parameters. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that FairToT reduces group-level disparities while maintaining stable and reliable toxicity predictions, demonstrating that inference-time refinement offers an effective and practical approach for fairness improvement in LLM-based toxicity assessment systems. The source code can be found at https://aisuko.github.io/fair-tot/.
Debiasing Large Language Models via Adaptive Causal Prompting with Sketch-of-Thought
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Despite notable advancements in prompting methods for Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT), existing strategies still suffer from excessive token usage and limited generalisability across diverse reasoning tasks. To address these limitations, we propose an Adaptive Causal Prompting with Sketch-of-Thought (ACPS) framework, which leverages structural causal models to infer the causal effect of a query on its answer and adaptively select an appropriate intervention (i.e., standard front-door and conditional front-door adjustments). This design enables generalisable causal reasoning across heterogeneous tasks without task-specific retraining. By replacing verbose CoT with concise Sketch-of-Thought, ACPS enables efficient reasoning that significantly reduces token usage and inference cost. Extensive experiments on multiple reasoning benchmarks and LLMs demonstrate that ACPS consistently outperforms existing prompting baselines in terms of accuracy, robustness, and computational efficiency.
PrivacyCD: Hierarchical Unlearning for Protecting Student Privacy in Cognitive Diagnosis
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:The need to remove specific student data from cognitive diagnosis (CD) models has become a pressing requirement, driven by users' growing assertion of their "right to be forgotten". However, existing CD models are largely designed without privacy considerations and lack effective data unlearning mechanisms. Directly applying general purpose unlearning algorithms is suboptimal, as they struggle to balance unlearning completeness, model utility, and efficiency when confronted with the unique heterogeneous structure of CD models. To address this, our paper presents the first systematic study of the data unlearning problem for CD models, proposing a novel and efficient algorithm: hierarchical importanceguided forgetting (HIF). Our key insight is that parameter importance in CD models exhibits distinct layer wise characteristics. HIF leverages this via an innovative smoothing mechanism that combines individual and layer, level importance, enabling a more precise distinction of parameters associated with the data to be unlearned. Experiments on three real world datasets show that HIF significantly outperforms baselines on key metrics, offering the first effective solution for CD models to respond to user data removal requests and for deploying high-performance, privacy preserving AI systems
P-MIA: A Profiled-Based Membership Inference Attack on Cognitive Diagnosis Models
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:Cognitive diagnosis models (CDMs) are pivotal for creating fine-grained learner profiles in modern intelligent education platforms. However, these models are trained on sensitive student data, raising significant privacy concerns. While membership inference attacks (MIA) have been studied in various domains, their application to CDMs remains a critical research gap, leaving their privacy risks unquantified. This paper is the first to systematically investigate MIA against CDMs. We introduce a novel and realistic grey box threat model that exploits the explainability features of these platforms, where a model's internal knowledge state vectors are exposed to users through visualizations such as radar charts. We demonstrate that these vectors can be accurately reverse-engineered from such visualizations, creating a potent attack surface. Based on this threat model, we propose a profile-based MIA (P-MIA) framework that leverages both the model's final prediction probabilities and the exposed internal knowledge state vectors as features. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets against mainstream CDMs show that our grey-box attack significantly outperforms standard black-box baselines. Furthermore, we showcase the utility of P-MIA as an auditing tool by successfully evaluating the efficacy of machine unlearning techniques and revealing their limitations.
Unbiased Reasoning for Knowledge-Intensive Tasks in Large Language Models via Conditional Front-Door Adjustment
Aug 23, 2025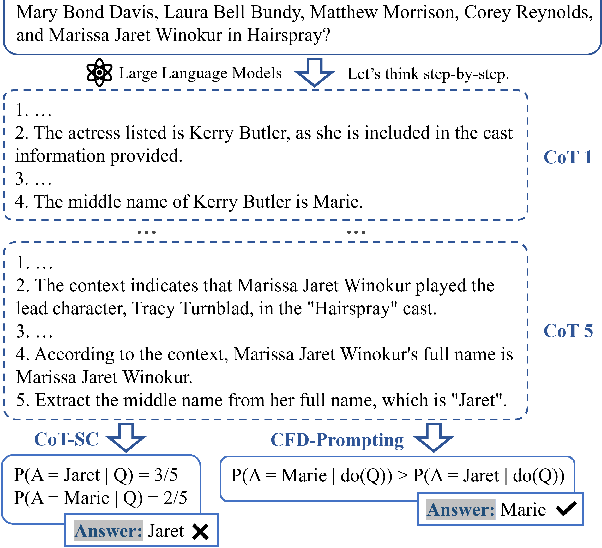
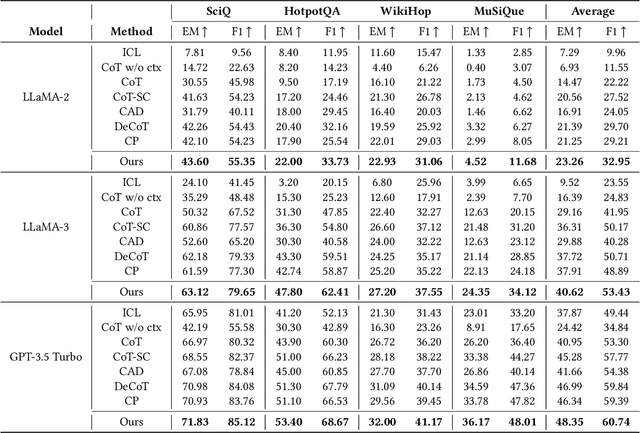
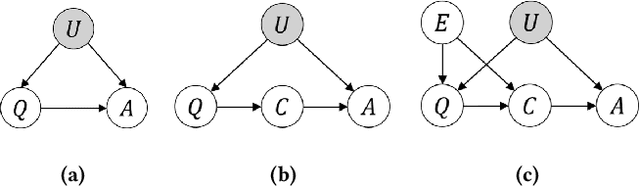
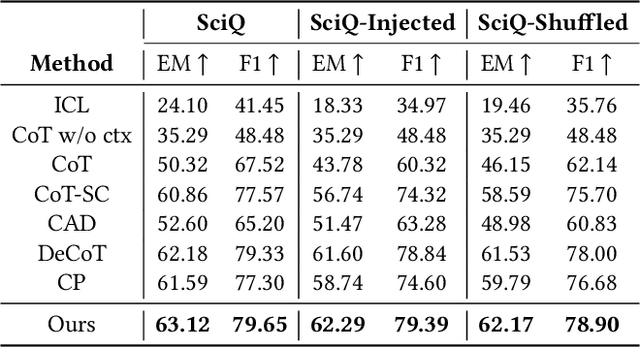
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in natural language processing but still struggle to perform well on knowledge-intensive tasks that require deep reasoning and the integration of external knowledge. Although methods such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) have been proposed to enhance LLMs with external knowledge, they still suffer from internal bias in LLMs, which often leads to incorrect answers. In this paper, we propose a novel causal prompting framework, Conditional Front-Door Prompting (CFD-Prompting), which enables the unbiased estimation of the causal effect between the query and the answer, conditional on external knowledge, while mitigating internal bias. By constructing counterfactual external knowledge, our framework simulates how the query behaves under varying contexts, addressing the challenge that the query is fixed and is not amenable to direct causal intervention. Compared to the standard front-door adjustment, the conditional variant operates under weaker assumptions, enhancing both robustness and generalisability of the reasoning process. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs and benchmark datasets demonstrate that CFD-Prompting significantly outperforms existing baselines in both accuracy and robustness.
Fairness in Graph Learning Augmented with Machine Learning: A Survey
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Augmenting specialised machine learning techniques into traditional graph learning models has achieved notable success across various domains, including federated graph learning, dynamic graph learning, and graph transformers. However, the intricate mechanisms of these specialised techniques introduce significant challenges in maintaining model fairness, potentially resulting in discriminatory outcomes in high-stakes applications such as recommendation systems, disaster response, criminal justice, and loan approval. This paper systematically examines the unique fairness challenges posed by Graph Learning augmented with Machine Learning (GL-ML). It highlights the complex interplay between graph learning mechanisms and machine learning techniques, emphasising how the augmentation of machine learning both enhances and complicates fairness. Additionally, we explore four critical techniques frequently employed to improve fairness in GL-ML methods. By thoroughly investigating the root causes and broader implications of fairness challenges in this rapidly evolving field, this work establishes a robust foundation for future research and innovation in GL-ML fairness.
Factor Graph-based Interpretable Neural Networks
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Comprehensible neural network explanations are foundations for a better understanding of decisions, especially when the input data are infused with malicious perturbations. Existing solutions generally mitigate the impact of perturbations through adversarial training, yet they fail to generate comprehensible explanations under unknown perturbations. To address this challenge, we propose AGAIN, a fActor GrAph-based Interpretable neural Network, which is capable of generating comprehensible explanations under unknown perturbations. Instead of retraining like previous solutions, the proposed AGAIN directly integrates logical rules by which logical errors in explanations are identified and rectified during inference. Specifically, we construct the factor graph to express logical rules between explanations and categories. By treating logical rules as exogenous knowledge, AGAIN can identify incomprehensible explanations that violate real-world logic. Furthermore, we propose an interactive intervention switch strategy rectifying explanations based on the logical guidance from the factor graph without learning perturbations, which overcomes the inherent limitation of adversarial training-based methods in defending only against known perturbations. Additionally, we theoretically demonstrate the effectiveness of employing factor graph by proving that the comprehensibility of explanations is strongly correlated with factor graph. Extensive experiments are conducted on three datasets and experimental results illustrate the superior performance of AGAIN compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge