Huafei Huang
FairGE: Fairness-Aware Graph Encoding in Incomplete Social Networks
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Graph Transformers (GTs) are increasingly applied to social network analysis, yet their deployment is often constrained by fairness concerns. This issue is particularly critical in incomplete social networks, where sensitive attributes are frequently missing due to privacy and ethical restrictions. Existing solutions commonly generate these incomplete attributes, which may introduce additional biases and further compromise user privacy. To address this challenge, FairGE (Fair Graph Encoding) is introduced as a fairness-aware framework for GTs in incomplete social networks. Instead of generating sensitive attributes, FairGE encodes fairness directly through spectral graph theory. By leveraging the principal eigenvector to represent structural information and padding incomplete sensitive attributes with zeros to maintain independence, FairGE ensures fairness without data reconstruction. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that the method suppresses the influence of non-principal spectral components, thereby enhancing fairness. Extensive experiments on seven real-world social network datasets confirm that FairGE achieves at least a 16% improvement in both statistical parity and equality of opportunity compared with state-of-the-art baselines. The source code is shown in https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairGE.
FairGU: Fairness-aware Graph Unlearning in Social Network
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Graph unlearning has emerged as a critical mechanism for supporting sustainable and privacy-preserving social networks, enabling models to remove the influence of deleted nodes and thereby better safeguard user information. However, we observe that existing graph unlearning techniques insufficiently protect sensitive attributes, often leading to degraded algorithmic fairness compared with traditional graph learning methods. To address this gap, we introduce FairGU, a fairness-aware graph unlearning framework designed to preserve both utility and fairness during the unlearning process. FairGU integrates a dedicated fairness-aware module with effective data protection strategies, ensuring that sensitive attributes are neither inadvertently amplified nor structurally exposed when nodes are removed. Through extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets, we demonstrate that FairGU consistently outperforms state-of-the-art graph unlearning methods and fairness-enhanced graph learning baselines in terms of both accuracy and fairness metrics. Our findings highlight a previously overlooked risk in current unlearning practices and establish FairGU as a robust and equitable solution for the next generation of socially sustainable networked systems. The codes are available at https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairGU.
Fairness in Graph Learning Augmented with Machine Learning: A Survey
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Augmenting specialised machine learning techniques into traditional graph learning models has achieved notable success across various domains, including federated graph learning, dynamic graph learning, and graph transformers. However, the intricate mechanisms of these specialised techniques introduce significant challenges in maintaining model fairness, potentially resulting in discriminatory outcomes in high-stakes applications such as recommendation systems, disaster response, criminal justice, and loan approval. This paper systematically examines the unique fairness challenges posed by Graph Learning augmented with Machine Learning (GL-ML). It highlights the complex interplay between graph learning mechanisms and machine learning techniques, emphasising how the augmentation of machine learning both enhances and complicates fairness. Additionally, we explore four critical techniques frequently employed to improve fairness in GL-ML methods. By thoroughly investigating the root causes and broader implications of fairness challenges in this rapidly evolving field, this work establishes a robust foundation for future research and innovation in GL-ML fairness.
FairGP: A Scalable and Fair Graph Transformer Using Graph Partitioning
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:Recent studies have highlighted significant fairness issues in Graph Transformer (GT) models, particularly against subgroups defined by sensitive features. Additionally, GTs are computationally intensive and memory-demanding, limiting their application to large-scale graphs. Our experiments demonstrate that graph partitioning can enhance the fairness of GT models while reducing computational complexity. To understand this improvement, we conducted a theoretical investigation into the root causes of fairness issues in GT models. We found that the sensitive features of higher-order nodes disproportionately influence lower-order nodes, resulting in sensitive feature bias. We propose Fairness-aware scalable GT based on Graph Partitioning (FairGP), which partitions the graph to minimize the negative impact of higher-order nodes. By optimizing attention mechanisms, FairGP mitigates the bias introduced by global attention, thereby enhancing fairness. Extensive empirical evaluations on six real-world datasets validate the superior performance of FairGP in achieving fairness compared to state-of-the-art methods. The codes are available at https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairGP.
Higher-order Structure Based Anomaly Detection on Attributed Networks
Jun 07, 2024
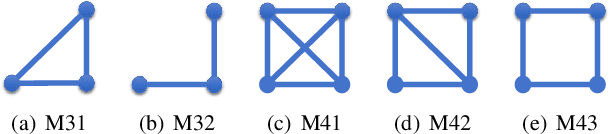
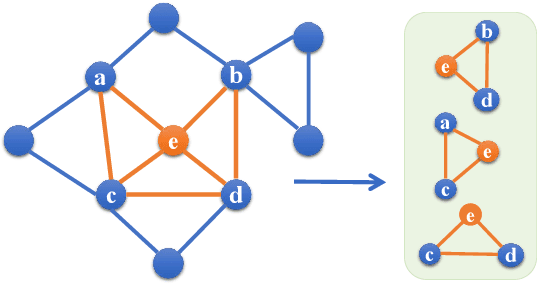
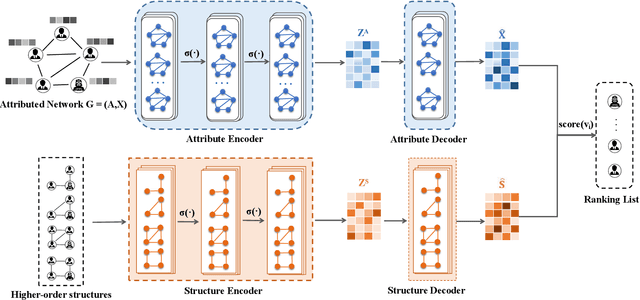
Abstract:Anomaly detection (such as telecom fraud detection and medical image detection) has attracted the increasing attention of people. The complex interaction between multiple entities widely exists in the network, which can reflect specific human behavior patterns. Such patterns can be modeled by higher-order network structures, thus benefiting anomaly detection on attributed networks. However, due to the lack of an effective mechanism in most existing graph learning methods, these complex interaction patterns fail to be applied in detecting anomalies, hindering the progress of anomaly detection to some extent. In order to address the aforementioned issue, we present a higher-order structure based anomaly detection (GUIDE) method. We exploit attribute autoencoder and structure autoencoder to reconstruct node attributes and higher-order structures, respectively. Moreover, we design a graph attention layer to evaluate the significance of neighbors to nodes through their higher-order structure differences. Finally, we leverage node attribute and higher-order structure reconstruction errors to find anomalies. Extensive experiments on five real-world datasets (i.e., ACM, Citation, Cora, DBLP, and Pubmed) are implemented to verify the effectiveness of GUIDE. Experimental results in terms of ROC-AUC, PR-AUC, and Recall@K show that GUIDE significantly outperforms the state-of-art methods.
FUGNN: Harmonizing Fairness and Utility in Graph Neural Networks
May 27, 2024Abstract:Fairness-aware Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) often face a challenging trade-off, where prioritizing fairness may require compromising utility. In this work, we re-examine fairness through the lens of spectral graph theory, aiming to reconcile fairness and utility within the framework of spectral graph learning. We explore the correlation between sensitive features and spectrum in GNNs, using theoretical analysis to delineate the similarity between original sensitive features and those after convolution under different spectrum. Our analysis reveals a reduction in the impact of similarity when the eigenvectors associated with the largest magnitude eigenvalue exhibit directional similarity. Based on these theoretical insights, we propose FUGNN, a novel spectral graph learning approach that harmonizes the conflict between fairness and utility. FUGNN ensures algorithmic fairness and utility by truncating the spectrum and optimizing eigenvector distribution during the encoding process. The fairness-aware eigenvector selection reduces the impact of convolution on sensitive features while concurrently minimizing the sacrifice of utility. FUGNN further optimizes the distribution of eigenvectors through a transformer architecture. By incorporating the optimized spectrum into the graph convolution network, FUGNN effectively learns node representations. Experiments on six real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of FUGNN over baseline methods. The codes are available at https://github.com/yushuowiki/FUGNN.
FairGT: A Fairness-aware Graph Transformer
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:The design of Graph Transformers (GTs) generally neglects considerations for fairness, resulting in biased outcomes against certain sensitive subgroups. Since GTs encode graph information without relying on message-passing mechanisms, conventional fairness-aware graph learning methods cannot be directly applicable to address these issues. To tackle this challenge, we propose FairGT, a Fairness-aware Graph Transformer explicitly crafted to mitigate fairness concerns inherent in GTs. FairGT incorporates a meticulous structural feature selection strategy and a multi-hop node feature integration method, ensuring independence of sensitive features and bolstering fairness considerations. These fairness-aware graph information encodings seamlessly integrate into the Transformer framework for downstream tasks. We also prove that the proposed fair structural topology encoding with adjacency matrix eigenvector selection and multi-hop integration are theoretically effective. Empirical evaluations conducted across five real-world datasets demonstrate FairGT's superiority in fairness metrics over existing graph transformers, graph neural networks, and state-of-the-art fairness-aware graph learning approaches.
Graph Augmentation Learning
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Graph Augmentation Learning (GAL) provides outstanding solutions for graph learning in handling incomplete data, noise data, etc. Numerous GAL methods have been proposed for graph-based applications such as social network analysis and traffic flow forecasting. However, the underlying reasons for the effectiveness of these GAL methods are still unclear. As a consequence, how to choose optimal graph augmentation strategy for a certain application scenario is still in black box. There is a lack of systematic, comprehensive, and experimentally validated guideline of GAL for scholars. Therefore, in this survey, we in-depth review GAL techniques from macro (graph), meso (subgraph), and micro (node/edge) levels. We further detailedly illustrate how GAL enhance the data quality and the model performance. The aggregation mechanism of augmentation strategies and graph learning models are also discussed by different application scenarios, i.e., data-specific, model-specific, and hybrid scenarios. To better show the outperformance of GAL, we experimentally validate the effectiveness and adaptability of different GAL strategies in different downstream tasks. Finally, we share our insights on several open issues of GAL, including heterogeneity, spatio-temporal dynamics, scalability, and generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge